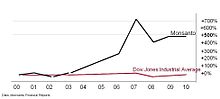
- Monsanto
-
Monsanto Company 
Type Public company Traded as NYSE: MON Industry Agribusiness Founded St. Louis, Missouri, US (1901) Founder(s) John Francis Queeny Headquarters Creve Coeur, Missouri, U.S. Key people Hugh Grant
(Chairman, President and CEO)Products Herbicides, pesticides, crop seeds Revenue  US$ 10.502 billion (FY 2010)[1]
US$ 10.502 billion (FY 2010)[1]Operating income  US$ 1.607 billion (FY 2010)[1]
US$ 1.607 billion (FY 2010)[1]Net income  US$ 1.109 billion (FY 2010)[1]
US$ 1.109 billion (FY 2010)[1]Total assets  US$ 17.867 billion (FY 2010)[1]
US$ 17.867 billion (FY 2010)[1]Total equity  US$ 10.143 billion (FY 2010)[1]
US$ 10.143 billion (FY 2010)[1]Employees 21,400 (August 2010)[1] Website Monsanto.com The Monsanto Company (NYSE: MON) is a US-based multinational agricultural biotechnology corporation. It is the world's leading producer of the herbicide glyphosate, marketed as "Roundup". Monsanto is also the leading producer of genetically engineered (GE) seed; it provides the technology in 90% of the genetically engineered seeds used in the US market.[2] It is headquartered in Creve Coeur, Missouri.[3]
Agracetus, owned by Monsanto, exclusively produces Roundup Ready soybean seed for the commercial market. In 2005, it finalized the purchase of Seminis Inc, making it the world's largest conventional seed company.
Monsanto's development and marketing of genetically engineered seed and bovine growth hormone, as well as its aggressive litigation, political lobbying practices, seed commercialization practices and "strong-arming" of the seed industry[4] have made the company controversial around the world and a primary target of the alter-globalization movement and environmental activists. As a result of its business strategies and licensing agreements, Monsanto came under investigation by the U.S. Justice Department in 2009.[4][5]
History

Agriculture General Agribusiness · Agricultural science
Agronomy · Animal husbandry
Extensive farming
Factory farming · Farm · Free range
Industrial agriculture
Intensive farming
Organic farming · Permaculture
Sustainable agriculture
Urban agricultureHistory History of agriculture
Arab Agricultural Revolution
British Agricultural Revolution
Green Revolution
Neolithic RevolutionTypes Aquaculture · Dairy farming
Grazing · Hydroponics
Livestock · Pig farming
Orchards · Poultry farming
Sheep husbandryCategories Agriculture
Agriculture by country
Agriculture companies
Biotechnology
Livestock
Meat industry
Poultry farming Agropedia portal
Agropedia portalMonsanto was founded in St. Louis, Missouri, in 1901, by John Francis Queeny, a 30-year veteran of the pharmaceutical industry. He funded the start-up with his own money and capital from a soft drink distributor, and gave the company his wife's maiden name. His father in law was Emmanuel Mendes de Monsanto, wealthy financier of a sugar company active in Vieques, Puerto Rico and based in St. Thomas in the Danish West Indies. The company's first product was the artificial sweetener saccharin, which it sold to the Coca-Cola Company. It also introduced caffeine and vanillin to Coca-Cola, and became one of that company's main suppliers.[citation needed]
In 1919, Monsanto established its presence in Europe by entering into a partnership with Graesser's Chemical Works at Cefn Mawr near Ruabon, Wales to produce vanillin, salicylic acid, aspirin and later rubber processing chemicals. This site was later sold and closed in 2010.
In its third decade, the 1920s, Monsanto expanded into basic industrial chemicals like sulfuric acid, and the decade ended with Queeny's son Edgar Monsanto Queeny taking over the company in 1928.
The 1940s saw Monsanto become a leading manufacturer of plastics, including polystyrene, and synthetic fibers. Since then, it has remained one of the top 10 US chemical companies. Other major products have included the herbicides 2,4,5-T, DDT, and Agent Orange used primarily during the Vietnam War as a defoliant agent (later found to be contaminated during manufacture with highly carcinogenic dioxin), the artificial sweetener aspartame (NutraSweet), bovine somatotropin (bovine growth hormone (BST)), and PCBs.[6] Also in this decade, Monsanto operated the Dayton Project, and later Mound Laboratories in Miamisburg, Ohio, for the Manhattan Project, the development of the first nuclear weapons and, after 1947, the Atomic Energy Commission.
Monsanto began manufacturing DDT in 1944, along with some 15 other companies.[7] This insecticide was much-welcomed in the fight against malaria-transmitting mosquitoes. The use of DDT in the U.S. was banned by Congress in 1972, due in large part to efforts by environmentalists, who persisted in the challenge put forth by Rachel Carson and her book Silent Spring in 1962, which sought to inform the public of the side effects associated with DDT. As the decade ended, Monsanto acquired American Viscose from England's Courtauld family in 1949.
In 1954, Monsanto partnered with German chemical giant Bayer to form Mobay and market polyurethanes in the US.
Monsanto was a pioneer of optoelectronics in the 1970s. In 1968 they became the first company to start mass production of (visible) Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs), using gallium arsenide phosphide. This ushered in the era of solid-state lights. From 1968 to 1970 sales doubled every few months. Their products (discrete LEDs and seven-segment numeric displays) became the standards of industry. The primary markets then were electronic calculators, digital watches, and digital clocks.[8]
In the 1960s and 1970s, Monsanto became one of the most important producers of Agent Orange for US Military operations in Vietnam. Agent Orange caused an immense damage to health, also for US-soldiers, not at least by genetic modification.[9][10]
In 1979, Monsanto established the Edgar Monsanto Queeny safety award in honor of its former CEO (1928–1960), to encourage accident prevention.[11]
Monsanto scientists became the first to genetically modify a plant cell in 1982. Five years later, Monsanto conducted the first field tests of genetically engineered crops.
Through a process of mergers and spin-offs between 1997 and 2002, Monsanto made a transition from chemical giant to biotech giant. Part of this process involved the 1999 sale by Monsanto of their phenylalanine facilities to Great Lakes Chemical Corporation (GLC) for $125 million. In 2000, GLC sued Monsanto because of a $71 million dollar shortfall in expected sales.
In 2001, retired Monsanto chemist William S. Knowles was named a co-winner of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his research on catalytic asymmetric hydrogenation, which was carried out at Monsanto beginning in the 1960s until his 1986 retirement.
Throughout 2004 and 2005, Monsanto filed lawsuits against many farmers in Canada and the U.S. on the grounds of patent infringement, specifically the farmers' sale of seed containing Monsanto's patented genes. In some cases, farmers claimed the seed was unknowingly sown by wind carrying the seeds from neighboring crops, a claim rejected in Monsanto Canada Inc. v. Schmeiser.[12] These instances began in the mid to late 1990s, with one of the most significant cases being decided in Monsanto's favor by the Canadian Supreme Court. By a 5–4 vote in late May 2004, that court ruled that "by cultivating a plant containing the patented gene and composed of the patented cells without license, the appellants (canola farmer Percy Schmeiser) deprived the respondents of the full enjoyment of the patent." With this ruling, the Canadian courts followed the U.S. Supreme Court in its decision on patent issues involving plants and genes.
As of February 2005, Monsanto has patent claims on breeding techniques for pigs which would grant them ownership of any pigs born of such techniques and their related herds. Greenpeace claims Monsanto is trying to claim ownership on ordinary breeding techniques.[13] Monsanto claims that the patent is a defensive measure to track animals from its system. They furthermore claim their patented method uses a specialized insemination device that requires less sperm than is typically needed.[14]
In 2006, the Public Patent Foundation filed requests with the United States Patent and Trademark Office to revoke four patents that Monsanto has used in patent lawsuits against farmers. In the first round of reexamination, claims in all four patents were rejected by the Patent Office in four separate rulings dating from February through July 2007.[15] Monsanto has since filed responses in the reexaminations.
In October 2008, the company's Canadian division, Monsanto Canada Inc., was named one of Canada's Top 100 Employers by Mediacorp Canada Inc., and was featured in Maclean's newsmagazine. Later that month, Monsanto Canada Inc. was also named one of Manitoba's Top Employers, which was announced by the Winnipeg Free Press newspaper.[16]
In January 2010, Monsanto was named company of the year by Forbes.
