- Portal:British Empire
-
- Wikipedia portals:
- Culture
- Geography
- Health
- History
- Mathematics
- Natural sciences
- People
- Philosophy
- Religion
- Society
- Technology
History: Ancient Egypt • Ancient Germanic Culture • Ancient Greece • Ancient Japan • Ancient Near East • Ancient Rome • Archaeology • Austria-Hungary • British Empire
 • Bulgarian Empire • Byzantine Empire • History of Canada • Imperial China • Classical Civilisation • Colonialism • Disasters • Heraldry • History of Science
• Bulgarian Empire • Byzantine Empire • History of Canada • Imperial China • Classical Civilisation • Colonialism • Disasters • Heraldry • History of Science • Indian independence movement • Khitan • Middle Ages • New France • Russian Empire • War
• Indian independence movement • Khitan • Middle Ages • New France • Russian Empire • War British Empire
British Empire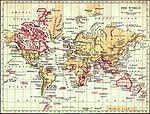
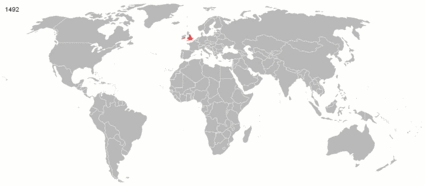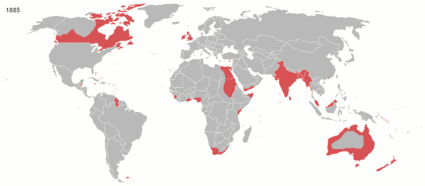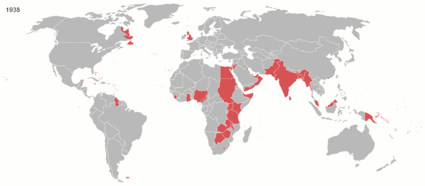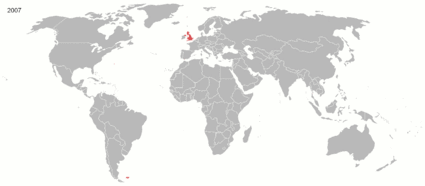
The British Empire was the largest empire in history and for a substantial time was the foremost global power. It was a product of the European age of discovery, which began with the maritime explorations of the 15th century, that sparked the era of the European colonial empires.
By 1921, the British Empire held sway over a population of about 458 million people, approximately one-quarter of the world's population. It covered about 36.6 million km² (14.2 million square miles), about a quarter of Earth's total land area. As a result, its legacy is widespread, in legal and governmental systems, economic practice, militarily, educational systems, sports (such as cricket, rugby and football), traffic practices (such as driving on the left), and in the global spread of the English language. At the peak of its power, it was often said that "the sun never sets on the British Empire" because its span across the globe ensured that the sun was always shining on at least one of its numerous colonies or subject nations.
During the five decades following World War II, most of the territories of the Empire became independent. Many went on to join the Commonwealth of Nations, a free association of independent states.
Selected articleThe Pitcairn Islands (Pitkern: Pitkern Ailen), officially named the Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie, and Oeno Islands, are a group of four islands in the southern Pacific Ocean. The islands are a British overseas territory (formerly British colony), the last remaining in the Pacific. Only Pitcairn Island — the second largest — is inhabited.
The islands are best known for being the home of the descendants of the Bounty mutineers and the Tahitians who accompanied them, an event retold in numerous books and films. This story is still apparent in the surnames of many of the islanders. With only 50 inhabitants (from nine families), Pitcairn is also notable for being the least populated jurisdiction in the world (although it is not a sovereign nation). The United Nations Committee on Decolonisation includes the Pitcairn Islands on the United Nations list of Non-Self-Governing Territories.
Selected pictureThe Rhodes Colossus, an iconic editorial cartoon of the Scramble for Africa period, depicting British colonialist Cecil John Rhodes as a giant standing over the continent.
Did you know...- ...that the Singapore Stone (fragment pictured), a sandstone slab bearing an undeciphered 13th century inscription, was blown up by the British in 1843 to make way for a fort?
