- Duke of Wellington's Regiment
-
The Duke of Wellington's Regiment
(West Riding)
Cap badge of the Duke of Wellington's RegimentActive 1 July 1702 - 6 June 2006 Country United Kingdom Branch Army Type Line Infantry Role Armoured infantry (Warrior IFV) Size One Battalion (at final amalgamation) Garrison/HQ Battlesbury Barracks, Warminster Nickname "The Dukes",
"The Havercake Lads",
"The Pattern",
"The Immortals",
"The Pigs",
"The Old Seventy-Sixth",
"The Old Seven and Sixpennies"Motto Virtutis Fortuna Comes (Latin: "Fortune Favours the Brave") Colours and facings Colours: 2 Regulation & 2 Honorary
RedMarch Quick: The Wellesley Mascot Indian Elephant Anniversaries St George's Day (23 April)
Waterloo Day (18 June)Engagements See #Battle honours Commanders Last Commanding Officer Lieutenant Colonel Phil Lewis OBE Last Colonel in Chief His Grace Arthur Valerian Wellesley KG LVO OBE MC DL, 8th Duke of Wellington Last Colonel of the Regiment Major-General Sir Evelyn John Webb-Carter KCVO OBE Notable
commandersLt Col Brian Webb-Carter
General Sir Charles Huxtable KCB OBE DLThe Duke of Wellington's Regiment (West Riding) was an infantry regiment of the British Army, forming part of the King's Division.
In 1702 Colonel George Hastings, 8th Earl of Huntingdon, was authorised to raise a new regiment, which he did in and around the city of Gloucester. As was the custom in those days the regiment was named Huntingdon's Regiment after its Colonel. As Colonel succeeded Colonel the name changed, but in 1751 regiments were given numbers, and the regiment was from that time officially known as the 33rd Regiment of Foot. In 1782 the regiment's title was changed to the 33rd (or First Yorkshire West Riding) Regiment, thus formalising an association with the West Riding of Yorkshire which, even then, had been long established. The first Duke of Wellington died in 1852 and in the following year Queen Victoria, in recognition of the regiment's long ties to him, ordered that the regiment's title be changed to the 33rd (or The Duke of Wellington's) Regiment. In 1881, following the Cardwell Reforms, the 33rd was linked with the 76th Regiment of Foot, who shared their depot in Halifax. The 76th had first been raised in 1745, by Simon Harcourt and disbanded in 1746, re-raised in 1756 disbanded again in 1763, before being raised again in 1777, disbanded in 1784 and finally re-raised, in 1787, for service in India, by the Honorable East India Company.[1][2] The two regiments became, respectively, the 1st and 2nd Battalions of The Duke of Wellington's Regiment. In 1948 the 1st and 2nd Battalions were amalgamated into a single battalion, the 1st Battalion. On 6 June 2006 The 'Dukes' were amalgamated with the Prince of Wales's Own Regiment of Yorkshire and The Green Howards to form the Yorkshire Regiment.
Battalions from the regiment had served in most land conflicts involving British forces since its formation, from the Wars of the Austrian and Spanish succession's, through the American war of Independence and various campaigns in India and Africa, the Napoleonic Wars, the Second Boer War and many of the greatest battles of World War I (the Battle of Mons, the Battle of the Somme (1916), the Battle of Passchendaele, the Battle of Cambrai) and the Third Anglo-Afghan War in 1919. In World War II the regiment fought as part of the British Expeditionary Force in France, forming part of the rearguard at Dunkirk; in North Africa; Italy and in France, following the D-Day landings, and as Chindits in Burma. In Korea, the 'Dukes' desperate defence of the Hook position halted the last major Chinese attempt to break the United Nations Line before the truce, in July 1953, brought the war to an end. In Cyprus the battalion was successful in Operation Golden Rain, destroying a major EOKA terrorist group operating in the Troodos Mountains in 1956. In 1964 the battalion joined the NATO deterrence in Germany on the front line in the Cold War and from 1971 was regularly engaged in 'the Troubles' in Ulster until 1997. They were amongst the first units to cross the border from Kuwait in the 2003 Iraq War.
Nine soldiers from the regiment have been awarded the Victoria Cross, and Corporal Wayne Mills of the 1st Battalion became the first recipient of the Conspicuous Gallantry Cross in 1994, whilst serving with the United Nations forces in Bosnia.
Formation and name
The Duke of Wellington's Regiment was originally formed in 1702 as Huntingdon's Regiment. As regiments at that time took the name of the Colonel taking it over it became:- Henry Leigh's Regiment; then Robert Duncansons Regiment and George Wade's Regiment. It was disbanded on 25 March 1714, but was officially registered as the 33rd Regiment of Foot in January 1715 and re-raised on 25 March 1715, as George Wade's Regiment; then Henry Hawley's Regiment; Robert Dalzell's Regiment and John Johnson Regiment. The regiment served in Austria, France, The Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, America, Canada, Germany and India and the Indian Ocean islands as part of a Royal Navy Raiding Squadron and the Crimean War.
Owing to its links with the Duke of Wellington, the title 'The Duke of Wellington's Regiment' was granted to the 33rd Regiment on 18 June 1853, on the anniversary of the Battle of Waterloo in the year following Wellington's death. Subsequently, the regiment was presented with a new stand of Regulation Colours, on 28 February 1854, emblazoned with its new distinctions of the name of the Duke of Wellington, his crest and motto, by the then Colonel of the Regiment, Lieutenant General Sir Henry D'Oyley. The regiment departed for the Crimea the following day.
The 76th Regiment was originally raised, by Simon Harcourt as Lord Harcourts Regiment on 17 November 1745 and disbanded in June 1746. Following the loss of Minorca, to the French, it was reraised in November 1756 as the 61st Regiment, but renumbered to 76th, by General Order in 1758, and again disbanded in 1763. A second battalion raised by that regiment in October 1758, for service in Africa, was renumbered as the 86th Regiment and also disbanded in 1763. On 25 December 1777, the 76th was again re-raised, as the 76th Regiment of Foot (Macdonald's Highlanders), by Colonel John MacDonell of Lochgarry, in the West of Scotland and Western Isles, as a Scottish Light Infantry regiment. It was disbanded at Stirling Castle in March 1784. The regiment was again raised for service in India by the Honorable East India Company in 1787.[3]
In 1881 the 76th Regiment, which shared the same Depot in Halifax as the 33rd, was linked to the 33rd, under the Cardwell Reforms, to become the 2nd Battalion. Although retitled as the Halifax Regiment (Duke of Wellington's) this title only lasted six months until it was changed on 30 June 1881, in a revised appendix to General order 41, to:- The Duke of Wellington's (West Riding Regiment), or 'W Rid R' for short. In January 1921 it was again retitled to The Duke of Wellington's Regiment (West Riding), or 'DWR' for short. On 6 June 2006 The 'Dukes' were amalgamated with the Prince of Wales's Own Regiment of Yorkshire and The Green Howards, all Yorkshire-based regiments in the King's Division, to form the Yorkshire Regiment.
1702–1881
Within months of its original raising the regiment was despatched to join Malborough's army in Holland. After five months and only two battles it, along with five other of Malborough's best regiments, was sent to Portugal, where it remained for the next six years. The 33rd fought in many battles including: Valencia de Alcantara (1705), Zaragossa (1710) and less favourably at Almansa and Brihuega. It was only one of the two foot regiments not to be disbanded and in 1743 the regiment was sent to Germany, where it distinguised itself in the Battle of Dettingen, gaining its first battle honour, then again at the Battle of Fontenoy in 1745 and again in Rocoux and Lauffeld in 1747.
American Revolution
The 33rd itself had a good reputation for its professionalism and capability, which was seemingly unequalled by any other regiment of the British Army for some time. It was because of their professionalism in the field during the American War of Independence, that the regiment was given the nickname 'The Pattern'; the regiment then became the standard of soldiering which all other regiments should attain.