Spin-offs and mergers
Through a series of transactions, the Monsanto that existed from 1901 to 2000 and the current Monsanto are legally two distinct corporations. Although they share the same name and corporate headquarters, many of the same executives and other employees, and responsibility for liabilities arising out of activities in the industrial chemical business, the agricultural chemicals business is the only segment carried forward from the pre-1997 Monsanto Company to the current Monsanto Company. This was accomplished beginning in the 1980s:
- 1985: Monsanto purchases G. D. Searle & Company. In this merger, Searle's aspartame business becomes a separate Monsanto subsidiary, the NutraSweet Company. CEO of NutraSweet, Robert B. Shapiro, goes on to become CEO of Monsanto from 1995 to 2000.
- 1996: Acquires 49.9% of Calgene, creators of the Flavr Savr tomato in April and another ~5% in November. Monsanto first entered the maize seed business when it purchased 40% of DEKALB Genetics Corporation in 1996. It purchased the remainder of the corporation in 1998.[17]
- 1997: Monsanto spins off its industrial chemical and fiber divisions into Solutia Inc. This transfers the financial liability related to the production and contamination with PCBs at the Illinois and Alabama plants. In January, Monsanto announces the purchase of Holden's Foundations Seeds, a privately held seed business owned by the Holden family, along with its sister sales organization, Corn States Hybrid Service, of Williamsburg and Des Moines, Iowa, respectively. The combined purchase price totals $925 million. Also, in April, Monsanto purchases the remaining shares of Calgene.
- 1999: Monsanto sells off NutraSweet Co. and two other companies.
- 2000: Monsanto merges with Pharmacia and Upjohn, and ceases to exist. Later in the year, Pharmacia forms a new subsidiary, also named Monsanto, for the agricultural divisions, and retains the medical research divisions, which includes products such as Celebrex.
- 2002: Pharmacia spins off its Monsanto subsidiary into a new company, the "new Monsanto." As part of the deal, Monsanto agrees to indemnify Pharmacia against any liabilities that might be incurred from judgments against Solutia. As a result, the new Monsanto continues to be a party to numerous lawsuits that relate to operations of the old Monsanto.
- 2005: Monsanto purchases Seminis, a leading global vegetable and fruit seed company, for $1.4 billion.[18]
- 2007: In June, Monsanto completes its purchase of Delta and Pine Land Company, a major cotton seed breeder, for $1.5 billion.[19] Monsanto exits the pig breeding business by selling Monsanto Choice Genetics to Newsham Genetics LC in November, divesting itself of "any and all swine-related patents, patent applications, and all other intellectual property."[20][21]
- 2008: Monsanto purchases the Dutch seed company De Ruiter Seeds for €546 million,[22] and sells its POSILAC bovine somatotropin brand and related business to Elanco Animal Health, a division of Eli Lilly and Company in August for $300 million plus "additional contingent consideration".[23]
Sponsorships
Monsanto has been the corporate sponsor of many attractions at Disneyland and Walt Disney World.
At Disneyland they include:
- Hall of Chemistry (until 1967)
- Fashions and Fabrics through the Years (from 1965 to 1966)
- Monsanto House of the Future (from 1957 to 1967)
- Adventure Thru Inner Space (from 1967 to 1985)
And at Walt Disney World they include:
- Magic Eye Theatre at Epcot
- Circle Vision 360
All attractions that the company has ever sponsored (except for the Magic Eye Theatre, in the Future World section of Epcot) were located in Tomorrowland.
Monsanto is cited as one of the major sponsors behind the Svalbard Global Seed Vault in many web sites but not in the home page of the Svalbard Global Seed Vault.[24] Monsanto does share technology and patents with following companies mentioned in the referred document: The Australia based Grains Research & Development Corporation (GRDC)[25] and the Swiss based company Syngenta AG[26]
Corporate governance
Current members of the board of directors of Monsanto are: Frank V. AtLee III, the former President of American Cyanamid and former chairman of Cynamid International, John W. Bachmann, Hugh Grant, the chairman of Monsanto, Arthur H. Harper, Gwendolyn S. King, president of McDonald’s USA, Sharon R. Long, C. Steven McMillan, the former chairman and CEO of Sara Lee Corporation, William U. Parfet, George H. Poste, Robert J. Stevens, the current chairman and CEO of Lockheed Martin Corporation.[27]
Former Monsanto employees currently hold positions in US government agencies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Supreme Court. These include Clarence Thomas, Michael R. Taylor, Ann Veneman, Linda Fisher, Michael Friedman, William D. Ruckelshaus, and Mickey Kantor.[28] Linda Fisher has been back and forth between positions at Monsanto and the EPA.[28]
Environmental and health record
According to an anonymous 2001 document[29] obtained by the Center for Public Integrity, Monsanto has been identified by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency as being a "potentially responsible party" for 56 contaminated sites (Superfund sites) in the United States. Monsanto has been sued, and has settled, multiple times for damaging the health of its employees or residents near its Superfund sites through pollution and poisoning.[6][30][31] In 2004 The Wildlife Habitat Council and U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's National Environmental Performance Track presented a special certificate of recognition to Monsanto Company during WHC's 16th Annual Symposium.
Monsanto is the largest producer of glyphosate herbicides through its popular brand, Roundup. A report released in June 2011 linked glyphosate to birth defects in frog and chicken embryos at dilutions much lower than those used in agricultural and garden spraying. http://www.scribd.com/doc/57277946/RoundupandBirthDefectsv5
Phil Angell, Monsanto's director of corporate communications (referring to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration) explained the company's regulatory philosophy to Michael Pollan in 1998: "Monsanto should not have to vouchsafe the safety of biotech food. Our interest is in selling as much of it as possible. Assuring its safety is FDA's job."[32]
Genetically modified organisms
Many of Monsanto's seed products are specifically genetically modified to make them resistant to Monsanto produced agricultural chemicals, such as "Round Up" herbicide. In a study published in the International Journal of Biological Sciences, researchers applied a different statistical analysis on raw data obtained from Monsanto and concluded that these GM corn (maize) varieties induced a state of hepatorenal toxicity.[33] They suggested that the presence of the new pesticides associated with the inserted genes were responsible, although the possibility that this could be due to a mutation during the transformation process was not excluded.[33]
Monsanto was drawn into the Genetically modified food controversies over the Pusztai affair.[34] Dr. Arpad Pusztai's experiments suggested that it was the process of genetic engineering, not the presence of the inserted lectin gene that altered the thickness of the gut epithelium in rats when fed genetically modified potatoes.[35] In other words it was the process of genetic engineering itself, not the presence of pesticides caused by the engineering which caused the damage to rats. The publication of this study has resulted in much controversy.[36]
Terminator seed controversy
In June 2007,[37] Monsanto acquired Delta & Pine Land Company, a company that had patented a seed technology nicknamed Terminators. This technology, which was never known to have been used commercially, produces plants that have sterile seeds so they do not flower or grow fruit after the initial planting. This prevents the spread of those seeds into the wild, however it also requires customers to repurchase seed for every planting in which they use Terminator seed varieties. In recent years, widespread opposition from environmental organizations and farmer associations has grown, mainly out of the concerns that seeds using this technology could increase farmers' dependency on seed suppliers.
In 1999, Monsanto pledged not to commercialize Terminator technology[38]. Delta Vice President, Harry Collins, stated in an October 2000 press interview in the Agra/Industrial Biotechnology Legal Letter, ‘We’ve continued right on with work on the Technology Protection System (TPS or Terminator). We never really slowed down. We’re on target, moving ahead to commercialize it. We never really backed off.’[39]
rBGH (recombinant Bovine Growth Hormone)
Monsanto sparked controversy nationwide with the introduction of Bovine somatotropin, abbreviated as rBST and commonly known as rBGH. It is a synthetic hormone that is injected into cows to increase milk production. IGF-1 is a hormone stimulated by rBGH in the cow's blood stream, which is directly responsible for the increase in milk production. IGF-1 is a natural hormone found in the milk of both humans and cows causing the quick growth of infants.
Though this IGF-1 occurs naturally in mothers' milk to be fed to their infants it produces adverse effects in non-infants, behaving as a cancer accelerator in adults and non-infants; this biologically active hormone is associated with breast cancer (correlation shown in premenopausal women),[40] prostate cancer,[41] lung cancer[42] and colon cancers.[42][43]
A Monsanto-sponsored survey of milk showed no significant difference in rBST levels in milk labeled as "rBST-Free" or "organic milk" vs milk not labeled as such.[44]
According to The New York Times[45] Monsanto's brand of rBST, Posilac, has recently (March 2008) been the focus for a pro-rBST advocacy group called AFACT, made up of large dairy business conglomerates and closely affiliated with Monsanto itself. This group has engaged in large-scale lobbying efforts at the state level to prevent milk which is rBST-free from being labeled as such. As milk labeled as hormone-free has proved enormously popular with consumers, the primary justification by AFACT for their efforts has been that rBST is approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and that the popularity of milk sold without it is damaging what they claim to be the right of dairy producers to use a technology that maximizes their profits.
