- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(2-fluoroethyl)amphetamine
-
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-(2-fluoroethyl)amphetamine 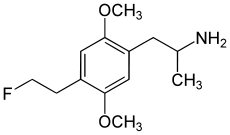 (RS)-2-[4-(2-Fluoro-ethyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-phenyl]-1-methyl-ethylamineOther names1-[4-(2-fluoroethyl)-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl]propan-2-amine
(RS)-2-[4-(2-Fluoro-ethyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-phenyl]-1-methyl-ethylamineOther names1-[4-(2-fluoroethyl)-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl]propan-2-amineIdentifiers CAS number 121649-01-2 ChemSpider 21106293 
ChEMBL CHEMBL123685 
Jmol-3D images Image 1
Image 2- C1(=CC(=C(C=C1CC(C)N)OC)CCF)OC
COc1cc(CC(C)N)c(cc1CCF)OC
Properties Molecular formula C13H20NO2F Molar mass 241.31 g/mol  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references DOEF, or 4-fluoroethyl-2,5-methoxyamphetamine, is a lesser-known psychedelic drug and a substituted amphetamine. DOEF was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines i Have Known And Loved), the dosage range is listed as 2-3.5[mg], and the duration is listed as 12–16 hours. DOEF produces increased appreciation of music, closed-eye visuals, increased sexual pleasure, and intense slowing of time. Shulgin gives it a +++ on the Shulgin Rating Scale. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of DOEF.
See also
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-Substituted Amphetamines
External links

This psychoactive drug-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. - C1(=CC(=C(C=C1CC(C)N)OC)CCF)OC
