- NASA World Wind
-
NASA World Wind 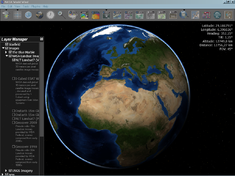
Screenshot of World Wind showing Blue Marble Next Generation layerDeveloper(s) NASA Ames Research Center Initial release 2004 Stable release 1.2.0 / July 18, 2011 Written in C#, Java Operating system Cross platform Available in English Type Virtual globe License NASA Open Source Agreement v1.3 Website www.goworldwind.org  Rapid Fire MODIS - Hurricane Katrina
Rapid Fire MODIS - Hurricane Katrina
 Mars (THEMIS layer) - Olympus Mons
Mars (THEMIS layer) - Olympus Mons
 Hurricane Dean in NASA World Wind
Hurricane Dean in NASA World Wind
World Wind is an open-source (released under the NOSA license) virtual globe developed by NASA and the open source community for use on personal computers. Old versions need Microsoft Windows but the more recent Java version, World Wind Java, is cross platform and provides a suite of demo apps. The World Wind Java version was awarded NASA Software of the Year in November 2009. The program overlays NASA and USGS satellite imagery, aerial photography, topographic maps, Keyhole Markup Language (KML) and Collada files.
Contents
Overview
World Wind was released as open source in 2004 by NASA. The latest version (1.4), developed mainly by open source community members from World Wind Central/Free Earth Foundation, had its premiere on February 14, 2007.
Apart from the Earth there are several worlds in World Wind: Moon, Mars, Venus, Jupiter (with the four Galilean moons of Io, Ganymede, Europa and Callisto) and SDSS (imagery of stars and galactics). All these worlds are available in the File menu.
Users can interact with the selected planet by rotating it, tilting the view, and zooming in and out. Five million place names, political boundaries, latitude/longitude lines, and other data can be displayed. World Wind provides the ability to browse maps and geospatial data on the internet using the OGC's WMS servers (version 1.4 also uses WFS for downloading placenames), import ESRI shapefiles and kml/kmz files. This is an example of how World Wind allows anyone to deliver their data.
Other features of World Wind include support for .X (DirectX 3D polygon mesh) models and advanced visual effects such as atmospheric scattering or sun shading.
The resolution inside the US is high enough to clearly discern individual buildings, houses, cars (USGS Digital Ortho layer) and even the shadows of people (metropolitan areas in USGS Urban Ortho layer). The resolution outside the US is at least 15 meters per pixel.
Microsoft has allowed World Wind to incorporate Virtual Earth high resolution data for non-commercial use.[1]
World Wind uses digital elevation model (DEM) data collected by NASA's Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM), National Elevation Dataset (NED) and Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER). This means one can view topographic features such as the Grand Canyon or Mount Everest in three dimensions. In addition, WW has bathymetry data which allows users to see ocean features, such as trenches and ridges, in 3D.
Many people using the applications are adding their own data and making them available through various sources, such as the World Wind Central or blogs mentioned in the link section below.
All images and movies created with World Wind using Blue Marble, Landsat, or USGS public domain data can be freely modified, re-distributed, and used on web sites, even for commercial purposes.
Add-ons and plugins
World Wind can be expanded by using one of many add-ons - small extensions that add new functionality to the program.
Possible types of add-ons:- Point layers - simple XML files displaying placemarks (point of interest) as icons
- Trail layers - paths (routes, boundaries)
- Line features - XML with a list of points visualized as a line or wall
- Polygon features - XML with a list of points visualized as a filled polygon (flat or extruded)
- Model features - XML used to load 3D textured meshes
- Place names - specific points (such as cities, hills and buildings) that are assigned text labels
- Image layers - high resolution imagery for various places in the world
- Scripts - files that control camera movement
Plugins are small programs written in C#, VB or J# which are loaded and compiled by World Wind at startup. Plug-in developers can add features to World Wind without changing the program's source code.
World Wind Java
The original recipe for World Wind was restricted to Windows, relying on the .NET libraries and DirectX. A new SDK version of World Wind has been developed in Java with JOGL referred to as World Wind Java. This new version has an API-centric architecture with functionalities 'off-loaded' to modular components, leaving the API at the core. This makes World Wind itself a plugin so that it can be used as interchangeably as possible (i.e. via Python). This refactoring exercise allows World Wind to be accessed via a browser as a Java Applet. A preview of the World Wind Java SDK[2] was released on May 11, 2007 during Sun Microsystem's annual JavaOne conference.
Since WWj is an SDK there is no single application, instead there are any number of apps using WWj, each with different functionalities, created by government agencies and commercial developers from around the world. These applications include simple virtual globe viewers, satellite tracker, GIS platforms, photo editor, F-16 simulator, mission planning software and many more. The (incomplete) list can be found here and here.
Forks and clones
- Dapple is a fork of the NASA World Wind project, it is an Open Source project created by developers at Geosoft. Dapple is aimed at geoscience professionals, and has features aimed at them, such as easy addition of WMS servers and a simpler UI very similar to Google Earth's.
- SERVIR-VIZ is a customized version of World Wind developed by IAGT for the SERVIR project.
- WW2D was a cross-platform, free and open-source application based on Java and OpenGL technologies and can be run on Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, Linux (x86 and x86-64) and Solaris on SPARC. WW2D uses images from World Wind's servers.