The 33rd saw much action during the American War of Independence, with its first engagement at the First Siege of Charleston in early 1776, when British forces attempted an assault on that city's defences. In August of that year, the 33rd were involved in the Battle of Long Island. After heavy fighting which lasted several days, the Americans evacuated their remaining forces to Manhattan. The British were victorious. The British forces suffered about 400 casualties, and the Americans over 2,000. The New York area remained in British control until late 1783.
The regiment's next action came a month later, in September at the Battle of Harlem Heights. It was a small skirmish: besides some Hessian troops, the only other British regiment was the 42nd Regiment of Foot, now the famous Black Watch, an equally fearsome and professional regiment. The British force, initially without the 33rd, encountered Knowlton's Rangers, a scouting force sent by George Washington. A small skirmish ensued with the Americans subsequently retreating. Washington then sent another force to lure the British further up the northern plateau, which he held, along with a second force to move around the flank of the British. The British took the bait and advanced further up the plateau. The American flanking force was encountered by the British, which showed them the imminent danger they faced. After some further fighting, the British retreated to a field, where they were joined by the 33rd and a number of Hessian battalions. After further fighting, the Americans retreated.
The regiment was also involved in the Battle of Fort Washington. After that, the 33rd were not involved in a major battle until September 1777, when they took part in the Battle of Brandywine, where the British suffered 550 casualties and the Americans about 1,000. The regiment took part in further action that year, at the Battle of Germantown and at Whitemarsh, where they fought the Americans who had retreated from the fighting at Germantown.
The following year was just as active, with the 33rd seeing action at the Battle of Monmouth, an engagement that became the largest one-day battle of the war. The 33rd was also part of the defence of Newport and Quaker Hill[disambiguation needed
 ], as well as the Battle of Old Tappan, which occurred in the closing months of the year.
], as well as the Battle of Old Tappan, which occurred in the closing months of the year.Two years later, in 1780, the 33rd Regiment was again besieging Charleston. By 11 May, the American General Benjamin Lincoln began to negotiate terms of surrender. The following day Lincoln, along with over 7,000 American soldiers, surrendered to the British forces under the command of Lieutenant-General Henry Clinton. In August that year, the 33rd were involved at the Battle of Camden. It was a victory for the British. Approximately 324 British were killed or wounded and about 1,000 Americans were killed or wounded, with another 1,000 being taken prisoner.
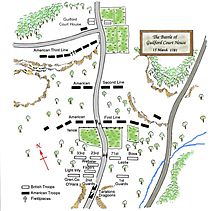
Guilford Court House
The year 1781 proved to be the deadliest but most successful year for the 33rd. The regiment took part in the Battle of Wetzell's Mill, but the more famous action took place that same month during a battle at Guilford Court House.
On 14 March 1781, Lord Cornwallis, the British commander, was informed that General Richard Butler was marching to attack his army. With Butler was a body of North Carolina Militia, plus reinforcements from Virginia, consisting of 3,000 Virginia Militia, a Virginia State regiment, a Corp of Virginian "eighteen-month men" and recruits for the Maryland Line. They had joined the command of Major General Nathanael Greene, creating a force of some nine to ten thousand men in total. During the night, further reports confirmed the American force was at Guilford Court House, some 12 miles (20 km) away. Cornwallis decided to give battle, though he had only 1,900 men at his disposal.
At dawn on 15 March 1781, before the men had a chance to have breakfast, Cornwallis started for Guilford, arriving there at mid-day.[4] Banastre Tarleton's Light Dragoons had been in the vanguard of the approach up the road and were briefly engaged by Henry "Light Horse Harry" Lee's Dragoons (Lee's Legion) some 4 miles (6 km) short of the Guilford Court House. The British 23rd Regiment of Foot sent reinforcements forward, and Lee withdrew, having suffered badly at the hands of Tarleton's Light Dragoons in previous actions at Tarrant's House and Weitzell's Mill.
Unknown to Cornwallis, the Americans were actually deployed in three lines across the Salisbury road. The first, mostly manned by North Carolina Militia units, was behind the fence. To the west of this line were Colonel William Washington's 3rd Continental Light Dragoons and Virginian light infantry. To the east were Lieutenant Colonel Lee's Dragoons. His second, manned by Virginian Militia was about 300 yards to the rear of the first. To the rear of this final line was the court house and General Greene's command post.
After a twenty-minute cannonade, Cornwallis began his attack around 1:30 pm. His left flank, under the command of Lieutenant-Colonel James Webster, was made up of the 33rd and the 23rd Regiments, supported by the Grenadier company and 2nd Battalion of the Brigade of Guards, (fifteen men from each company of the 1st Regiment of Foot Guards, Coldstream Regiment of Foot Guards and the 3rd Regiment of Foot Guards, formed a composite battalion of Foot Guards to be sent to North America. The composite battalion was subsequently split into two battalions). At Guilford Court House, they were then under the command of Brigadier General O'Hara. The Light infantry of the Guards and the German Yäegers (Jagers) remained in the woods to the west. To the right, under the command of Maj-Gen Leslie were the 71st Frasers Highlanders and the Prussian General, Julius von Bose's, Hessians, with the 1st Battalion of Guards in support. Following on were Tarleton's Light Dragoons, plus 1 troop of the 17th Light Dragoons, ready to go where circumstances required.
The British moved forward in line. However, the wooded terrain, the width of the battlefield, and uneven resistance hindered a coordinated advance, and British forces arrived piecemeal at the third line. At the climax of the battle, British Guards and American Continentals engaged in hand-to-hand combat.
The 71st Regiment then came through the woods. The 2nd Battalion of Guards turned and charged back on the Americans, supported by the Grenadiers who had also advanced, pushing Washington's men back into the woods. Over to the left, elements of the 23rd Regiment started to appear, and part of Tarleton's Light Dragoons charged up the road. The Americans turned and retreated, leaving behind their field guns and ammunition wagons. The 33rd Regiment then appeared, having overcome many difficulties on their advance. They had been heavily engaged by the American right flank, first crossing then re-crossing a ravine to consolidate and regroup. They were soon followed by the Light Infantry of the Guards. Cornwallis ordered the 23rd and 71st Regiments with part of the Cavalry to pursue the Americans, though not for any great distance.
The battle had lasted only ninety minutes, and although the British technically defeated the American force, they lost over a quarter of their own men. The 33rd suffered 11 killed and 63 wounded out of a force of 300 all ranks, having already lost 28 men in preceding actions.
Green Spring
The 33rd also fought at the Battle of Green Spring in July of that year. Their last engagement of the war was at the Siege of Yorktown, when they were part of the outnumbered British forces. The British surrendered on 19 October, having little ammunition, food and supplies left. There was also no sign of Henry Clinton's relieving force, which arrived in the Chesapeake Bay on 24 October, far too late to affect the outcome.
England, West Indies, Flanders
After 10 years in America the 33rd finally returned to England in 1786. The following year they were posted to Windsor and took up duty as 'The Kings Guard', until 1789. It was then posted to various barracks around Devon & Cornwall, being at that time the only regiment in the south of England.
In 1793 the 'Honourable Arthur Wesley', 3rd son of the Earl of Mornington, the future Duke of Wellington, purchased a 'Majority' in the 33rd.
By 1794 the 33rd was under the command of Lieutenant-Colonel (promoted to full Colonel in 1797) Arthur Wellesley. They had taken part in the disastrous Flanders Campaign and the retreat from Germany, and embarked, from Bremen, for England on 13 April 1795. Though having suffered only six men killed in combat, over 200 more died from disease and other causes during the 10 months of campaigning. A further 192 remained behind, sick in hospital. The regiment returned to Warley in Yorkshire to rest, recruit and retrain.
