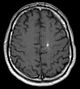
- Cavernous hemangioma
-
Cavernous hemangioma Classification and external resources ICD-10 D18 (ILDS D18.014) ICD-9 228.0x DiseasesDB 30031 eMedicine radio/95 MeSH D006392 Cavernous angioma, also known as cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM), cavernous haemangioma, and cavernoma, is a vascular disorder that alternately has been classified as neoplastic or hamartomatous. It is characterized by grossly dilated blood vessels with a single layer of endothelium and an absence of neuronal tissue within the lesions. These thinly walled vessels resemble sinusoidal cavities filled with stagnant blood. Blood vessels in patients with CCM can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. Most lesions occur in the brain, but any organ may be involved.
Contents
Incidence
The incidence in the general population is roughly 0.5%, and clinical symptoms typically appear between 20 to 30 years of age. Once thought to be strictly congenital, these vascular lesions have been found to occur de novo. It may appear either sporadically or exhibit autosomal dominant inheritance.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Clinical symptoms of CNS origin include recurrent headaches, focal neurological deficits, hemorrhagic stroke, and seizures, but CCM can also be asymptomatic. The nature and severity of the symptoms depend on the lesion's location.
Diagnosis is generally made by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), particularly using a specific imaging technique known as a gradient-echo sequence MRI, which can unmask small or punctate lesions that may otherwise remain undetected. These lesions are also more conspicuous on FLAIR imaging compared to standard T2 weighing. FLAIR imaging is different from Gradient sequences, rather, it is similar to T2 weighing but suppresses free-flowing fluid signal. Sometimes quiescent CCMs can be revealed as incidental findings during MRI exams ordered for other reasons. Many cavernous hemangiomas are detected "accidentally" during MRIs searching for other pathologies. These "incedentalomas" are generally asymptomatic. In the case of hemorrhage, however, a CT scan is more efficient at showing new blood than an MRI, and when brain hemorrhage is suspected, a CT scan may be ordered first, followed by an MRI to confirm the type of lesion that has bled.
Sometimes the lesion appearance imaged by MRI remains inconclusive. Consequently neurosurgeons will order a cerebral angiogram or magnetic resonance angiogram (MRA). Since CCMs are low flow lesions (they are hooked into the venous side of the circulatory system), they will be angiographically occult (invisible). If a lesion is discernible via angiogram in the same location as in the MRI, then an arteriovenous malformation (AVM) becomes the primary concern.
CCMs & venous angiomas
In up to 30% there is a coincidence of CCM with a venous angioma, also known as a developmental venous anomaly (DVA). These lesions appear either as enhancing linear blood vessels or caput medusae, a radial orientation of small vessels that resemble the hair of Medusa from Greek mythology. These lesions are thought to represent developmental anomalies of normal venous drainage. These lesions should not be removed, as venous infarcts have been reported. When found in association with a CCM that needs resection, great care should be taken not to disrupt the angioma.
Familial forms
Familial forms of CCM occur at four known genetic loci. The gene for CCM1 encodes KRIT1 (krev interaction trapped 1) and has been found to bind to ICAP1alpha (integrin cytoplasmic domain associated protein alpha), a beta1 integrin associated protein. The gene for CCM2 encodes a novel protein named malcavernin that contains a phosphotyrosine (PTB) binding domain. The exact biological function of CCM2 is not clear. Recently, it has been shown that CCM1 and CCM2 proteins as well as ICAP1alpha form a macromolecular complex in the cell. In addition, it appears that CCM2 protein may function as a scaffolding protein for MAP kinases that are essential in p38 activation responding to osmotic stress including MEKK3 and MKK3. It also binds to Rac and actin. Therefore, CCM2 protein is also called OSM (osmosensing scaffold for MEKK3). The CCM3 gene is the most recently identified CCM gene . CCM3 is known as PDCD10 (programmed cell death 10), which was initially identified as a gene that is up-regulated during the induction of apoptosis (cell death) in TF-1, a human myeloid cell line. The precise role of the PDCD10 protein in the CCM pathway is not clear. It is recently shown that PDCD10 forms a complex with CCM1 protein (KRIT1) and CCM2 protein (OSM). PDCD10 interacts directly with OSM independent of KRIT1-OSM interaction. Research is ongoing to determine the function and properties of all three CCM gene products as well as the reaction pathways in which they are involved. A fourth gene, CCM4, has been identified but not yet fully elucidated
Mutations in these genes account for 70 to 80 percent of all cases of cerebral cavernous malformations. The remaining 20 to 30 percent of cases may be due to other, still unidentified, genes.