- ...that Ethel Benjamin was the first woman in the British Empire to present a legal case in court?
- ...that Major Sir Hamish Forbes, 7th Baronet was awarded the MBE (Military Division) for his many escape attempts while a prisoner-of-war in Germany from 1940 to 1945, and was later patron of the Lonach Highlanders?
- ...that Albert F. A. L. Jones, awarded the Order of the British Empire in 1987 for his services to astronomy, is an amateur astronomer in New Zealand?
- ...that the first shot fired by British Empire forces in World War I was targeted at the German ship Pfalz which was departing Melbourne, Australia as Britain declared war on Germany?
Selected biographyVictoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was the Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837, and the first Empress of India from 1 May 1876, until her death on 22 January 1901. Her reign lasted 63 years and seven months, longer than that of any other British monarch. In general, the period centred on her reign is known as the Victorian era.
The Victorian era was at the height of the Industrial Revolution, a period of significant social, economic, and technological progress in the United Kingdom. Victoria's reign was marked by a great expansion of the British Empire; during this period it reached its zenith, becoming the foremost Global Power of the time. (more...)
Evolution of the British EmpireCategoriesClick the "+" below to see all subcategories: WikiProjectsBritish Empire and Commonwealth of NationsLegend
Current territory · Former territory
* now a Commonwealth Realm · now a member of the Commonwealth of Nations18th century
1708–1757 Minorca
since 1713 Gibraltar
1782–1802 Minorca19th century
1800–1964 Malta
1807–1890 Heligoland
1809–1864 Ionian Islands
1878–1960 Cyprus20th century
since 1960 Akrotiri and Dhekelia16th century
1583–1907 Newfoundland
17th century
1607–1776 Thirteen Colonies
since 1619 Bermuda
1670–1870 Rupert's Land
18th century
Canada (British Imperial)
1763–1791 Quebec
1791–1841 Lower Canada
1791–1841 Upper Canada19th century
Canada (British Imperial)
1841–1867 Province of Canada
1849–1866 Vancouver Island
1858–1871 British Columbia
1859–1870 North-Western Territory
1862–1863 Stikine Territory
*Canada (post-Confederation)
1867–1931 Dominion of Canada120th century
*Canada (post-Confederation)
1907–1934 Dominion of Newfoundland21 In 1931, Canada and other British dominions obtained self-government through the Statute of Westminster. "Dominion" remains Canada's legal title; see Canada's name.
2 Remained a de jure dominion until 1949 (when it became a Canadian province); from 1934 to 1949, Newfoundland was governed by the Commission of Government.17th century
1605–1979 *Saint Lucia
1623–1883 Saint Kitts (*Saint Kitts & Nevis)
1624–1966 *Barbados
1625–1650 Saint Croix
1627–1979 *St. Vincent and the Grenadines
1628–1883 Nevis (*Saint Kitts & Nevis)
1629–1641 St. Andrew and Providence Islands3
since 1632 Montserrat
1632–1860 Antigua (*Antigua & Barbuda)
1643–1860 Bay Islands
since 1650 Anguilla
1651–1667 Willoughbyland (Suriname)
1655–1850 Mosquito Coast (protectorate)
1655–1962 *Jamaica
since 1666 British Virgin Islands
since 1670 Cayman Islands
1670–1973 *Bahamas
1670–1688 St. Andrew and Providence Islands3
1671–1816 Leeward Islands
18th century
1762–1974 *Grenada
1763–1978 Dominica
since 1799 Turks and Caicos Islands19th century
1831–1966 British Guiana (Guyana)
1833–1960 Windward Islands
1833–1960 Leeward Islands
1860–1981 *Antigua and Barbuda
1871–1964 British Honduras (*Belize)
1882–1983 *St. Kitts and Nevis