Thus far, a large-scale negative consumer response to AFACT's legislative and regulatory efforts has kept state regulators from pushing through restrictions that would ban hormone-free milk labels, though several politicians have tried, including Pennsylvania's agriculture secretary Dennis Wolff, who tried to ban rBST-free milk labeling on the grounds that "consumers are confused". The statement by Agriculture Secretary Wolff was reported by pro-biotech site Earth Friendly-Farm Friendly which elaborated on the issues of rBGH/rBST labelling:
"Consumers are getting confused with the extra labels," said Pennsylvania Ag Secretary Dennis Wolff. "They deserve a choice, and so do producers. But from the standpoint of safety, all milk is healthy milk. Our milk is a safe product. The Pennsylvania Department of Agriculture is not in a position to say use rBST or not. The key word is: choice. I used rBST from day one of its approval to the last day that I milked cows. It was an important management tool on my dairy farm. What we oppose is the negative advertising or the selling of fear. If producers are asked to give up a production efficiency, and if that efficiency nets them $3000 or $10,000 a year for their dairy farm… That's a lot of money.[46]
Proposed labeling changes have been floated by AFACT lobbyists in New Jersey, Ohio, Indiana, Kansas, Utah, Missouri and Vermont thus far.[citation needed]
In October 2008, Monsanto sold this business, in full, to Eli Lilly for a price of $300 million plus additional considerations.[47]
Pollution in Anniston, Alabama
In 2002, The Washington Post carried a front page report on Monsanto's legacy of environmental damage in Anniston, Alabama related to its legal production of polychlorinated biphenyls(PCBs), a chemical once used as a common electrical insulator, 40 years ago. Plaintiffs in a pending lawsuit provided documentation showing that the local Monsanto factory knowingly discharged both mercury and PCB-laden waste into local creeks for over 40 years.[48] In a story on 27 January, The New York Times reported that during 1969 alone Monsanto had dumped 45 tons of PCBs into Snow Creek, a feeder for Choccolocco Creek which supplies much of the area's drinking water. The company also buried millions of pounds of PCB in open-pit landfills located on hillsides above the plant and surrounding neighborhoods.[49] In August 2003, Solutia and Monsanto agreed to pay plaintiffs $700 million to settle claims by over 20,000 Anniston residents related to PCB contamination.[50]
Legal issues
Monsanto is notable for its involvement in high profile lawsuits, as both plaintiff and defendant. It has been involved in a number of class action suits, where fines and damages have run into the hundreds of millions of dollars, usually over health issues related to its products. Monsanto has also made frequent use of the courts to defend its patents, particularly in the area of biotechnology.
Monsanto has received media coverage for its alleged unfair suing of farmers, highlighted in the documentary, 'The World according to Monsanto.'[51]
As defendant
In 1971, the US government filed suit against Monsanto over the safety of its original product, saccharin; Monsanto eventually won, after several years in court.[52]
It was sued, along with Dow and other chemical companies by veterans for the side effects of its Agent Orange defoliant, used by the US military in the Vietnam War.[53]
Monsanto was the defendant in the longest civil jury trial in U.S. history, Kemner v. Monsanto. This case ran from February 1984 through October 1987. The case involved a group of plaintiffs who claimed to have been poisoned by dioxin in a 1979 chemical spill that occurred in Sturgeon, Missouri.[54]
In 2000, GLC sued Monsanto for the $71 million shortfall in expected sales.
In 2004, the world's largest agrichemical company, Switzerland's Syngenta, launched a US lawsuit charging Monsanto with using coercive tactics to monopolize markets.[55] There are several lawsuits going both ways between Monsanto and Syngenta.
In 2005, the US DOJ filed a Deferred Prosecution Agreement[56] in which Monsanto admitted to violations of the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (15 U.S.C. § 78dd-1) and making false entries into its books and records (15 U.S.C § 78m(b)(2) & (5)).
In late 2006, the Correctional Tribunal of Carcassone, France, ordered two directors of Monsanto subsidiary Asgrow to pay a €15,000 fine related to their knowledge of the presence of unauthorized GMOs in bags of seeds imported by Asgrow on 13 April 2000.[57]
Tue 30 Nov 2010 Monsanto GMO sugarbeets are to be destroyed. A federal judge ordered the destruction of plantings of genetically modified sugar beets developed by Monsanto Co after ruling previously the U.S. Agriculture Department illegally approved the biotech crop.[58]
As plaintiff
Since the mid-1990s, it has sued 145 individual US farmers for patent infringement in connection with its genetically engineered seed.[59] The usual claim involves violation of a technology agreement that prohibits farmers from saving seed from one season's crop to plant the next, a common farming practice.[60] One farmer received an eight-month prison sentence for violating a court order to destroy seeds,[61] in addition to having to pay damages, when a Monsanto case turned into a criminal prosecution.[62]
In 2003, Monsanto sued Oakhurst Dairy in Maine for advertising that its milk products did not come from cows treated with bovine growth hormone, claiming that such advertising hurt its business. The president of Oakhurst responded by saying,
"We ought to have the right to let people know what is and is not in our milk."[63]
In 1998, Monsanto's patented genes were discovered in the canola grown on Percy Schmeiser's farm. As a result, Monsanto sued Percy Schmeiser for patent infringement for growing genetically modified Roundup-resistant canola. The trial judge ruled that Schmeiser had intentionally planted the seeds, ruling that the "infringement arises not simply from occasional or limited contamination of his Roundup susceptible canola by plants that are Roundup resistant. He planted his crop for 1998 with seed that he knew or ought to have known was Roundup tolerant."[12] This high profile case, Monsanto Canada Inc. v. Schmeiser, went to the Supreme Court level.
Monsanto representative Trish Jordan commented: "This is very good news for us, Mr. Schmeiser had infringed on our patent." After years of legal wrangling, in 2004 the case was heard by the Canadian Supreme Court. The Court ruled in favor of Monsanto, rejecting Schmeiser's argument that by not using Roundup herbicide on the canola, he did not "use" the plant gene. The Court ruled that farming is an activity that requires human intervention, and so by planting the crops, Schmeiser was "using" the plant gene. However, Schmeiser also won a partial victory, with the Supreme Court disagreeing with the damages given by the trial judge. The Supreme Court stated that since Schmeiser did not gain any profit from the infringement, he did not owe Monsanto any damages. Though the amount of damages were low (C$19,382), this also meant that Schmeiser did not have to pay Monsanto's substantial legal bills.
The case did cause Monsanto's enforcement tactics to be highlighted in the media over the years it took to play out.[64]
Monsanto has asked Spanish customs officials to inspect soymeal shipments to determine if they use Monsanto's "Roundup Ready" technology. Monsanto claims that 30% of Argentina's production uses black market-purchased Roundup Ready seed. Monsanto has petitioned to change the royalty collection system so that royalties are collected at harvest rather than upon purchase of the seed.[citation needed]
Related legal actions
In USA
In 1997, it was alleged a local FOX affiliate cooperated with Monsanto in suppressing an investigative report on the health risks associated with Monsanto's bovine growth hormone product, Posilac.[65] Posilac, a synthetic hormone used to increase milk production in cows, while banned in many first-world countries, is used in the United States. Steve Wilson and Jane Akre disagreed with the inclusion of material in the story they felt was slanted or misleading. Both reporters were eventually fired. Wilson and Akre alleged the firing was for retaliation, while the FOX affiliate contended they were fired for insubordination. The reporters then sued Fox in Florida state court, claiming they could not be fired for refusing to do something that they believed to be illegal. In 2000, a Florida jury found that while there was no evidence FOX had bowed to any pressure from Monsanto to alter the story, Akre, but not Wilson, was unjustly fired.[66] The decision in Akre's favor was then overturned in 2003 by an appeals court because the whistleblower's statute under which the original case had been filed did not actually apply to the case.
Monsanto vs Andhra Pradesh Government in India
The state of Andhra Pradesh, India, at first resisted Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) cotton; however, as it has proved immensely popular with farmers, they have attempted to control its price.[citation needed] In 2005, after the Genetic Engineering Approval Committee, the Indian regulatory authority, released a fact-finding statement,[67] the state agriculture minister barred the company from selling cotton seeds in the state of Andhra Pradesh.[68] The order was later lifted. More recently, the Andhra Pradesh state government filed several cases[69] against Monsanto and its Mumbai based licensee Maharashtra Hybrid Seeds, after they challenged the order directing the company not to charge a trait price of more than Rs. 900 per pack of 450 grams of Bt. Cotton seed.[70] The Andhra Pradesh State Government has also sought a compensation package of about Rs 4.5 crore (about 1 Million US$) to be paid by the company to farmers affected in some districts.