On 16 November 1795 the 33rd was again deployed to the West Indies. However the ships ran into a storm, almost immediately and had to take shelter in ports around the south coast, before resuming sail on 3 December. The ship the 33rd was in had been sent to Lymington and the 33rd debarked to recuperate. It remained there until April 1796 when it was despatched to Calcutta, arriving on 17 February 1797, under the command of 'Colonel Arthur Wesley'.
India
In 1799 the regiment took part in the Fourth Anglo-Mysore War in a Division commanded by Colonel Arthur Wellesley, as part of a British East India Company army, commanded by Major General Harris, with Major General Sir David Baird as second in command. Arthur's eldest brother Richard Wellesley, 2nd Earl of Mornington, later 1st Marquess Wellesley, had just become Governor General of India and so, in addition to the 33rd, Arthur, who had now become Colonel Arthur Wellesley, was given command of the 10,000 men of the Nizam of Hyderabad [5]. They had a decisive part to play in the Battle of Seringapatam. The regiment, involved in bitter fighting with the Tippu Sultan's warriors, were repulsed with heavy losses when they attacked a wood, which was strongly defended by the Sultan's forces. The 33rd rallied and fought further actions throughout the battle, with the British emerging decisively victorious and the Tippoo Sultan being killed. The regiment won a battle honour for its involvement in the action.
The siege of Seringapatam is featured in the Richard Sharpe novel Sharpe's Tiger by Bernard Cornwell. It is also the setting for the first British detective novel, Wilkie Collins's 'The Moonstone' (1868).
In 1857 the 33rd took part in operations against the Indian Mutiny being involved in a number of actions there, notably at Dwarka, which ultimately led to the restoration of stability.
Napoleons Return and Waterloo
 Reenactors in the red-coated uniform of the 33rd Regiment of Foot as worn during the Napoleonic Wars between 1812 and 1816. Note the brighter scarlet of the officer on the right.
Reenactors in the red-coated uniform of the 33rd Regiment of Foot as worn during the Napoleonic Wars between 1812 and 1816. Note the brighter scarlet of the officer on the right.
The 33rd landed at Willemstad on 17 December 1814, and worked in conjunction with the Russian contingent under Benckendorff and the Prussians under Bülow the regiment, under the command of Lt-Col Elphinstone. There was a considerable amount of inconclusive manoeuvring before finally action against the French near Antwerp on 13 January, around the village of Merxem. The French were routed at bayonet point with no casualties suffered by the 33rd.
By early March 1815, the Regiment was again under the command of the Duke of Wellington, this time during the Hundred Days campaign of Napoleon. Having taken part in the action of the previous day, at the Battle of Quatre Bras, they took up positions at Waterloo, the 33rd was part of the 5th Brigade under the command of Major General Sir Colin Halkett, which comprised, in addition the 2nd Bn 30th Foot, and 2nd Bn 69th Foot. The brigade was part of the 3rd Division under the command of General Count Sir Charles Alten, which was in turn part of I Corps, under the command of William, Prince of Orange.
The 33rd was involved in heavy fighting during the Battle of Waterloo and at the end of the battle the regiment's casualties numbered 11 officers and 128 men killed or wounded. The British and their Allies were victorious, but at a price of suffering about 15,000 casualties. The Prussians suffered 7,000 casualties. The French suffered 32,000 dead or wounded, as well as around 8,000 taken prisoner.
West Indies
Having departed from Paris on 23 December 1815, the regiment spent the post Waterloo period, from January 1816 to 1821, in uneventful garrison duties in Glasgow, Guernsey and Dublin. The regiment was able to recruit, re-equip and retrain, gaining the approval of many visiting Generals.
In 1822, the regiment was posted to Jamaica. The West Indies were notorious as the death bed of the British Army because of the high mortality rate from Malaria, Dysentery, Yellow fever and other such endemic diseases. Many thousands of soldiers never made it back to Britain. The 33rd was not to escape its harsh environment. Within two months, three officers and 49 other ranks had died. By the end of the tour in 1832, 11 officers and 560 NCOs and men had died from diseases. They arrived in Portsmouth in March 1832 with a command of 12 officers and 240 other ranks. 142 had opted to remain behind, having married and taken up residence with their families, and transferred to the 22nd (Cheshire) and the 84th (York and Lancaster) Regiments.
Crimea
Owing to its links with Wellington, the title '33rd (The Duke of Wellington's) Regiment' was granted to the 33rd, on 18 June 1853 (the 38th Anniversary of the Battle of Waterloo) by Queen Victoria, in honour of the 1st Duke of Wellington, who had died on 14 September the previous year.
At the Battle of Alma, bitter fighting took place, with the 33rd being part of the Light Division under the command of Sir George Brown. The British advanced up the slope towards the Russian positions. The British formations became intermingled, turning into a mass of soldiers, rather than the professional, neat formations used on parade. As they charged, numerous Russian troops came down the slope to meet them. The British halted and fired, causing so many casualties the Russians were forced to retreat. The British line reorganised and moved up the slope towards the Great Redoubt, with the 33rd being the first to attack the defence works. The 33rd suffered heavy casualties in the hand-to-hand combat that ensued.
The British forces prevailed in taking the objective. However, Russian forces advance on the Great Redoubt to counter-attack. An officer shouted to the British soldiers not to fire, claiming them to be French, despite the fact that they were not. Other British officers soon contradicted him, ordering the men to fire at the massed ranks of soldiers advancing on their position. The soldiers were confused, and the British officers soon decided the prudent option would be to get back down the hill to safety. The Russians failed to pursue, mostly because some French artillery pieces were firing a few shells in the direction of the Russian forces. The Guards Division, comprising the most elite infantry regiments of the British Army, advanced and crossed the river. However, the Scots Guards were shattered when retreating soldiers from the Royal Welch Fusiliers, who had been attacked by a mass of Russian soldiers, crashed into the Scots Guards and caused chaos amongst the formation. The Russians seized the moment, launching a mass bayonet charge resulting in heavy hand-to-hand fighting. The Scots Guards suffered 200 casualties and were forced to retreat.
An unknown officer ordered the Grenadier Guards, who were preparing to meet the advancing Russian forces, to withdraw. The officer commanding a company of the Grenadiers ordered them to reform to meet the advancing Russians. They poured a large amount of fire into the Russian troops, causing many casualties. The British then began to advance, and the Russians retreated. The Great Redoubt was once again in British control. On the right flank, the Highland Brigade—just two lines deep—advanced whilst firing, which was an unusual manoeuvre in those days. The Russians soon fled, and victory was assured. The British forces suffered 2,000 casualties, the French 1,000, and the Russians 6,000. The 33rd received a Battle Honour for their actions during that battle.
At the Battle of Inkerman, the 33rd were again involved in some bitter fighting, in which the British infantry advanced despite heavy losses and a strong defence by the Russians. The fighting was fierce, at times some soldiers resorting to attacking their enemy with the butts of their guns. The British suffered some 2,357 killed or wounded, and the French lost about 939 soldiers. Russian casualties were immense with some 11,800 killed or wounded.
The 33rd was involved in the Siege of Sevastopol, which lasted for 11 months. By 1856, the war was over but at a high price. The British had lost approximately 22,182 dead and 18,280 wounded, out of a total force of over 97,000. The majority were lost not because of fighting with the Russians, but to disease. In total, the Allies lost over 160,000 dead and the Russians lost over 450,000.
Abyssinia
The 33rd were part of an expedition sent to the East African nation of Abyssinia, now known as Ethiopia after several European citizens had been taken hostage by the self appointed 'King' Emperor Tewodros II in 1864. In March 1866 a British envoy had been despatched to secure the release of a group of missionaries who had first been seized when a letter Tewdros II had sent to Queen Victoria, delivered by an envoy (Captain Cameron), requesting munitions and military experts from the British, had gone unanswered. They were released; however Tewdros II changed his mind and sent a force after them and they were returned to the fortress and imprisoned again, along with Captain Cameron.