References
External links
- Angioma Alliance, provides information and support for those affected
- Cavernoma Alliance UK - a charity created for and by people affected by cavernoma.
- International Cavernous Angioma Patient Registry
Malformation, Familial]
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=gene&part=ccm GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Cerebral Cavernous
- Atlas of Pathology
- Brain Blood Vessel Disorder Help Site
- Incidental Findings with Brain MRI
- Imaging MR and CT of Cavernous Malformations
Vascular tissue neoplasm (ICD-O 9120–9179) (C49+C46/D18, 171+176/215) Blood Hemangioma/hemangiosarcoma · Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome · Hemangioendothelioma (Infantile hemangioendothelioma · Endovascular papillary hemangioendothelioma · Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma · Spindle cell hemangioendothelioma · Composite hemangioendothelioma · Proliferating angioendotheliomatosis · Retiform hemangioendothelioma) · Hemangiopericytoma · Angiokeratoma · Capillary hemangioma (Hemangioblastoma) · Cavernous hemangioma · Venous lakeKaposi's sarcoma: African cutaneous Kaposi sarcoma · African lymphadenopathic Kaposi sarcoma · AIDS-associated Kaposi sarcoma · Classic Kaposi sarcoma · Immunosuppression-associated Kaposi sarcoma · Kaposiform hemangioendotheliomaAngioma serpiginosum · Cherry angioma · Glomeruloid hemangioma · Microvenular hemangioma · Spider angioma · Targetoid hemosiderotic hemangioma · Tufted angioma · Universal angiomatosis
Pyogenic granulomaLymphatic Lymphangioma/lymphangiosarcoma · PEComa (Lymphangioleiomyomatosis) · Cystic hygroma · Lymphangioma circumscriptumEither Tumors: digestive system neoplasia (C15–C26/D12–D13, 150–159/211) GI tract Upper GI tractGastric carcinoma · Signet ring cell carcinoma · Gastric lymphoma (MALT lymphoma) · Linitis plasticaUpper and/or lowerAccessory exocrine pancreas: Adenocarcinoma · Pancreatic ductal carcinoma
cystic neoplasms: Serous microcystic adenoma · Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm · Mucinous cystic neoplasm · Solid pseudopapillary neoplasm
PancreatoblastomaPeritoneum Nervous tissue tumors/NS neoplasm/Neuroectodermal tumor (ICD-O 9350–9589) (C70–C72, D32–D33, 191–192/225) Endocrine/
sellar (9350–9379)other: PinealomaCNS
(9380–9539)Astrocytoma (Pilocytic astrocytoma, Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, Fibrillary (also diffuse or lowgrade) astrocytomas, Anaplastic astrocytoma, Glioblastoma multiforme)Ependymoma · SubependymomaMultiple/unknownMature
neuronNeuroblastoma (Esthesioneuroblastoma, Ganglioneuroblastoma) · Medulloblastoma · Atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumorPrimitiveMeningiomas
(meninges)HematopoieticPNS: NST
(9540–9579)cranial and paraspinal nerves: Neurofibroma (Neurofibrosarcoma, Neurofibromatosis) · Neurilemmoma/Schwannoma (Acoustic neuroma) · Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumornote: not all brain tumors are of nervous tissue, and not all nervous tissue tumors are in the brain (see brain metastases)
Categories:- Neurological disorders
- Genetic disorders with no OMIM
- Benign neoplasms
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.