- WW2D Plus One - an update to WW2D providing a 3D view.
- Punt was a fork of the NASA World Wind project, and was started by two members of the free software community who had made contributions to World Wind. Punt was based on the code in World Wind 1.3.2, but its initial release has features not found in World Wind 1.3.2 or 1.3.3 (such as support for multiple languages). Currently, Punt is only available for Windows, but long term goals include a desire to move to a cross-platform solution.
Datasets available
Low resolution Blue Marble datasets are included with the initial download; as a user zooms in to certain areas, additional high resolution data is downloaded from the NASA servers. The size of all currently available data sets is about 4.6 terabytes.
Earth
- Animated data layers
- Image/terrain datasets
- Blue Marble Next Generation imagery
- Landsat 7 imagery
- USGS imagery
- Digital Ortho (DOQ - scanned black and white aerial images [1])
- Urban Area Ortho (montaged color aerial photography of many major US metropolitan areas)
- Topographic maps
- Zoomit! imagery (community produced layer)
- SRTM (SRTM30Plus[6]/SRTMv2/USGS NED) terrain data (includes bathymetry)
Extraterrestrial datasets
Moon
- Clementine (40xx - Colour, 30xx - Greyscale)
- Hypsometric Map
Mars
- MOC (Mars Global Surveyor - Mars Orbiter Camera)
- MOLA (MGS - Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter hypsometric map)
- THEMIS (Mars Odyssey - Thermal Emission Imaging System)
- MDIM (Viking - Mars Digital Image Model)
Venus
- Magellan Imaging Radar (Color/Greyscale)
- Hypsometric Map
Jupiter
- Jupiter
- Callisto
- Europa
- Ganymede
- Io
Sloan Digital Sky Survey
- Survey Imagery
- SDSS Server
- WMAP Image Server
- Footprint Imagery
- SDSS Footprint
- FIRST (Faint Images of the Radio Sky at Twenty-cm [2]) Footprint
Specifications
- Baseline resolutions
- 500 m (Blue Marble Next Generation)
- 15 m (Landsat imagery; except for polar areas)
- Typical high resolutions
- U.S.
- New Zealand
- Zoomit! (from LINZ data): 2.5 m (colour and grayscale)
- Western Australia
- Zoomit! (from GSWA): 250K surface geology mosaic, 250K topographic data, Magnetic Intensity, Bouger Gravity
- South Africa
- Zoomit!: Spot5 10m[9] (colour near full coverage), Robben Island 0.5 m, Johannesburg 2.5 m
- Altitude resolution
- U.S.: 30 m (1 arcsecond; USGS NED)
- Global: 90 m (3 arcseconds; SRTM)
- Oceans: 2 arcminutes and better
- Age
- Some USGS aerial images were taken in the early 1990s.
- Landsat 7 images are all taken after 1999 (except for Geocover 1990).
See also
- Celestia
- GeoServer
- Geoweb
- Bhuvan
- Google Earth
- Google Maps
- Marble (KDE)
- Starry Night
- Stellarium
- TerraServer-USA
- Universe Sandbox
- Virtual Earth
- Web mapping
- Bing Maps
References
- ^ Virtual Earth plugin: http://www.worldwindcentral.com/wiki/Virtual_Earth
- ^ World Wind Java SDK: http://goworldwind.org/demos/
- ^ GLOBE - World Wind Wiki
- ^ Land Information New Zealand's internet home page
- ^ Department of Industry and Resources - Geological Survey of Western Australia
- ^ Satellite Geodesy, IGPP, SIO, UCSD | Global Topography | SRTM30, Multibeam, & predicted
- ^ List of covered cities: http://www.worldwindcentral.com/wiki/USGS_Urban_Areas
- ^ ZoomIt! - Areas and dates: http://www.worldwindcentral.com/wiki/Add-on:ZoomIt%21
- ^ http://www.madmappers.com/htm/za_spot5.html
External links
- Official website
- Official website
- NASA World Wind Java (current)
- NASA World Wind.NET (legacy) at SourceForge
Community
- World Wind Central
- World Wind Forums
- The Earth Is Square source of news about WW from one of the developers
- Bull's Rambles open source community project manager's blog
- World Wind add-ons
Miscellaneous
Earth-related topics History Geography
and geologyEcology - Earth Day
- Gaia philosophy
- Global warming
- Human impact on the environment
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment
Imaging - Bhuvan
- Bing Maps
- Google Earth
- Google Maps
- NASA World Wind
- OpenStreetMap
- Ovi Maps
- Remote sensing
- WikiMapia
- Yahoo! Maps
Arts, culture
and society- Earth in culture
- Earth in fiction
- Etymology of the word "Earth"
- Flat Earth and Hollow Earth
- History of the world
- International law
- Landscape art
- List of countries
- World economy
Spirituality
and teleology- Creation myth
- Creationism
- Earth Mother
- Gaia (Ancient Greece)
- New Age Gaian
- Planetary Logos (Theosophy)
- Tellus Mater (Ancient Rome)
- Earth sciences portal
- Solar System portal
Categories:- Virtual globes
- Keyhole Markup Language
- NASA online
- Windows software
- Earth sciences graphics software
- Free software programmed in Java
- Science education software
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.