The 33rd was committed to Abyssinia in October 1867 and embarked on 21 November, arriving at Annesley Bay on 4 December; but did not disembark for three days due to the chaos on shore.[6] Thousands of mules had been sent from Egypt and other countries before adequate arrangements had been made to feed and water them. Initially two companies of the 33rd went ashore to capture and contain the mules and condensed sea water was pumped ashore from a warship and then carried by hand to makeshift wooden troughs. A base camp was set up at Zula where officers celebrated Christmas Day with local chicken and a plum pudding made from pounded ships biscuits.
Having left Karachi during the Indian winter the 33rd were still dressed in 'Waterloo-red' full Dress Tunic and khaki Drill Trousers. The Serge was quickly changed for the more appropriate Khaki Drill jacket and also a white cloth covered Cork Helmet called a 'Topi'. The troops had been issued the new breech loading Snider-Enfield rifles the previous year, which increased the soldiers fire power from one round per minute to ten rounds per minute. Besides the 33rd of Foot, the expeditionary force included 12,000 British and Indian troops, as well as Royal Artillery and Royal Engineers.
Lord Napier arrived in early January 1868 and the expedition started from the advance camp at Senafe at the beginning of February. It took two months to reach their objective, advancing through rough terrain. From Senafe the force passed through Adigrat, Antalo, to the west of Lake Ashangi, and on to Dildi before finally arriving via the road King Theodore built through the Chetta Ravine to get his heavy artillery to Magdala. Yet before they could actually storm the fortress, they had to cross the plateau at Arogye, which lay across the only route to Magdala and was held by Tewodros' forces. It certainly looked formidable to attack, with the way barred by many thousands of warriors camped around the hillsides, and as many as 30 artillery pieces visible on a nearby hilltop.
The British did not expect that the Abyssinian warriors would leave their defences to attack them and paid little regard to their defensive positions as they formed up to deploy. But the Emperor did order an attack, with many thousands of foot warriors armed with little more than spears. The 4th of Foot quickly redeployed to meet the charging mass of warriors and poured a devastating fire into their ranks. When two Indian infantry regiments also fired on them the onslaught became even more devastating. Despite this the Ethiopian warriors continued their attack, losing over 500 with thousands more wounded during the ninety minutes of fighting, most of them at little over 30 yards from the British lines. During the chaotic battle an advance guard unit of the 33rd Regiment overpowered some of the Ethiopian artillerymen and captured their artillery pieces. The survivors of the assault then retreated back to Magdala.
In his despatch to London Lord Napier reported: "Yesterday morning (we) descended three thousand nine hundred feet to Bashilo River and approached Magdala with 'First Brigade' to reconnoiter it. Theodore opened fire with seven guns from outwork, one thousand feet above us, and three thousand five hundred men of the garrison made a gallant sortie which was repulsed with very heavy loss and the enemy driven into Magdala. British loss, twenty wounded"
The following day as the British force moved on to Magdala, Tewodros II sent two of the hostages on parole to offer terms. Napier insisted on the release of all the hostages and an unconditional surrender. Tewodros refused to cede to the unconditional surrender, but did release the European hostages. The British continued the advance and assaulted the fortress. (The native hostages were later found to have had their hands and feet cut off before being sent over the edge of the precipice surrounding the plateau.)[7]
The bombardment began with mortars, rockets and artillery. Infantry units then opened fire, covering the Royal Engineers sent to blow up the gates of the fortress. The path lay up a steep boulder strewn track one one side of which was a sheer drop and the other by a perpendicular cliff face, leading to the main gateway, known as the Koket-Bir, which consisted of a thick timber doors set in a 15-foot-long (4.6 m) stone archway. Each side of the gate was protected by a thorn and stake hedge. After this gate was a further uphill path to a second fortified gateway, which lead onto the final plateau, or 'amba'
On reaching the gate there was a pause in the advance, as it was discovered the engineer unit had forgot their powder kegs and scaling ladders and were ordered to return for them. General Staveley was not happy at any further delay and ordered the 33rd to continue the attack. Several officers and the men of the 33rd Regiment, along with an officer from the Royal Engineers, parted from the main force and, after climbing the cliff face, found their way blocked by a thorny hedge over a wall. Private James Bergin, a very tall man, used his bayonet to cut a hole in the hedge and Drummer Michael Magner climbed onto his shoulders through the hedge in the gap and dragged Bergin up behind him as Ensign Conner and Corporal Murphy helped shove from below. Bergin kept up a rapid rate of fire on the Koket-Bir as Magner dragged more men through the gap in the hedge. As more men poured through and opened fire as they advanced with their bayonets the defenders withdrew through the second gate. The party rushed the Koket-bir before it was fully closed and then took the second gate breaking through to the Amba. Ensign Wynter scrambled up onto the top of the second gate and fixed the 33rd Regiments Colours to show the Plateau had been taken. Private Bergin and Drummer Magner were later awarded the Victoria Cross for their part in the action.[8]
Tewodros II was found dead inside the second gate, having shot himself with a pistol that had been a gift from Queen Victoria. When his death was announced all opposition ceased. The regiment later received the battle honour Abyssinia.[9]
Duties of Empire (1881–1914)
1st Battalion
The 1st Battalion returned to England in 1889 after a number of years stationed in India. In 1895, the battalion deployed to Malta in the Mediterranean and returned home again in 1898.
The 1st Battalion began the first year of the 20th century at war when it arrived in South Africa, in 1900, as reinforcements for British forces fighting Boers, in the Second Boer War. The battalion took part in the Relief of Kimberley, in February 1901, which had been under siege by the Boers since October 1899. The battalion also took part in the Battle of Paardeberg, which was eventually captured by the British, after the Boers surrendered on 27 February 1901. The battalion saw action at the British victory at Driefontein on 10 March 1901.
On 29 November 1901, Lieutenant Colonel George Evan Lloyd, the commanding officer of the 1st Battalion, was killed in action at Rhenoster Kop. The 1st Battalion saw numerous small-scale actions against the elusive Boer commandos for the duration of the war, returning home in 1902. The regiment gained the battle honour "Relief of Kimberley" and the theatre honour "South Africa 1900-02".
The 1st Battalion's stay in England was relatively brief, as it departed for India in 1905, where it remained until 1921.
2nd Battalion
Meanwhile, the 2nd Battalion (formerly the 76th Regiment) had deployed to Bermuda in 1886 for garrison duty, where they remained until 1888 when it arrived in Nova Scotia, Canada. In 1891 they moved to the West Indies and in 1893 moved to South Africa leaving just before the start of the Boer War, for service in Burma. The Battalion was stationed in Ireland when the First World War began in 1914.
World War I (1914–1918)
The 1st Battalion (Regular) remained in India throughout the war, but the 2nd Battalion (Regular) first saw action at the Battle of Mons. It then fought a rearguard action at the Battle of Le Cateau, a vital action during the retreat from Mons. Despite being heavily outnumbered, the British forces inflicted severe casualties on the Germans. The British soldier's ability to fire the Lee-Enfield rifle with deadly accuracy and speed was certainly a deciding factor in the engagement. Although it was a victory for the Germans, at least tactically, the brave actions of the British soldiers that fought the rearguard effectively saved the war for the Allies.
The 2nd Battalion also fought at the First Battle of the Marne, the Battle of the Aisne, the Battle of La Bassée and the brutal first Battle of Ypres. First Ypres began as an offensive battle, with the attacking and exposed British infantry taking heavy casualties from German machine guns. The battle soon bogged down into trench warfare. The British Expeditionary Force suffered some 54,100 casualties, astonishing figures that would be eclipsed within two years.