In USA and Canada
On 30 March 2011 a group consisting of over 60 family farmers, seed businesses and organic agricultural organizations in Canada and the US, filed a lawsuit against Monsanto Company to challenge the chemical giant’s patents on genetically modified seed. The plaintiffs say they are being forced to sue pre-emptively to protect themselves from being accused of patent infringement should they ever become contaminated by Monsanto’s genetically modified seed.
The case, Organic Seed Growers & Trade Association, et al. v. Monsanto, was filed in federal district court in Manhattan,[71]
Dumping of toxic waste in the UK
Between 1965 and 1972, Monsanto paid contractors to illegally dump thousands of tons of highly toxic waste in UK landfill sites, knowing that their chemicals were liable to contaminate wildlife and people. The Environment Agency said the chemicals were found to be polluting groundwater and the atmosphere 30 years after they were dumped.[72]
The Brofiscin quarry, near Cardiff, erupted in 2003, spilling fumes over the surrounding area, but the local community was unaware that the quarry housed toxic waste.
A UK government report shows that 67 chemicals, including Agent Orange derivatives, dioxins and PCBs exclusively made by Monsanto, are leaking from one unlined porous quarry that was not authorized to take chemical wastes. It emerged that the groundwater has been polluted since the 1970s.[73] The government was criticised for failing to publish information about the scale and exact nature of this contamination. According to the Environment Agency it could cost £100m to clean up the site in south Wales, called "one of the most contaminated" in the UK.[74]
Indonesian bribing convictions
In January 2005, Monsanto agreed to pay a $1.5m fine for bribing an Indonesian official. Monsanto admitted a senior manager at Monsanto directed an Indonesian consulting firm to give a $50,000 bribe to a high-level official in Indonesia's environment ministry in 2002, in a bid to avoid Environmental impact assessment on its genetically modified cotton. Monsanto told the company to disguise an invoice for the bribe as "consulting fees". Monsanto also has admitted to paying bribes to a number of other high-ranking Indonesian officials between 1997 and 2002. Monsanto faced both criminal and civil charges from the Department of Justice and the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Monsanto has agreed to pay $1m to the Department of Justice and $500,000 to the SEC to settle the bribe charge and other related violations.[75]
On 5 March 2008 the deferred prosecution agreement against Monsanto was dismissed with prejudice (unopposed by the Department of Justice) by the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia, thereby indicating that Monsanto had complied fully with the terms of the agreement.
Fined in France for false advertising
Monsanto was fined $19,000 in a French court on 26 January 2007 for misleading the public about the environmental impact of its herbicide Roundup. A former chairman of Monsanto Agriculture France was found guilty of false advertising for presenting Roundup as biodegradable and claiming that it left the soil clean after use.
Environmental and consumer rights campaigners brought the case in 2001 on the basis that glyphosate, Roundup's main ingredient, is classed as "dangerous for the environment" and "toxic for aquatic organisms" by the European Union. Monsanto's French distributor Scotts France was also fined 15,000 euros. Both defendants were ordered to pay damages of 5,000 euros to the Brittany Water and Rivers association and 3,000 euros to the CLCV consumers group.[76]
Cooperation with BASF
Monsanto is cooperating with BASF in research, development and marketing of biotechnology.[77]
Resistance in Europe
Europeans have been resisting genetically modified food for a long time. Monsanto has been facing stiff resistance from the European Union over its portfolio of GM foods. Their approval is important for Monsanto as the EU’s position on GM foods influences the global debate. The GM industry has never gained wholehearted approval from the public in the EU. There have been several laws passed on this subject, and EU legislation of 2003 asked for strict rules on labeling, traceability and risk assessments of GM foods by all the biotech companies. The Regulation of 2004 laid down procedures on traceability and labeling of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and all products produced using GMOs. The mandatory labeling legislation extends its requirement to all food and food ingredients produced from GMOs regardless of the detectable presence of DNA or protein within the final food product. These actions severely affected Monsanto as labeling foods as GM would stigmatise the foods.[78] In the EU, there has been a moratorium on the approval of new GM crops since 1998 caused by the public anxiety over the potential risks of GM foods.[79]
Among the documents obtained by Wikileaks include Monsanto asking the US government to maintain its strong pressure on the European Union legislation for the introduction of GMO foods.[80] After moves in France to ban a Monsanto GM corn variety, the US embassy recommended that 'we calibrate a target retaliation list that causes some pain across the EU'.[81]
Soybean in Argentina
Monsanto claims one of its greatest success stories has been genetically modified soybean (Roundup Ready soya) grown and sold in Argentina, South Africa, and across the USA. There are claims that its use increased soya production by 75% and increased yields by 173% over five years until 2002, giving good profitability to farmers. This was good news for the farmers who saw GM soya as a cash crop which had a good export potential as feed for cattle. Therefore, Argentine farmers relied on GM soya as their only produce. In 2004, there were questions being raised about the actual benefits, scientists claimed that the consequences of growing RR soya in Argentina included a massive exodus of small farmers from the countryside because they could no longer make a living (as they could not afford GM soya) or were driven off their land.[82]
Monsanto reasoned that the soil degradation and increased use of pesticides was not due to the use of its GM Soya. It maintains that farmers need to rotate crops in order to allow the soil to recover. Farmers should grow GM soya and then rotate it with corn or other food crops. However, due to the growing demand of soya, farmers in Argentina did not rotate crops and grew only soya, resulting in damage to the soil.[83]
Criticism
In Germany
In 2004, Monsanto filed two patent applications for processes which controlled the breeding of pigs with a specific marker gene which attracted criticism from Greenpeace.[84] Both applications were sold to Newsham Genetics in 2007. Although one of the applications was objected to by the European Patent Office as relating to an essentially biological process excluded from patent protection and later abandoned,[85] the second application was granted in 2008[86] and became the target for demonstrations in Germany.[87] Protests were caused by allegations that Monsanto was patenting the breeding of all pigs, although German Agriculture Minister Ilse Aigner strongly opposes the patent.[88] Monsanto says that the patent applies only to pigs which were bred using a specific Monsanto technology capable of locating genes which increase pig size.[89]
In Brazil
In 2003, a Brazilian organization of farmers protested Monsanto by invading a Monsanto research center in Goias.[90]
In China
Monsanto is criticized by Chinese economist Lang Xianping for having controlled the Chinese soybean market, and for trying to do the same to Chinese corn and cotton.[91]
In India
Monsanto has had a controversial history in India, starting with the accusation that Monsanto used terminator genes in its seeds, causing demonstrations against the company. Later, its GM cotton seed was the subject of NGO agitation because of its higher cost. Indian farmers cross GM varieties with local varieties using plant breeding to yield better strains, an illegal practice termed "seed piracy".[92][93] In 2009, high prices of Bt Cotton were blamed for forcing farmers of the district Jhabua into severe debts when the crops died due to lack of rain.[94]
In March 2010, Monsanto admitted that insects had developed resistance to the Bt Cotton planted in Gujarat. The company advised farmers to switch to its second generation of Bt cotton – Bolguard II – which had two resistance genes instead of one.[95] However, this advice was widely slammed by critics and even the Government of India who claimed that the admission by Monsanto was more of a business strategy. Maharastra Seeds, a Monsanto subsidiary, conducted several illegal trials in India and fields growing the GM seed were eventually burned in large scale protests.[96][97]
Child labor
A subsidiary of Monsanto is alleged to employ child labor in the manufacture of cotton-seeds in India. The work involves handling of poisonous pesticides such as Endosulfan and the children get less than Rs.20 (less than half a US dollar) per day.[98]
Farmer suicides
A short documentary by Frontline (U.S. TV series) suggested that farmers using genetically modified seeds promoted by Cargill and Monsanto have led to rising debts and forced some into the equivalent of indentured servitude to the moneylenders.[99] Every thirty minutes an Indian farmer commits suicide and in the last sixteen years, more than a quarter of a million farmers have died.[100] Some claim a major cause is poor yields leading to mounting debt, an increased need for pesticides, and the higher cost of the Bt cotton seed sold by Monsanto.[101][102][103][104] Monsanto has responded by pointing to reports that link suicides to other factors, and argues that if it was the major cause of suicides then "why is it that Indian farmers represent the fastest-growing users of biotech crops in the world?”[100]