1889–1962 Trinidad and Tobago20th century
1958–1962 West Indies Federation3 Now the San Andrés y Providencia Department of Colombia
18th century
1792–1961 Sierra Leone
1795–1803 Cape Colony19th century
1806–1910 Cape Colony
1816–1965 Gambia
1856–1910 Natal
1868–1966 Basutoland (Lesotho)
1874–1957 Gold Coast (Ghana)
1882–1922 Egypt
1884–1966 Bechuanaland (Botswana)
1884–1960 British Somaliland
1887–1897 Zululand
1888–1894 Matabeleland
1890–1980 Southern Rhodesia (Zimbabwe)
1890–1962 Uganda
1890–1963 Zanzibar (Tanzania)
1891–1964 Nyasaland (Malawi)
1891–1907 British Central Africa
1893–1968 Swaziland
1895–1920 British East Africa
1899–1956 Anglo-Egyptian Sudan20th century
1900–1914 Northern Nigeria
1900–1914 Southern Nigeria
1900–1910 Orange River Colony
1906–1954 Nigeria Colony
1910–1931 South Africa
1911–1964 Northern Rhodesia (Zambia)
1914–1954 Nigeria Protectorate
1915–1931 South West Africa (Namibia)
1919–1960 Cameroons (Cameroon) 4
1920–1963 Kenya
1922–1961 Tanganyika (Tanzania) 4
1954–1960 Nigeria
since 1965 British Indian Ocean Territory18th century
1757–1947 Bengal (West Bengal (India) and Bangladesh)
1762–1764 Philippines
1795–1948 Ceylon (Sri Lanka)
1796–1965 Maldives19th century
1819–1826 Singapore
1826–1946 Straits Settlements
1839–1967 Colony of Aden
1841–1997 Hong Kong
1841–1941 Kingdom of Sarawak
1858–1947 British India (India, Pakistan and Bangladesh, Burma)
1882–1963 British North Borneo (Malaysia)
1885–1946 Unfederated Malay States
1891–1971 Muscat and Oman protectorate
1892–1971 Trucial States protectorate
1895–1946 Federated Malay States
1898–1930 Weihai Garrison20th century
1918–1961 Kuwait protectorate
1920–1932 Iraq4
1921–1946 Transjordan4
1923–1948 Palestine4
1946–1948 Malayan Union
1946–1963 Sarawak (Malaysia)
1948–1957 Federation of Malaya (Malaysia)18th century
1788–1901 New South Wales
1794–1843 Sandwich Islands (Hawaii)19th century
1803–1901 Van Diemen's Land / Tasmania
1807–1863 Auckland Islands6
1824–1980 New Hebrides (Vanuatu)
1824–1901 Queensland
1829–1901 Swan River Colony / Western Australia
1836–1901 South Australia
since 1838 Pitcairn Islands
1840–1907 *Colony of New Zealand
1850–1901 Victoria (Australia)
1874–1970 Fiji5
1877–1976 British Western Pacific Territories
1884–1949 Territory of Papua
1888–1965 Cook Islands6
1888–1984 Sultanate of Brunei
1889–1948 Union Islands (Tokelau)6
1892–1979 Gilbert and Ellice Islands7
1893–1978 British Solomon Islands820th century
1900–1970 Tonga (protected state)
1900–1974 Niue6
1901–1942 *Commonwealth of Australia
1907–1953 *Dominion of New Zealand
1919–1949 Territory of New Guinea
1949–1975 Territory of Papua and New Guinea95 Suspended member
6 Now part of the *Realm of New Zealand
7 Now Kiribati and *Tuvalu
8 Now the *Solomon Islands
9 Now *Papua New Guinea17th century
since 1659 St. Helena19th century
since 1815 Ascension Island9
since 1816 Tristan da Cunha9
since 1833 Falkland Islands1120th century
since 1908 British Antarctic Territory10
since 1908 South Georgia and
the South Sandwich Islands10, 119 Dependencies of St. Helena since 1922 (Ascension Island) and 1938 (Tristan da Cunha)
10 Both claimed in 1908; territories formed in 1962 (British Antarctic Territory) and 1985 (South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands)
11 Occupied by Argentina during the Falklands War of April–June 1982Things to doRelated portalsWikimediaCategories:- Colonialism portal
- History portals
- Civilizations
- Cultural geography
- Political geography
- British Empire
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.