The 2nd Battalion was also at the Battle of Hill 60. The British placed six mines under Hill 60. Most of the hill was blown away when the mines were detonated, causing many casualties to the German forces defending it. The British then launched a massive bombardment, followed by an assault that led to vicious hand-to-hand fighting. About 150 Germans were killed in the action and the British lost seven. That night the Germans counter-attacked, inflicting numerous casualties on the British defenders, and retook the hill. The 'Dukes', along with the 2nd Kings Own Yorkshire Light Infantry assaulted the hill, recapturing it after some fighting. They were subsequently relieved by four regiments, with one in reserve. The Germans counter-attacked two days later, but were repelled by those regiments, in which an officer from the 1st Surreys won a Victoria Cross for his actions during the defence of the hill.
The 'Dukes' raised twenty three battalions for service during the First World War, including two labour Battalions. Fourteen of these Battalions (Regular, Territorial Force and Service) took part in several of the greatest battles of World War I: , the 8th Battalion saw service in the Gallipoli Campaign and the 10th Battalion was in action at Piave in Italy. In all, during the course of World War I, the Regiment suffered many casualties, with over 8,300 killed. Having fought in nearly every theatre of the war the Regiment's service was recognised by the award of 197 Battle Honours, many of which were to separate battalions in the same theatre of action, 10 of which are emblazoned on the King's Colour.
Inter-war (1919–1938)
In 1919, the 1st Battalion took part in the Third Anglo-Afghan War and eventually returned home in 1921 where it arrived in Ireland during tumultuous times there. It was stationed in Germany as part of the British Army of the Rhine in 1922. It was posted to Malta in 1935, the last overseas deployment for the battalion in the inter-war period. The Battalion returned to the UK in 1937.
The 2nd Battalion was posted to Ireland in 1919 before it deployed to Egypt in 1922. It was based in Singapore in 1926, and returned to India in 1928.
Meanwhile, the Regiment's title had altered slightly in 1921 to its present-name of the Duke of Wellington's Regiment (West Riding).
World War II (1939–1945)
1st Battalion
 Men of 1st Battalion, The Duke of Wellington's Regiment, advance past a burning fuel store on Pantelleria during Operation Corkscrew
Men of 1st Battalion, The Duke of Wellington's Regiment, advance past a burning fuel store on Pantelleria during Operation Corkscrew
In World War II, the 1st Battalion was immediately sent to France as part of the British 3rd Infantry Brigade of the 1st Infantry Division of 1st Corps of the BEF. During the retreat to Dunkirk, the 'Dukes' forming part of the rearguard.
The 'Dukes' next fought in North Africa, fighting with distinction in a number of actions and gaining several Battle Honours. They fought at the Battle of Medjez Plain, as well as the Battle of Djebel bou Aoukaz, taking the town on 27 April 1943. The town however, was re-taken by German forces on 30 April, after heavy fighting. On 5 May, the British forces re-took the town from the Germans.
The 'Dukes' also fought in Italy, taking part in the Anzio Campaign in early 1944 in an attempt to outflank the Gustav Line and force a German retreat from Monte Cassino. The Regiment was involved at the Battle of Campoleone, when two veteran German divisions (one armoured, the other a parachute division) attacked. The British forces defended stoutly, suffering 1,000 casualties in the first day alone. They only withdrew after further heavy fighting took place. The 'Dukes' fought with distinction at the Battle of Monte Ceco in October 1944 where Private Richard Henry Burton, of the 1st Battalion, was awarded a Victoria Cross for his courageous action in the battle. The regiment also won a Battle Honour for the engagement.
2nd Battalion
In the Far East, the 2nd Battalion took part in the rearguard action at the Battle of Sittang Bridge in February 1942 and in the Battle of Paungde in March that year. The plan was to advance and occupy Paungde. The strike force advanced on 29 March, but had to fight Japanese forces just north-east of their objective in the area of Padigon. The force made some progress in the Paungde area before meeting stiff resistance. Due to their orders not to be cut off, the 2nd 'Dukes' and the 7th Hussars withdrew. A Japanese regiment had crossed the west bank of the Irawaddy River, digging in at Shwedaung, just behind the British strike force. An engagement ensued, with the Indian 17th Infantry Division attacking, the Japanese held the town. The British force suffered heavy casualties in fighting their way through Shwedaung to rejoin the 17th Indian Division.
They were trained as Chindits, to operate behind Japanese lines, who were at that time attacking India, they were formed into two columns, the 33rd and 76th, to operate behind the Japanese lines during the fierce battles for Imphal and Kohima.
6th and 7th Battalions
Having spent 1942 providing a defensive force in Iceland based mostly around Reykjavík the 1/6th and 1/7th battalions were replaced by American troops and returned to England to train and prepare for the invasion of Normandy.
On 9 June 1944 the 1/6th and 1/7th Battalions embarked on HMS Cheshire arriving off the Normandy coast on 11 June. By late evening of that day they were five miles inland. The 1/6th, under the command of Lt Col RK Exham, was the first to engage the enemy. On 16 June the battalion was ordered to attack Parc de Boislonde, a thickly wooded ridge overlooking Fontenay le Pesnil. The attack was supported by a squadron of tanks and artillery from four field regiments. The attack was successful, but resulted in heavy losses to the battalion. The following day the German forces counter attacked, forcing the 6th Battalion back, the bitter fighting saw the battalion lose 16 Officers and 220 other ranks in the first two days.
The battalion was then withdrawn to a nearby Chateau to rest, but was spotted by a reconnaissance aircraft and was heavily shelled by German artillery, resulting in another 20 casualties. That same afternoon, 20 June, the battalion paraded for the Brigade Commander and was promptly shelled again, with even more casualties. At that point Lt Col Exham was switched to command another battalion. On 25 June, under the command of Lt Col AJD Turner MC Suffolk Regiment, the 1/6th battalion was moved up to support the flank of 147 Brigades attack on Fontenay le Pesnil and then the village of Rauray.
Heavy fighting ensued, with a number of German units, from the elite 12th SS Panzer Division, putting up stiff resistance. The objectives were taken but the 1/6th had come under withering Mortar fire, suffering further heavy losses. The new Commanding Officer felt the battalion needed a rest and reorganisation and put in a report to General Montgomery:
1. I arrived at 6DWR on the evening of 26 June. From am 27 June until am 30 June we have been in contact with the enemy and under moderately heavy mortar and shell fire.
2. The following facts make it clear that this report makes no reflection on the state of 6 DWR when they left UK:
- a) In 14 days there have been some 23 officers and 350 OR casualties
- b) Only 12 of the original officers remain and they are all junior. The CO and every rank above Cpl (except for 2 Lt's) in Battalion HQ have gone, all company commanders have gone. One company has lost every officer, another has only one left.
- c) Since I took over I have lost two second-in-commands in successive days and a company commander on the third day.
- d) Majority of transports, all documents, records and a large amount of equipment was lost
3. State of Men
- a) 75% react adversely to enemy shelling and are "jumpy"
- b) 5 cases in 3 days of self inflicted wounds
- c) Each time men are killed or wounded a number of men become casualties through shell shock or hysteria.
- d) In addition to genuine hysteria a large number of men have left their positions after shelling on one pretext or another and gone to the rear until sent back by the M.O. or myself
- e) The new drafts have been affected, and 3 young soldiers became casualties with hysteria after hearing our own guns
- f) the situation has got worse each day as more key personnel have become casualties
4. Discipline and Leadership
- a) State of Discipline is bad, although the men are a cheerful pleasant type normally
- b) NCOs do not wear stripes and some officers have no badges of rank. This makes the situation impossible when 50% of the Battalion do not know each other.
- c) NCO leadership is weak in most cases and the newly drafted officers are in consequence having to expose themselves unduly to try to get anything done. It is difficult for the new officers (60%) to lead the men under fire as they do not know them.
Conclusion
- a) 6DWR is not fit to take its place in the line.