A report released by the International Food Policy Research Institute in October 2008 provided evidence that the cause of farmer suicide in India was due to several causes[clarification needed] and that the introduction of Bt cotton was not a major factor.[105] It argues that the suicides predate the introduction of the cotton in 2002 and has been fairly consistent since 1997.[105][106] Other studies also suggest the increase in farmer suicides is due to a combination of various socio-economic factors.[107] These include debt, the difficulty of farming semi-arid regions, poor agricultural income, absence of alternative income opportunities, the downturn in the urban economy forcing non-farmers into farming, and the absence of suitable counseling services.[107][108]
In the United Kingdom
Prior to 1977 Monsanto dumped thousands of tons of toxic waste containing PCBs in a quarry near Groesfaen, Wales.[28]
In the United States
The Center for Food Safety[109] listed 112 lawsuits by Monsanto against farmers for claims of seed patent violations.[28] The Center for Food Safety's analyst stated that many innocent farmers settle with Monsanto because they cannot afford a time consuming lawsuit. Monsanto is frequently described by farmers as "Gestapo" and "Mafia" both because of these lawsuits and because of the questionable means they use to collect evidence of patent infringement.[28]
Monsanto is responsible for more than 50 United States Environmental Protection Agency Superfund sites, attempts to clean up Monsanto Chemical's formerly uncontrolled hazardous waste sites.[28]
As of May 2008, Monsanto is currently engaged in a campaign to prohibit dairies which do not inject their cows with artificial bovine growth hormone from advertising this fact on their milk cartons.[28]
When the Federal Trade Commission did not side with Monsanto on this issue, the company started lobbying state lawmakers to implement a similar ban. Pennsylvania Agriculture Secretary Dennis Wolfe attempted to prohibit dairies from using labels stating that their milk does not contain artificial bovine growth hormone, but public outcry led Governor Edward Rendell to step in and reverse his secretary's position, stating: "The public has a right to complete information about how the milk they buy is produced."[28]
Missouri
Gary Rinehart of Eagleville, Missouri was sued by Monsanto in 2002, which claimed he had violated their Roundup Ready Soybean patent. Rinehart was not a farmer or seed dealer, but he still had to spend money for his legal defense. Monsanto eventually dropped the lawsuit, but never issued an apology, admitted to making a mistake, or was compelled to pay for Rinehart's legal expenses.[110] The company has also been accused of showing up at farmers' houses, making accusations, and demanding records.[110]
Monsanto sued the Pilot Grove Cooperative Elevator in Pilot Grove, Missouri, claiming that offering seed cleaning services to farmers was tantamount to inducing them to pirate Monsanto seeds. The Pilot Grove Cooperative Elevator had been cleaning seeds for decades before companies such as Monsanto could patent organisms.[28]
Illinois
In 1926, when environmental policy was generally governed by local governments, Monsanto Chemical Company founded and incorporated the town of Monsanto, later renamed Sauget, Illinois, to provide a more business friendly environment for one of its chemical plants. For years, the Monsanto plant in Sauget was the nation's largest producer of polychlorinated biphenyls. And although polychlorinated biphenyls were banned in the 1970s, they remain in the water along Dead Creek in Sauget.[111]
Alabama
Monsanto is accused of encouraging residents of Anniston, Alabama to use soil known by the company to be contaminated with PCBs as topsoil.[28]
Political contributions
Monsanto gave $186,250 to federal candidates in the 2008 election cycle through its political action committee (PAC) – 42% to Democrats, 58% to Republicans. For the 2010 election cycle they have given $72,000 – 51% to Democrats, 49% to Republicans.[112]
Lobbying
The company spent $8,831,120 for lobbying in 2008. $1,492,000 was to outside lobbying firms with the remainder being spent using in-house lobbyists.[113]
Former Monsanto lobbyist Michael R. Taylor was appointed as a senior adviser to the Food and Drug Administration (United States) Commissioner on food safety on 7 July 2009.[114]
Public officials formerly employed by Monsanto
- Justice Clarence Thomas worked as an attorney for Monsanto in the 1970s. Thomas wrote the majority opinion in the 2001 Supreme Court decision J. E. M. Ag Supply, Inc. v. Pioneer Hi-Bred International, Inc.|J. E. M. AG SUPPLY, INC. V. PIONEER HI-BREDINTERNATIONAL, INC.[115] which found that "newly developed plant breeds are patentable under the general utility patent laws of the United States." This case benefitted all companies which profit from genetically modified crops, of which Monsanto is the largest.[28][116][115]
- Michael R. Taylor was an assistant to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) commissioner before he left to work for a law firm on gaining FDA approval of Monsanto’s artificial growth hormone in the 1980s. Taylor then became deputy commissioner of the FDA from 1991 to 1994.[28] Taylor was later re-appointed to the FDA in August 2009 by President Barack Obama.[117]
- Dr. Michael A. Friedman was a deputy commissioner of the FDA before he was hired as a senior vice president of Monsanto.[28]
- Linda J. Fisher was an assistant administrator at the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) before she was a vice president at Monsanto from 1995 – 2000. In 2001, Fisher became the deputy administrator of the EPA.[28]
- Former Secretary of Defense Donald Rumsfeld was chairman and chief executive officer of G. D. Searle & Co., which Monsanto purchased in 1985. Rumsfeld personally made at least $12 million USD from the transaction.[28]
Representation in the media
Documentaries:
- American Drug War
- The Esoteric Agenda.
- Food, Inc.
- The Corporation
- The Future of Food. Critical of Monsanto's activities in Canada and the US.
- Patent For A Pig
- The World According to Monsanto
- Seeds of Deception
- Plan Colombia: Cashing in the Drug War Failure
- The Monsanto Story[118]
- Life Running Out Of Control[119]
- David Versus Monsanto[120]
- Deconstructing Supper
Books:
- Fast Food Nation: The Dark Side of the All-American Meal (2001)
- Silent Spring
- Stolen Harvest: The Hijacking of the Global Food Supply by Vandana Shiva
Le Monde selon Monsanto
In March 2008, French journalist Marie-Monique Robin released the results of her three years of research worldwide into Monsanto. A book was published by La Découverte, a French editor, and a video documentary, Le Monde selon Monsanto (The World according to Monsanto), was released on DVD and shown on Arte, the Franco-German culture TV channel.[121][122]
It reveals numerous controversial facts about Monsanto. Marie-Monique Robin traveled the world to meet scientists and political figures in order to investigate the consequences of several Monsanto products. Those interviewed include Shiv Chopra, a Canadian researcher who was fired by Health Canada for revealing an attempted bribe by Monsanto regarding the attempted introduction of Bovine Growth Hormone into Canada. The author of the research met several independent scientists around the world who tried to warn the political authorities about the use of GM seeds. According to the journalist, most of these scientists actually lost their jobs as a consequence of their speaking out. The "revolving door syndrome" is also pointed out in the research as a threat to the quality and independence of the scientific conclusions about the effects of Monsanto products, especially the Food and Drug Administration.
Robin travels to India, Mexico, Argentina, and Paraguay to see how Monsanto's genetically modified organisms (GMOs) have affected local farmers using it for their crops. The claim is that suicide rates of farmers in India have increased as farmers are finding it harder to earn a living using more expensive Monsanto seeds that despite claims still require specific pesticide and fertilizer (see above). Mexico, having banned GMOs, is trying to limit contamination and crossbreeding from subsidized U.S. GMO corn imported in via North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) for eating. Argentinian farmers are giving up farming and moving to urban slums because they cannot compete with GM crops and are finding their farms, livestock, and children being negatively affected by pesticide runoff. Paraguay was forced to accept GMO crops as it was being anonymously imported and grown en masse, so not allowing its export would have negatively impacted the economy. In all cases genetic variation is reduced as a result of monocropping and ownership is increasingly concentrated.
At the end, Monsanto declined to participate in the documentary.
In popular culture
- In the 2008 film Michael Clayton, the fictional chemical company U-North is loosely based on Monsanto.
- The folk band Seize The Day released a song entitled "Food `n health `n hope (Monsanto Song)".
- The documentary film Food, Inc. contains numerous references to Monsanto and its business practices.
- Punk rock band The Adolescents released a song entitled "Monsanto Hayride" criticizing corporate wrongdoing.
- Punk rock band Anti-Flag released a song entitled "The W.T.O. Kills Farmers" which accuses Monsanto of murder as a result of their business practices.
- The Greek low-bap/rap band Active Member released a song entitled "Allios Skapste" criticizing Monsanto of its business practices.
- In the second episode of the first season of Futurama, "The Series Has Landed", a Moon carnival ride named "The Goophy Gopher Revue" is said to have been sponsored/owned by "Moonsanto".[123]
- In the 2010 Indian film Peepli Live, the head of an Indian state asks his assistant to award all government agricultural contracts to a company called 'Somanto'.
- TV Show CSI: Miami (season 8) episode Bad Seed involves a corporation using tactics similar to Monsanto's.
- In 2010 New Zealand band The Mark Of Man released a song entitled "Death To Monsanto" from their self-titled debut album.