- b) Even excluding the question of nerves and morale 6DWR will not be fit to go back into the line until it is remobilised, reorganized, and to an extent retrained. It is no longer a battalion but a collection of individuals. There is naturally no espirit-de-corps for those who are frightened (as we all are to one degree or another) to fall back on. I have twice had to stand at the end of a track and draw my revolver on retreating men.
Recommendation. If it is not possible to withdraw the battalion to the base or UK to re-equip, reorganize and train, then it should be disbanded and split among other units. If it is not possible to do either of the above and it is essential that the battalion should return to the line, I request that I may be relieved of my command and I suggest that a CO with 2 or 3 years experience should relieve me, and that he should bring his adjutant and a signals officer with them.
Being a Regular officer I realise the seriousness of this request and its effect on my career. On the other hand I have the lives of the new officer personnel (which is excellent) to consider. Three days running a Major has been killed or seriously wounded because I have ordered him to, in effect, stop them running during mortar concentrations. Unless withdrawn from the division I do not think I can get the battalion to fight normally and this waste of life would continue. My honest opinion is if you continue to throw new officer and other rank replacements into 6DWR as casualties occur, you are throwing good money after bad.
I know my opinion is shared by two other Command officers who know the full circumstances.
On receipt of the report General Montgomery instantly dismissed the new CO, disbanded the battalion and used it to provide drafts for the 1/7th battalion. It arrived back in Guildford on 17 August 1944 having lost 19 Officers and 350 other ranks. It was replaced in the Line by the 1st Battalion, Leicestershire Regiment.
7th battalion
The 1/7th had been issued with 350 folding bicycles to aid them in moving forward into France, However the Commanding Officer felt the 8-foot-high (2.4 m) banks and deep ditches unsuitable country in which to use them, so they were stored in a wood; and almost instantly crushed by a passing squadron of tanks. The fighting around Fontenay-le-Pesnel saw the battalion lose some 120 men, killed and wounded.
Further fighting saw the battalion advancing daily, bolstered up to a force of 30 officers and 850 men, after the merger of the 1/6th battalion, and on 3 September they had crossed the Seine. On 10 September they were involved in heavy fighting around Le Havre and by 23 September they were on the southern bank of the Leopold Canal, approximately 18 miles east of Antwerp. On 30 October the 1/7th had advanced as far as Roosendaal in the North Brabant region of the Netherlands, just north of the Belgian border.
On 1 November 1944 the 1/7th battalion was placed under the command of the Canadian army, where they defeated an attempt by a German parachute battalion to capture the Nijmegen bridge, capturing over 100 prisoners, with a further 50 killed or wounded. in April 1945 the battalion was involved in the breakout from the Nijmegen salient and by 7 May it was in Utrecht disarming three German divisions, the day before the war in the European theatre was finished.
Korean War (1952–1956)
The 1st Battalion was deployed to Korea in 1952, two years after the Korean War had broken out. They were part of the 1st Commonwealth Division.
Battle of The Hook
In 1953, the 1st Battalion relieved the Black Watch, who had been defending a position known as The Hook, a crescent shaped ridge, which was of tactical importance in the Commonwealth sector. From 10 to 28 May, the 1st Battalion suffered 58 casualties, from artillery and mortar fire.
The third Battle of the Hook began on 28 May. An initial bombardment of the British positions took place, with the Chinese forces charging the forward British positions once the bombardment ceased. The fighting that ensued was bloody and more akin to the battles that the 'Dukes' had fought in World War I. Shells were now raining down on the Hook from artillery and mortars, from both the Chinese and UN forces. The Chinese launched a second attack but were cut down by heavy fire from UN the forces. Further attacks occurred on 28 May, but all were defeated in heavy fighting.
Just 30 minutes into 29 May, the Chinese forces launched another attack but, as before, they were beaten back. Alma Company of 'The 'Dukes' then began advancing up the line of the original trenches to dislodge the remaining Chinese forces in the forward trenches. The 'Dukes' secured the Hook at 3:30 a.m. The 'Dukes' losses were 3 officers and 17 other ranks killed and two officers and 84 other ranks wounded, plus 20 other ranks missing.[10] The Chinese had about 250 killed, with over 800 being wounded. For their action, the Regiment was awarded the Battle Honour 'The Hook 1953'. Later, the 1st Battalion's Headquarter Company was renamed 'Hook Company'.
The 'Dukes' embarked for Gibraltar on (13 November 1953), where they arrived on 10 December. In May 1954, during a visit to Gibraltar by Queen Elizabeth II and the Duke of Edinburgh, the Commanding Officer of the 'Dukes' (Lieutenant Colonel FR St P Bunbury) and a further 10 officers and other ranks received decorations for their actions in Korea. The 'Dukes' was the last of the British infantry regiments to leave Korea.
General Franco of Spain objected to the Queen visiting Gibraltar and promptly closed the Spanish/Gibraltar border, thus confining the 'Dukes' to Gibraltar until September 1955 when they left to return to the UK. The border did not reopen until 1985, when the 'Dukes' were again stationed in Gibraltar.
Post-Korean War (1956–2005)
Garrison duties
After the bloody encounters in the Korean War, the 'Dukes' were occupied by a series of garrison duties. The 'Dukes' were first deployed to Gibraltar, then to Cyprus in 1956, where they participated in anti-terrorist operations against EOKA. The following year, the 'Dukes' deployed to Northern Ireland. They moved back to the mainland in 1959, joining the new UK Strategic Reserve, as part of 19 Infantry Brigade).
In 1960, the 'Dukes' deployed to Kenya at the request of the Governor. In 1968, the 'Dukes' deployed to Hong Kong for internal security duties, just a year after the riots there, when young followers of Chairman Mao besieged Government House. Thousands of bombs were planted during the riots, which killed fifteen people in that terror campaign.
The 'Dukes' returned to the UK in 1970. Then deployed to Northern Ireland a number of times during 'The Troubles'. Their first deployment was in 1971, during one of the bloodiest times in the Province in which 43 British soldiers and many civilians and terrorists lost their lives. They had further tours to the Province in 1973, 1976, 1977 and 1979. The 'Dukes' lost one officer and four soldiers during these deployments.
In 1985, the 'Dukes' deployed to Belize for a six-month tour of duty, taking part in operation 'Holdfast'. During this tour a jungle patrol by members of the regiments 'Alma Company' located a Marijuana processing camp hidden in the jungle. Although the occupants had all run away a large amount of Marijuana, estimated at over £250,000 in value, was found and subsequently destroyed by fire.
In 1987 the 'Dukes' deployed again to Northern Ireland for a two year tour, based in Palace Barracks, just outside the city of Belfast. Following this tour the 'Dukes' returned to Tern Hill Barracks in Market Drayton, Shropshire. Shortly after arriving the barracks was attacked by the IRA, in the form of a bomb in one of the accommodation blocks. Although the building was occupied no injuries were sustained.
Bosnia (1994–1995)
In March 1994, the 'Dukes' deployed to Bosnia, with an area of responsibility covering Bugojno, Vitez, Travnik and the besieged enclave of Goražde. The latter was under siege for much of the war. It was declared a UN Safe Zone in that year. The 'Dukes' were one of the first units to enter the town. The Regiment pushed the Bosnian-Serb Army from their positions around the town to a distance of over one mile. Their objective in doing this was to create a safe zone for the town. While at Goražde, Private Shaun Taylor of C Company was killed during an engagement with Bosnian-Serb forces while manning an observation post. The engagement lasted fifteen minutes, with over 2,000 rounds of ammunition being expended by the 'Dukes'. Seven of the Bosnian-Serb soldiers were killed in the fire-fight. Goražde remained a safe zone, being held by British troops from 1994-95. It was the only safe zone to survive the war and avoided the tragedies that occurred in other UN safe zones such as Srebrenica and Žepa.
Corporal Wayne Mills of the 1st Battalion became the first recipient of the Conspicuous Gallantry Cross, second only to the Victoria Cross. On (29 April 1994), a patrol led by Corporal Mills came under heavy small-arms fire from a group of Bosnian-Serbs. The patrol returned fire, killing two of the attackers. The patrol then withdrew, but the attackers persisted in firing on the patrol. The patrol soon reached an open clearing, where it was obvious they would be highly vulnerable to fire from the attackers. Corporal Mills then performed an astonishing feat of bravery. He turned back and engaged the group in a fire-fight, delaying the attackers long enough to allow the rest of his patrol to cross the clearing. While doing this brave act, Corporal Mills shot the leader of the group, with the rest scattering into the woods. Due to that action he returned to his patrol safely, who were giving covering fire.
Lieutenant-Colonel David Santa-Olalla received the Distinguished Service Order for his inspirational leadership and courage during the 'Dukes' deployment to Bosnia. He arranged for the mutual withdrawal of both Serbian and Muslim forces, from the besieged town of Goražde, just as the Geneva talks were being held on the town.
1995–2005
In March 1995, the 'Dukes' were again posted to Northern Ireland for a two year tour of duty. In March 1997, a composite company from the 1st Battalion was deployed to the Falkland Islands. In 1998, C Company deployed for a tour of duty in South Armagh. During the period 1998-2000, the 1st Battalion served as a public duties unit in London, where one of its roles was the provision of the Queen's Guard.
In February 2001, a company from the 'Dukes' deployed to Kosovo, with the objective of preventing arms and munitions being transported from Albania into Kosovo, then onto the Former Yugolav Republic Of Macedonia, now known as the Republic of Macedonia. In March the Dukes Battlegroup followed and deployed on Op Agricola V, taking over the role from 45 Commando Royal Marines at 4 pm on 3 March. The Battlegroup included:- 2nd Royal Tank Regiment, 3 Royal Horse Artillery and a battalion each from Sweden, Finland and Norway. The battlegroup was under the command of 19th Mechanised Brigade and covered Pristina City and the rural area to the north. The deployment ended in July that year.
In 2003, the 'Dukes' were part of Operation Telic, the invasion of Iraq, as part of 1 (United Kingdom) Armoured Division. The 'Dukes' returned, as part of 4 (Armoured) Brigade, to the South-East of Iraq, in October 2004, to join the British-led Multi-National Division (South-East), as a fully equipped armoured infantry battalion with Warrior Armoured Personnel Carriers.
During 2003, in Osnabrück, Germany, where the 'Dukes' were then based, the Regiment celebrated its 300th year in existence. Over 2000 past and present members converged on the town to take part in the celebrations. The 'Dukes' were presented with new colours by HM Queen Elizabeth II, represented by The Colonel of The Regiment Major-General Sir Evelyn John Webb-Carter KCB, due to the ill health of the Queen's representative, the regiments Colonel-in-Chief the Duke of Wellington. The regiment had a beer called Havercake Ale named in their honour by the Timothy Taylor Brewery, Leeds, to mark the regiments tercentenary. Timothy Taylor the founder of the brewery had served in an antecedent unit of the regiment during 1859. Since then other members of the family and employees had also enlisted as a 'Duke' one employee a Drayman called Arthur Poulter was awarded a World War I VC for his action in saving lives during the Battle of the Lys[disambiguation needed
 ].
].On 12 November 2005, the Regiment was awarded the "Keys to the Town" of Erquinghem-Lys in France.[11] It is the only British Regiment to have been awarded the Freedom of a French town.
Amalgamation
In December 2004, as part of the re-organisation of the infantry, it was announced that the Duke of Wellington's Regiment would be amalgamated with the Prince of Wales's Own Regiment of Yorkshire and the Green Howards', all Yorkshire-based regiments in the King's Division, to form the Yorkshire Regiment. The re-badging parade took place on 6 June 2006.
The 'Dukes' were the last British Regiment to have a Colonel-in-Chief who was not a member of a Royal family. Prince Andrew, The Duke of York was appointed to be the Colonel-in-Chief of the new Yorkshire Regiment.
The 'Dukes' had five companies, named to commemorate five significant campaigns and battles, in which the Dukes took part and were awarded a Battle honour, which have been retained by the battalion in the Yorkshire Regiment.[12]:
- A Company - Alma - commemorating the Battle of Alma, during the Crimean War 1853–1856
- B Company - Burma - commemorating the Burma Campaign, during the Second World War 1941-1944
- C Company - Corunna - commemorating the Battle of Corunna, during the Peninsular War of 1809-1813
- Support Company - Somme - commemorating the Battle of the Somme, during the First World War 1914-1918
- Headquarter Company - Hook - commemorating the Battle of the Hook, during the Korean war 1952-1953
When required an additional rifle company may be formed:- D Company - Dettingen - commemorating the Battle of Dettingen, during the War of the Austrian Succession in 1743 and an additional administration company:- W Company - Waterloo - commemorating the Battle of Waterloo, during the Waterloo campaign in 1815. Both companies having previously existed during the Dukes existence.
Regimental colours
The Duke of Wellington's Regiment had four colours on parade. The first pair of colours were the standard set of Regulation Colours, which all Regiments are presented with. The second pair was a set of Honorary Colours, which were originally presented to the 76th Regiment of Foot in 1808 for their actions during the Battle of Ally Ghur and Delhi in 1803.
The Honorary Colours were approximately 6-foot 6 inch by 6-foot. Following rebadging, on 6 June 2006 the 'Dukes' retained the Honorary Colours as:- The 3rd Battalion the Yorkshire Regiment (Duke of Wellington's). The Honorary Colours will only be paraded by the 3rd Battalion (Duke of Wellington's).
On Saturday 31 March 2007 the stand of Regimental Regulation colours taken out of service in 2002, in Osnabrück, Germany, at the Regiments Tercentenary parade were laid up in the Halifax Parish church. The Colour party, with two escorts of 40 troops, marched from the Town hall to the Parish Church, preceded by the Regimental Drums and the Heavy Cavalry and Cambrai Band. There was a short ceremony in the church grounds where the Troops were inspected by the Mayor of Halifax, Councillor Colin Stout, and the Lord Lieutenant of West Yorkshire Dr Ingrid Roscoe.