- In the 2008 French documentary film "The World According to Monsanto", Marie-Monique Robin shows the corruption of various government officials & the silencing of dissenting scientists by Monsanto. It also shows the effect Monsanto has had on some of the world's agricultural markets. http://www.imdb.com/title/tt1189345/
See also
- Pioneer Hi-Bred International
- Temporal analysis of products
References and notes
- ^ a b c d e f "2010 Form 10-K, Monsanto Company". United States Securities and Exchange Commission. http://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1110783/000095012310096537/c60329e10vk.htm.
- ^ The World According to Monsanto, 11 March 2008, "New movie damns Monsanto's deadly sins"
- ^ "Monsanto CFO to retire." St. Louis Business Journal. Wednesday 12 August 2009. Retrieved on 19 August 2009.
- ^ a b "AP: Monsanto Strong-Arms Seed Industry". CBS News. 14 December 2009. http://www.cbsnews.com/stories/2009/12/14/business/main5978152.shtml. Retrieved 15 June 2010.
- ^ "Monsanto Focus of Antitrust Investigation". CBS News. 8 October 2009. http://www.cbsnews.com/stories/2009/10/08/business/main5372772.shtml. Retrieved 15 June 2010.
- ^ a b "Monsanto Held Liable For PCB Dumping". The Washington Post. http://www.washingtonpost.com/ac2/wp-dyn/A54914-2002Feb22?language=printer. Retrieved 5 April 2010.
- ^ "Agribusiness, Biotechnology and War". Organicconsumers.org. http://www.organicconsumers.org/corp/tokaronwar120902.cfm. Retrieved 2011-10-28.
- ^ E. Fred Schubert (2003). "1". Light-Emitting Diodes. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0819439568.
- ^ Fawthrop, Tom (14 June 2004). "Vietnam's war against Agent Orange". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/health/3798581.stm. Retrieved 5 April 2010.
- ^ Agent Orange Victims Sue Monsanto, by Tom Fawthrop, 4 November 2004, CorpWatch
- ^ "SPY Award Interview". Asse.org. 1947-04-16. http://www.asse.org/practicespecialties/interviews/SPYAward.php. Retrieved 2011-10-28.
- ^ a b "''Monsanto Canada v. Schmeiser'', 2001 FCT 256". Decisions.fct-cf.gc.ca. http://decisions.fct-cf.gc.ca/en/2001/2001fct256/2001fct256.html. Retrieved 2011-10-28.
- ^ Greenpeace, 2 August 2005, "Monsanto files patent for new invention: the pig"
- ^ Stephanie Condron (11 August 2005). "GM crop giant wants to patent a super-pig". Daily Mail (London). p. 18. http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-358902/GM-crop-giant-wants-patent-super-pig.html.
- ^ "Monsanto Anti-Farmers Patents—Related Documents" from Public Patent Foundation
- ^ "Reasons for Selection, 2009 Canada's Top 100 Employers Competition". http://www.eluta.ca/top-employer-monsanto.
- ^ Troyer, A. Forrest. Development of Hybrid Corn and the Seed Corn Industry. In: Handbook of Maize Genetics and Genomics. Bennetzen, Jeff L.; Hake, Sarah (Eds.) Springer, 2009, pages 87–114.
- ^ "Seminis Acquisition – Investor Conference Call". 24 January 2005. http://www.monsanto.com/pdf/investors/2005/01-24-05_low.pdf. Retrieved 10 October 2009.[dead link]
- ^ "Monsanto Company Completes Acquisition of Delta and Pine Land Company, Seeks Approval of Related Divestitures". 1 June 2007. http://news.thomasnet.com/companystory/524921. Retrieved 10 October 2009.
- ^ "Monsanto – Pig Patent". 16 July 2009. http://www.monsanto.com/monsanto_today/for_the_record/pig_patent.asp. Retrieved 10 October 2009.[dead link]
- ^ "Newsham Choice Genetics". 14 November 2007. http://www.newsham.com/Newsham/news.aspx?Newsham=WebPointID%3d23%26NewsStoryID%3d1%26__TimeStamp__%3d12%2f31%2f9999+11%3a59%3a59+PM. Retrieved 10 October 2009.[dead link]
- ^ "De Ruiter Seeds Acquisition". 31 March 2008. http://www.monsanto.com/pdf/investors/deruiter_seed_acquisition.pdf. Retrieved 10 October 2009.[dead link]
- ^ "Eli Lilly and Company to Acquire Monsanto's POSILAC Brand Dairy Product and Related Business". 20 August 2008. http://monsanto.mediaroom.com/index.php?s=43&item=629. Retrieved 10 October 2009.
- ^ "Global Crop Diversity Trust donors". 29 September 2010. http://www.croptrust.org/documents/web/FundingStatus30-09-2010.pdf. Retrieved 22 October 2010.
- ^ "Monsanto – GRDC Collaboration". 26 August 2010. http://monsanto.mediaroom.com/intergrain-monsanto-new-wheat-breeding-collaboration. Retrieved 22 October 2010.
- ^ "Syngenta and Monsanto Settle and Share". Forbes. 29 September 2010. http://www.forbes.com/2008/05/23/syngenta-monsanto-settlement-markets-equity-cx_lkm_0523markets14.html. Retrieved 22 October 2010.
- ^ "Board of Directors". Monsanto. http://www.monsanto.com/responsibility/corp_gov/directors.asp.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o "Monsanto's Harvest of Fear". http://www.vanityfair.com/politics/features/2008/05/monsanto200805.
- ^ "Top 100 PRPs Based on Number of Sites At Which They Are Involved". CERCLIS3. 11 December 2001. http://projects.publicintegrity.org/superfund/includes/Top100PRPs.pdf. Retrieved 10 October 2009.
- ^ "The Politics Behind the Scientific Debate on Dioxin". http://consumerlawpage.com/article/truelies.shtml.
- ^ "Monsanto knew about PCB toxicity for decades". http://www.chemicalindustryarchives.org/dirtysecrets/annistonindepth/toxicity.asp.
- ^ Michael Pollan (25 October 1998). "Playing God in the Garden". The New York Times Magazine. p. Section 6; Page 44. http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9D03EFD8143DF936A15753C1A96E958260.
- ^ a b Joël Spiroux de Vendômois, François Roullier, Dominique Cellier1, Gilles-Eric Séralini (2009). "A Comparison of the Effects of Three GM Corn Varieties on Mammalian Health". Int J Biol Sci 5 (7): 706–726. PMC 2793308. PMID 20011136. http://www.biolsci.org/v05p0706.htm.
- ^ "WikiLeaks Cables Reveal U.S. Sought to Retaliate Against Europe over Monsanto GM Crops". http://www.democracynow.org/2010/12/23/wikileaks_cables_reveal_us_sought_to. Retrieved 13 January 2011.
- ^ Ewen SW, Pusztai A (October 1999). "Effect of diets containing genetically modified potatoes expressing Galanthus nivalis lectin on rat small intestine". Lancet 354 (9187): 1353–4. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(98)05860-7. PMID 10533866.
- ^ Harry A Kuiper, Hub PJM Noteborn, Ad ACM Peijnenburg (1999). "Adequacy of methods for testing the safety of genetically modified foods". The Lancet 354 (9187): 1315–1316. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(99)00341-4. http://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(99)00341-4/fulltext. Retrieved 11 November 2010.
- ^ "Monsanto Company History". Retrieved on 5 May 2010
- ^ John Vidal (1999-10-05). "World braced for terminator 2". Guardian. http://www.guardian.co.uk/science/1999/oct/06/gm.food2. Retrieved 2011-10-28.
- ^ Warwick, Hugh (October 2000). Wijeratna, Alex; Meienberg, François; Meienberg. eds (PDF). Syngenta – Switching off farmers' rights?. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http://www.fao.org/righttofood/KC/downloads/vl/docs/AH428.pdf. Retrieved Saturday, 23 October 2010.
- ^ Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Michaud DS, Deroo B, Rosner B, Speizer FE, Pollak M (May 1998). "Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I and risk of breast cancer". Lancet 351 (9113): 1393–6. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(97)10384-1. PMID 9593409. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0140-6736(97)10384-1.
- ^ Chan JM, Stampfer MJ, Giovannucci E, Gann PH, Ma J, Wilkinson P, Hennekens CH, Pollak M (January 1998). "Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study". Science 279 (5350): 563–6. doi:10.1126/science.279.5350.563. PMID 9438850. http://www.ejnet.org/bgh/igf-1science.html.
- ^ a b Pollak M (June 2000). "Insulin-like growth factor physiology and cancer risk". Eur. J. Cancer 36 (10): 1224–8. doi:10.1016/S0959-8049(00)00102-7. PMID 10882860. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0959-8049(00)00102-7.
- ^ Sandhu MS, Dunger DB, Giovannucci EL (July 2002). "Insulin, insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), IGF binding proteins, their biologic interactions, and colorectal cancer". J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 94 (13): 972–80. doi:10.1093/jnci/94.13.972. PMID 12096082. http://jnci.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12096082.
- ^ Vicini J., Etherton T., Kris-Etherton P., Ballam J., Denham S., Staub R., Goldstein D., Cady R., McGrath M., Lucy M. (July 2008). "Survey of retail milk composition as affected by label claims regarding farm-management practices". J Am Diet Assoc 108 (7): 1198–203. doi:10.1016/j.jada.2008.04.021. PMID 18589029. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0002-8223(08)00513-0.
- ^ Fighting on a Battlefield the Size of a Milk Label from The New York Times
- ^ "Frustrations Vented Over Questionable Milk Marketing Practices – October 26, 2006". Earthfarmfriendly.com. 26 October 2006. http://www.earthfarmfriendly.com/News/frustvenmilkmrkt-102606.html. Retrieved 24 September 2010.
- ^ "Eli Lilly to Buy Monsanto’s Dairy Cow Hormone for $300 million - DealBook Blog". The New York Times. 20 August 2008. http://dealbook.blogs.nytimes.com/2008/08/20/eli-lilly-to-buy-monsantos-dairy-cow-hormone-for-300-million/.
- ^ Grunwald, Michael (1 January 2002). "Monsanto Hid Decades Of Pollution". Washington Post. http://www.washingtonpost.com/ac2/wp-dyn?pagename=article&contentId=A46648-2001Dec31. Retrieved 11 October 2009.
- ^ Sack, Kevin (27 January 2002). "PCB Pollution Suits Have Day in Court in Alabama". The New York Times. http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9C04EED7143AF934A15752C0A9649C8B63. Retrieved 1 October 2008.
- ^ "$700 million deal announced in Anniston PCBs cases". Associated Press. 19 August 2003. http://www.ewg.org/node/15673. Retrieved 11 October 2009.
- ^ "The world's 10 most unethical companies | The Search Office Space Blog". News.searchofficespace.com. 2011-05-16. http://news.searchofficespace.com/sos-news/the-worlds-10-most-unethical-companies.html. Retrieved 2011-10-28.
- ^ Monsanto's Greatest Hits Metro, Silicon Valley's Weekly Newspaper. 11–17 May 2000.
- ^ Fawthrop, Tom (14 June 2004). "Vietnam's war against Agent Orange". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/health/3798581.stm.
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ Monsanto's Monopoly of Biotech Sector Spurs Lawsuit from Organic Consumers Association
- ^ "United States of America v. Monsanto Company (Foreign Corrupt Practices Act)". United States District Court for the District of Columbia. http://www.law.virginia.edu/pdf/faculty/garrett/monsanto.pdf. Retrieved 3 October 2010.
- ^ "French Monsanto subsidiary found guilty of GMO contamination". translation of a France Nature Environnement press release. 14 December 2006. http://www.laleva.org/eng/2006/12/french_monsanto_subsidiary_found_guilty_of_gmo_contamination.html. Retrieved 11 October 2009.
- ^ {{Cite news title = Monsanto GMO sugarbeets to be destroyed: court date = 30 November 2010 URL = http://www.reuters.com/article/idUSTRE6B00Y520101201}}
- ^ Monsanto Company. "Saved Seed and Farmer Lawsuits". http://www.monsanto.com/newsviews/Pages/saved-seed-farmer-lawsuits.aspx. Retrieved 23 October 2010.
- ^ "The World Trade Organization at Cancún – Agriculture and the Environment". Sierra Club of/du Canada. http://www.sierraclub.ca/national/programs/sustainable-economy/trade-environment/wto-cancun-agriculture-env.html. Retrieved Saturda, 23 October 2010.
- ^ Peter Shinkle, St. Louis Post-Dispatch (7 May 2003). "Farmer who lied in dispute with Monsanto will go to prison". http://www.gene.ch/genet/2003/May/msg00044.html. Retrieved 20 August 2009.
- ^ Andy Meek, Memphis Daily News (22 June 2006). "Down and Out in Covington – Farmer struggles to re-emerge after $3 million judgment, prison term in Monsanto case". Memphis Daily News. http://www.memphisdailynews.com/editorial/Article.aspx?id=30496. Retrieved 20 August 2009.
- ^ Democracy Now, Headlines (14 July 2003). "Monsanto Sues Milk Producer For Advertising It Sells Hormone-Free Milk". Democracy Now. http://www.democracynow.org/article.pl?sid=03/07/14/1437218. Retrieved 22 December 2006.
- ^ Gar Smith (2001 autumn). "Percy Schmeiser vs. Monsanto". Earth Island Journal.
- ^ "Wilson, Akre describe corporate influence over news". Proliberty.com. http://www.proliberty.com/observer/20001204.htm. Retrieved 2011-10-28.
- ^ "Reporter wins suit over firing". Sptimes.com. 2000-08-19. http://www.sptimes.com/News/081900/TampaBay/Reporter_wins_suit_ov.shtml. Retrieved 2011-10-28.
- ^ "Three varieties of BT cotton rejected in Andhra Pradesh, India". Malaysia. 4 June 2005. http://www.twnside.org.sg/title2/service215.htm.
- ^ "Angry Andhra uproots Monsanto". Hyderabad. 23 June 2005. http://www.financialexpress.com/fe_full_story.php?content_id=92868. Retrieved 16 January 2009.
- ^ A.P. Government files contempt petition before MRTPC against Monsanto from The Hindu
- ^ "India PM pledge over suicide farmers". BBC News. BBC. 1 July 2004. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/3855517.stm. Retrieved 16 January 2009.
- ^ "Canadian and US farmers sue Monsanto to protect themselves". CBAN (Canada). 30 March 2011. http://cban.ca/Press/Press-Releases/Farmers-and-Seed-Distributors-Sue-Monsanto-to-Protect-Themselves-from-Patents-on-Genetically-Modified-Seed.
- ^ Vidal, John (12 February 2007). "The wasteland: how years of secret chemical dumping left a toxic legacy". The Guardian (UK). http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/2007/feb/12/uknews.pollution1. Retrieved 27 September 2007.
- ^ "Brofiscin Quarry". Environment Agency. http://www.environment-agency.gov.uk/research/library/publications/33833.aspx. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- ^ Vidal, John (12 February 2007). "Monsanto dumped toxic waste in UK". Guardian (London). http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/2007/feb/12/uknews.pollution1. Retrieved 31 March 2009.
- ^ "Monsanto fined $1.5m for bribery". BBC. 7 January 2005. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/4153635.stm. Retrieved 28 September 2007.
- ^ "Monsanto Fined in France for 'False' Herbicide Ads". Organic Consumers Association. http://www.organicconsumers.org/articles/article_4114.cfm. Retrieved 28 September 2007.
- ^ "BASF-Gruppe: Interview Dr. Jürgen Hambrecht zur Zusammenarbeit mit Monsanto". Corporate.basf.com. 2007-03-21. http://www.corporate.basf.com/de/investor/veranstaltungen/termine/070321_interview.htm?id=V00-Eq3z_CNjlbcp.*0. Retrieved 2011-10-28.
- ^ Tough European line on GM labelling from The Guardian
- ^ Troubled Monsanto scales down GM hopes in Europe from The Guardian
- ^ "Spain's biotech crop under threat (Wikileaks telegram 09MADRID482)". U.S. Department of State. 19 May 2009. http://www.wikileaks.ch/cable/2009/05/09MADRID482.html. Retrieved 20. December 2010.
- ^ Vidal, John (3 January 2011). "WikiLeaks: US targets EU over GM crops". The Guardian (UK). http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/2011/jan/03/wikileaks-us-eu-gm-crops. Retrieved 3 January 2011.
- ^ Reboratti, Carlos (2010). "A sea of soybean: Consequences of the new agriculture in Argentina (Un mar de soja: La nueva agricultura en Argentina y sus consecuencias)" (in Spanish). Norte Grande Geography Journal (Revista de geografía Norte Grande) (Chile: Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile) (45): 63–76. ISSN 0379-8682. http://redalyc.uaemex.mx/src/inicio/ArtPdfRed.jsp?iCve=30012482005.
- ^ GM soya 'miracle' turns sour in Argentina from The Guardian
- ^ "Monsanto files patent for new invention: the pig". Greenpeace International. 2005-08-02. http://www.greenpeace.org/international/news/monsanto-pig-patent-111. Retrieved 2011-10-28.
- ^ European Patent Register entry for European patent application no. 1651030
- ^ European Patent Register entry for European patent no. 1651777
- ^ Peter, Laurence (16 April 2009). "Germans protest over pig patent". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/europe/8002503.stm. Retrieved 5 April 2010.