Battle honours
- War of the Austrian Succession
- India
- Hindoostan, Mysore, Seringapatam, Ally Ghur, Delhi 1803, Leswaree, Deig
- Spain:
- France:
- Crimean War:
- Abyssinia:
- South Africa:
- World War I:
- Mons, Le Cateau, Retreat from Mons, Marne 1914 and 1918, Aisne 1914, La Bassée 1914, Ypres 1914, 1915 and 1917, Nonne Bosschen, Hill 60, Gravenstafel, St. Julien, Aubers, Somme 1916 and 1918, Albert 1916 and 1918, Bazentin, Delville Wood, Pozières, Flers-Courcelette, Morval, Thiepval, Le Transloy, Ancre Heights, Arras 1917 and 1918, Scarpe 1917 and 1918, Arleux, Bullecourt, Messines 1917 and 1918, Langemarck 1917, Menin Road, Polygon Wood, Broodseinde, Poelcappelle, Passchendaele, Cambrai 1917 and 1918, St Quentin, Ancre 1918, Lys, Estaires, Hazebrouck, Bailleul, Kemmel, Bethune, Scherpenberg, Tardenois, Amiens, Bapaume 1918, Drocourt-Quéant, Hindenburg Line, Havrincourt, Épehy, Canal du Nord, Selle, Valenciennes, Sambre, France and Flanders 1914-18, Piave, Vittorio Veneto, Italy 1917-18, Suvla, Landing at Suvla, Scimitar Hill, Gallipoli 1915, Egypt 1916
- Third Anglo-Afghan War
- Afghanistan 1919
- World War II:
- Dunkirk 1940, St. Valery-en-Caux, Tilly sur Seulles, Odon, Fontenay Le Pesnil, North-West Europe 1940 and 1944-45, Banana Ridge, Medjez Plain, Gueriat el Atach Ridge, Tunis, Djebel Bou Aoukaz 1943, North Africa 1943, Anzio, Campoleone, Rome, Monte Ceco, Italy 1943-45, Sittang 1942, Paungde, Kohima, Chindits 1944, Burma Campaign (1942-44)
- Korea:
- Iraq:
- Iraq 2003 (Theatre Honour)
Uniforms
On formation in 1702 as the Earl of Huntingdon's Regiment a red coat lined with yellow was worn, together with yellow breeches. Later in the 18th Century the coats had red facings but white linings which showed in the turn-backed skirts. For the remainder of its history the Regiment was unusual in that the collars, cuffs and shoulder straps of its red coats were also red (most British regiments had facings of contrasting colours). This continued to be the case with the scarlet tunic worn by all ranks in full dress until 1914 and by bandsmen until amalgamation (see illustrations above). Officers were distinguished by silver buttons and braid until 1830 and thereafter by gold, After 1893 the badge of the Duke of Wellington was worn.[13]
Alliances
- les Voltigeurs de Québec, Canada
- 10th Battalion, The Baloch Regiment, Pakistan
- HMS Iron Duke, Royal Navy
Victoria Cross recipients
- Drummer Michael Magner
- Private James Bergin
- Sergeant James Firth
- Second Lieutenant James Palmer Huffam
- Second Lieutenant Henry Kelly
- Private Arnold Loosemore
- Private Arthur Poulter
- Private Richard Henry Burton
- Private Henry Tandey
- Private Henry Tandey was awarded his VC during his service with the 'Dukes' and donated his medals to the Regimental Museum in Halifax, West Yorkshire. On special occasions and parades he would sign them out to wear. The last time he signed them out he died. Unknowingly, the medals were sold and a private collector subsequently presented the medals to the Regimental Museum of The Green Howards, a regiment in which he had earlier served.
- Acting-Sergeant Hanson Victor Turner
- Although Hanson Victor Turner was 'originally' a 'Duke', he was serving with The West Yorkshire Regiment (The Prince of Wales's Own) when he was awarded his VC. When his medal was put up for sale it was purchased by the Halifax Town Council, as he was a Halifax resident. It is displayed in the Regimental Museum, in Halifax, for ease of access.
Colonels of the Regiment
- 1909-1934 Lt-General Sir Herbert Eversley Belfield KCB KCMG KBE DSO
- 1934-1938 Brigadier-General Percy Alexander Turner CMG
- 1938-1947 Colonel Charles James Pickering CMG DSO
- 1947-1957 General Sir Alexander Frank Philip Christison, Bart, GBE CB DSO MC
- 1957-1965 Major-General Kenneth Godfrey Exham KG CB DSO
- 1965-1975 General Sir Robert Napier Hubert Campbell Bray GBE KCB DSO
- 1975-1982 Major-General Donald Edward Isles CB OBE
- 1982-1990 General Sir Charles Richard Huxtable KCB CBE
- 1990-1999 Brigadier William Richard Mundell OBE
- 1999-2006 Major-General Sir Evelyn John Webb-Carter KCVO OBE
Sport
The 'Dukes' had a long and proud Rugby tradition. They produced in their history 11 international players, 7 English, 1 Irish and 3 Scottish, with over 50 players capped for the army against the Navy & Air Force since 1914.[14]
For Rugby union they list:- Capt (Bull) Faithfull, England (3 Caps) 1924. Lieutenant WF (Horsey) Brown, Army & Ireland (12 Caps), 1925-1928. Captain Mike Campbell-Lamerton, Army, London Scottish, Scotland (23 Caps), British Lions in South Africa in 1962, Captain of the British Lions in Australia & New Zealand in 1966. Lieutenant CF Grieve and FJ Reynolds Toured South Africa in 1938 with the British Lions. In the early 1950s DW Shuttleworth and EMP Hardy provided the Half Back pairing for England. Corporals Waqabaca and Ponjiasi played for Fiji. Brigadier DW Shuttleworth became the President of the English Rugby Football Union during the 1985/86 season. In 1957-1959, whilst stationed in Northern Ireland, the 'Dukes' played rugby throughout Ulster. At the end of the tour the Ulster Team honoured the regiment by playing them at Ravenhill, with the 'Dukes' winning 19 - 8. In 1961 during an emergency posting to Kenya the Kenyan Champions Nakuru heard the Dukes were there and challenged them to a match. The Kenyan Regiment loaned them their team strip to wear. The 'Dukes' won the match.
The regiment's Great Britain national rugby league team internationals include:- Brian Curry, England, 1956; Norman Field, GB, 1963; R Sabine, GB; Jack Scroby, Army 1959, GB Halifax RLFC & Bradford Bulls; Charlie Renilson, Scotland, GB, 1965 and Arthur 'Ollie' Keegan, GB.
Several members of the regiment played cricket for the Free Foresters Cricket Club and Pte Brian Stead played for the Yorkshire County Cricket Club.
Other information
- Regimental Headquarters: Wellesley Park, Halifax, West Yorkshire, UK, HX2 0BA
- E-Mail: rhq@dukesrhq.demon.co.uk
See also
- 76th Regiment of Foot
- East and West Riding Regiment
- Yorkshire Regiment
- Category:Duke of Wellington's Regiment officers
References
- ^ The Duke of Wellington's Regiment (West Riding) A Short History, by Major ACS Savoury MBE and Major General DE Isles CB OBE DL, (Page 4), printed By Reuben Holroyd's, Halifax, 19878
- ^ The History of The Duke of Wellington's Regiment (West Riding) 1702-1992, By JM Brereton AND Major ACS Savoury MBE, ISBN 0-9521552-0-6, Published by The Duke of Wellingtons Regiment Regimental Headquarters
- ^ The Duke of Wellington's Regiment (West Riding) A Short History, by Major ACS Savoury MBE and Major General DE Isles CB OBE DL, (Page 4, Lineage of the Duke of Wellington's Regiment (West Riding)), printed By Reuben Holroyd's, Halifax, 1987
- ^ History of the Duke of Wellington's Regiment, (page 69), Brereton / Savoury, ISBN 0-9521552-0-6
- ^ [Wellington - The Years of the Sword, by Elizabeth Pakenham, Countess of Longford)]
- ^ History of the Duke of Wellington's Regiment, (page 184), Brereton / Savoury, ISBN 0-9521552-0-6
- ^ History of the Duke of Wellington's Regiment, (page 189), Brereton / Savoury, ISBN 0-9521552-0-6
- ^ London Gazette 28 July 1868
- ^ 'The History of The Duke of Wellington's Regiment (West Riding) 1702-1992, page 191 - JM Brereton and ACS Savoury (ISBN 0-9521552-0-6)
- ^ The Korean War, Page 336. Brereton, JM; Savory, ACS (1993). The History of the Duke of Wellingtons (West Riding) 1702 - 1992. Halifax : The Duke of Wellington's Regiment. ISBN 0-9521552-0-6.
- ^ Erquinghem leys Freedom Award
- ^ 3rd Battalion The Yorkshire Regiment (Duke of Wellington's)
- ^ W.Y.Carman, page 61 "Uniforms of the British Army - the Infantry Regiments", ISBN 0-86350-031-5,
- ^ Dukes and Rugby - DWR Website
External links
Categories:- Infantry regiments of the British Army
- Regiments of Yorkshire
- The Duke of Wellington's Regiment
- Military units and formations established in 1702
- Military units and formations disestablished in 2006
- Military units and formations of the United Kingdom in the Korean War
- Regiments of the British Army in World War II
- Regiments of the British Army in World War I
- 1702 establishments in England
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.