- ^ gb/ncy, dpa/epd/Reuters/AP. "German farm minister rejects pig patent | Germany | Deutsche Welle | 18.04.2009". Dw-world.de. http://www.dw-world.de/dw/article/0,,4188153,00.html. Retrieved 24 September 2010.
- ^ [2][dead link]
- ^ Brazil activists target Monsanto from BBC News
- ^ "郎咸平:孟山都的转基因帝国-大豆、玉米与棉花". Wyzxsx.com. 28 January 2010. http://www.wyzxsx.com/Article/Class4/201001/128373.html. Retrieved 24 September 2010.
- ^ India's GM seed Piracy from BBC News
- ^ Farmers welcome halt of 'terminator' from BBC News
- ^ "Jhabua on its way to becoming Vidarbha-II?". Hindu.com. 2009-08-25. http://www.hindu.com/2009/08/25/stories/2009082554841400.htm. Retrieved 2011-10-28.
- ^ "Bt cotton ineffective against pest in parts of Gujarat, admits Monsanto". The Hindu (Chennai, India). 6 March 2010. http://www.hindu.com/2010/03/06/stories/2010030664831400.htm. Retrieved 12 March 2010.
- ^ "India cheers while Monsanto burns?". http://www.lightparty.com/Health/IndiaCheers.html. Retrieved 6 September 2010.
- ^ "Monsanto ‘admission' has business motives?". The Hindu (Chennai, India). 12 March 2010. http://www.hindu.com/2010/03/12/stories/2010031263690900.htm. Retrieved 12 March 2010.
- ^ Child Labour and Trans-National Seed Companies in Hybrid Cotton Seed Production in Andhra Pradesh from India Committee of the Netherlands
- ^ Seeds of Suicide: India's desperate farmers from the Public Broadcasting Service
- ^ a b http://www.chrgj.org/publications/docs/every30min.pdf
- ^ "Farmer's Suicides". Z Magazine. http://www.zmag.org/content/showarticle.cfm?ItemID=4871.
- ^ "Indian Farmer's Final Solution". countercurrents.org. http://www.countercurrents.org/gl-sharma290604.htm.
- ^ "Rough Cut Seeds of Suicide India's desperate farmers". PBS Frontline. 26 July 2005. http://www.pbs.org/frontlineworld/rough/2005/07/seeds_of_suicid.html. Retrieved 3 October 2010.
- ^ P. Sainath (August 2004). "Seeds of suicide – I I". InfoChange News and Features. http://infochangeindia.org/200408056392/Other/Features/Seeds-of-suicide-I-I.html.
- ^ a b Guillaume P. Gruère, Purvi Mehta-Bhatt and Debdatta Sengupta (2008). "Bt Cotton and Farmer Suicides in India: Reviewing the Evidence". International Food Policy Research Institute. http://www.ifpri.org/sites/default/files/publications/ifpridp00808.pdf.
- ^ Sheridan, C. (2009). "Doubts surround link between Bt cotton failure and farmer suicide". Nat Biotechnol. 27 (1): 9–10. doi:10.1038/nbt0109-9. PMID 19131979.
- ^ a b Nagraj, K. (2008). "Farmers suicide in India: magnitudes, trends and spatial patterns". http://www.macroscan.com/anl/mar08/pdf/Farmers_Suicides.pdf.
- ^ Mishra, Srijit (2007). "Risks, Farmers’ Suicides and Agrarian Crisis in India: Is There A Way Out?". Indira Gandhi Institute of Development Research (IGIDR). http://www.igidr.ac.in/pdf/publication/WP-2007-014.pdf.
- ^ Heather (30 September 2010). "Federal Court Strikes Down Ohio Ban On rBGH-Free Labels On Dairy Products". The center for food safety. http://www.centerforfoodsafety.org. Retrieved 3 October 2010.
- ^ a b "Barlett & Steele". Barlettandsteele.com. http://www.barlettandsteele.com/journalism/vf_monsanto_2.php. Retrieved 24 September 2010.
- ^ "Tiny Sauget, Illinois, likes business misfits". Post-gazette.com. 2006-10-03. http://www.post-gazette.com/pg/06276/727066-28.stm. Retrieved 2011-10-28.
- ^ 2008 PAC Summary Data, Open Secrets.
- ^ Monsanto lobbying expenses, Open Secrets.
- ^ "Noted Food Safety Expert Michael R. Taylor Named Advisor to FDA Commissioner". Fda.gov. 2009-07-07. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/2009/ucm170842.htm. Retrieved 2011-10-28.
- ^ a b "J. E. M. Ag Supply, Inc. V. Pioneer Hi-Bredinternational, Inc". Law.cornell.edu. http://www.law.cornell.edu/supct/html/99-1996.ZS.html. Retrieved 2011-10-28.
- ^ "Key Supreme Court ruling on plant patents * – McEowen, Harl March 2002". Extension.iastate.edu. 2002-01-18. http://www.extension.iastate.edu/agdm/articles/harl/HarlMar02.htm. Retrieved 2011-10-28.
- ^ "Monsanto's Man in the Obama Administration". Counterpunch.org. 2009-08-14. http://www.counterpunch.org/kenfield08142009.html. Retrieved 2011-10-28.
- ^ The Monsanto Story – Part 1 (1901–1994), 2007, 22 min, by Andy Radford, Google Video
- ^ "Life Running Out of Control | Bullfrog Films: 1-800-543-3764: Environmental DVDs and Educational DVDs". Bullfrog Films. http://www.bullfrogfilms.com/catalog/lroc.html. Retrieved 24 September 2010.
- ^ "Journeyman Features: David Vs Monsanto". Journeyman Pictures. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E42ndfjnP1g. Retrieved 6 September 2010.
- ^ Le monde selon Monsanto from Arte TV
- ^ The World according to Monsanto from Google Video
- ^ "The Series Has Landed at IMSDb". Internet Movie Database. http://www.imsdb.com/transcripts/Futurama-The-Series-Has-Landed.html. Retrieved 31 October 2010.
- Notes
- Business: More for Monsanto Time. 18 May 1936.
- Monsanto's road from saccharin to 'tolerant' crops Times Online (Times Newspapers). 16 October 2003.
Bibliography
- Monsanto fined for bribery
- Monsanto Canada Inc. v. Schmeiser, Federal Court of Canada decision
- Schmeiser v. Monsanto Canada Inc., Federal Court of Appeal decision
- Monsanto Canada Inc. v. Schmeiser, Supreme Court of Canada decision
- Monsanto Buys Final Calgene Shares
- Monsanto's part in Disneyland history
- Monsanto vs Bees
- Monsanto BGH lawsuit
- After killer cotton, killer brinjal?
- Jeffrey M Smith: Seeds of Deception. YES Books, 2003. (Book ISBN 0-9729665-8-7).
- Marie-Monique Robin: Le Monde selon Monsanto – De la dioxine aux OGM, une multinationale qui vous veut du bien. Coédition Arte / La Découverte, 2008. (Book ISBN 2-7071-4918-7 or 978-270714918 and DVD-ASIN: B001684BP0 ). English: "The World According to Monsanto"
- Marie-Monique Robin: "The World According to Monsanto, A Film by Marie-Monique Robin" Image & Compagnie – ARTE France – Productions Thalie – National Film Board of Canada – WDR 2008
External links
- Monsanto's Official Website
- Monsanto at the Open Directory Project
- Hoover's Online: Monsanto Company Capsule
- SourceWatch on Monsanto
- Monsanto Watch
- News articles
- AP investigation from Atlantic Business News
- Photos of the Monsanto Plant after the 1947 Texas City Disaster hosted by the Portal to Texas History
- Biotech Companies Race for Drought-Tolerant Crops
- Millions Against Monsanto
- Monsanto’s Harvest of Fear from Vanity Fair
- Monsanto has to Accept Full Responsibility for Genetic Contamination
- Monsanto Implicated as a Factor in the Suicides of 182,000 Indian Farmers Between 1997 and 2007
- Video:The World According to Monsanto
Genetic engineering Genetically
modified
organismsMammalsMaizePotatoAmfloraRiceSoybeanRoundup Ready soybean · Vistive GoldTomatoCottonBt cotton · Roundup Ready cottonOtherFishBacteria and virusesProcesses TypesUses In agricultureIn researchRelated articles Transgene · Detection of genetically modified organisms · Genetic pollution · Genetic engineering in fiction · Reverse transfectionSimilar fields Categories:- Companies listed on the New York Stock Exchange
- Genetic engineering and agriculture
- Agriculture companies of the United States
- Chemical companies of the United States
- Companies based in St. Louis County, Missouri
- Greater St. Louis
- Multinational companies
- Companies established in 1901
- Droughts
- Seed companies
- Biotechnology companies
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.