- Hernia
-
Hernia Classification and external resources
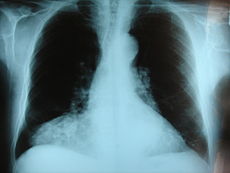
Frontal chest X-ray showing a hernia of MorgagniICD-10 K40-K46 ICD-9 550-553 MedlinePlus 000960 eMedicine emerg/251 ped/2559 MeSH D006547 A hernia is the protrusion[1] of an organ or the fascia of an organ through the wall of the cavity that normally contains it. A hiatal hernia occurs when the stomach protrudes into the mediastinum through the esophageal opening in the diaphragm.
By far the most common herniae develop in the abdomen, when a weakness in the abdominal wall evolves into a localized hole, or "defect", through which adipose tissue, or abdominal organs covered with peritoneum, may protrude. Another common hernia involves the spinal discs and causes sciatica.
Herniae may or may not present either with pain at the site, a visible or palpable lump, or in some cases by more vague symptoms resulting from pressure on an organ which has become "stuck" in the hernia, sometimes leading to organ dysfunction. Fatty tissue usually enters a hernia first, but it may be followed by or accompanied by an organ.
Most of the time, herniae develop when pressure in the compartment of the residing organ is increased, and the boundary is weak or weakened.
- Weakening of containing membranes or muscles is usually congenital (which explains part of the tendency of herniae to run in families), and increases with age (for example, degeneration of the annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc), but it may be on the basis of other illnesses, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome or Marfan syndrome, stretching of muscles during pregnancy, losing weight in obese people, etc., or because of scars from previous surgery.
- Many conditions chronically increase intra-abdominal pressure, (pregnancy, ascites, COPD, dyschezia, benign prostatic hypertrophy) and hence abdominal hernias are very frequent. Increased intracranial pressure can cause parts of the brain to herniate through narrowed portions of the cranial cavity or through the foramen magnum. Increased pressure on the intervertebral discs, as produced by heavy lifting or lifting with improper technique, increases the risk of herniation.
Contents
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms may not be present in some inguinal hernias while in some other hernias, including inguinal, they are. Symptoms and signs vary depending on the type of hernia. In the case of reducible hernias, you can often see and feel a bulge in the groin or in another abdominal area. When standing, such bulge becomes more obvious. Besides the bulge, other symptoms include pain in the groin that may also include a heavy or dragging sensation, and in men, there is sometimes pain and swelling in the scrotum around the testicular area.[2]
Irreducible hernias or incarcerated hernias may be painful, but their most relevant symptom is that they cannot return to the abdominal cavity when pushed in. They may be chronic, although painless, and can lead to strangulation. Nausea, vomiting, or fever may occur in these cases due to bowel obstruction. Also, the hernia bulge in this case may turn red, purple or dark and pink.
Strangulated hernias are always painful and pain is followed by tenderness. Nausea and vomiting also may occur as well due to bowel obstruction. The patient may also experience fever.[3]
In the diagnosis of abdominal hernias, imaging is the principal means of detecting internal diaphragmatic and other nonpalpable or unsuspected hernias. Multidetector CT (MDCT) can show with precision the anatomic site of the hernia sac, the contents of the sac, and any complications. MDCT also offers clear detail of the abdominal wall allowing wall hernias to be identified accurately.[4]
Causes
Causes of hiatal hernia vary depending on each individual. Among the multiple causes, however, are the mechanical causes which include: improper heavy weight lifting, hard coughing bouts, sharp blows to the abdomen, tight clothing and incorrect posture.[5]
Furthermore, conditions that increase the pressure of the abdominal cavity may also cause hernias or worsen the existing ones. Some examples would be: obesity, straining during a bowel movement or urination, chronic lung disease, and also, fluid in the abdominal cavity.[6]
Also, if muscles are weakened due to poor nutrition, smoking, and overexertion, hernias are more likely to occur.
The physiological school of thought contends that the above mentioned are not the true causes of hernia, but are instead an (anatomical) symptom of the true (physiological) cause. Based on hundreds of observations during dissection, they have concluded that the risk of hernia is due to a physiological difference between patients who suffer hernia and those who do not, namely the presence of aponeurotic extensions from the transversus abdominis aponurotic arch. [7]
When a hernia is not repaired, it may become incarcerated or strangulated. When strangulation occurs, there is a danger that part of the intestine be caught in the hernia cutting off blood supply to the tissue. Also, when a bowel obstruction occurs, it leads to severe pain, vomiting, nausea and inability to have a bowel movement or pass gas. Men are more prone to suffer inguinal hernias than women, and they risk a damage to their testicles if a hernia becomes strangulated.[8] Also, the pressure caused on the hernia's surrounding tissues may extend into the scrotum causing pain and swelling.
Diagnosis
A sportman's hernia is a syndrome characterized by chronic groin pain in athletes and a dilated superficial ring of the inguinal canal, although a true hernia is not present.
Inguinal
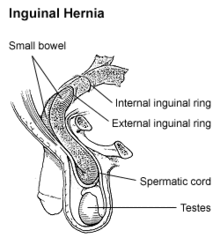
By far the most common hernias (up to 75% of all abdominal hernias) are the so-called inguinal hernias. Inguinal hernias are further divided into the more common indirect inguinal hernia (2/3, depicted here), in which the inguinal canal is entered via a congenital weakness at its entrance (the internal inguinal ring), and the direct inguinal hernia type (1/3), where the hernia contents push through a weak spot in the back wall of the inguinal canal. Inguinal hernias are the most common type of hernia in both men and women. Femoral hernias occur more often in women than men, but women still get more inguinal hernias than femoral hernias.
Femoral
Femoral hernias occur just below the inguinal ligament, when abdominal contents pass into the weak area at the posterior wall of the femoral canal. They can be hard to distinguish from the inguinal type (especially when ascending cephalad): however, they generally appear more rounded, and, in contrast to inguinal hernias, there is a strong female preponderance in femoral hernias. The incidence of strangulation in femoral hernias is high. Repair techniques are similar for femoral and inguinal hernia.
Umbilical
They involve protrusion of intraabdominal contents through a weakness at the site of passage of the umbilical cord through the abdominal wall. These hernias often resolve spontaneously. Umbilical hernias in adults are largely acquired, and are more frequent in obese or pregnant women. Abnormal decussation of fibers at the linea alba may contribute.
Incisional
An incisional hernia occurs when the defect is the result of an incompletely healed surgical wound. When these occur in median laparotomy incisions in the linea alba, they are termed ventral hernias. These can be the most frustrating and difficult to treat, as the repair utilizes already attenuated tissue.
Diaphragmatic

Higher in the abdomen, an (internal) "diaphragmatic hernia" results when part of the stomach or intestine protrudes into the chest cavity through a defect in the diaphragm.
A hiatus hernia is a particular variant of this type, in which the normal passageway through which the esophagus meets the stomach (esophageal hiatus) serves as a functional "defect", allowing part of the stomach to (periodically) "herniate" into the chest. Hiatus hernias may be either "sliding," in which the gastroesophageal junction itself slides through the defect into the chest, or non-sliding (also known as para-esophageal), in which case the junction remains fixed while another portion of the stomach moves up through the defect. Non-sliding or para-esophageal hernias can be dangerous as they may allow the stomach to rotate and obstruct. Repair is usually advised.
A congenital diaphragmatic hernia is a distinct problem, occurring in up to 1 in 2000 births, and requiring pediatric surgery. Intestinal organs may herniate through several parts of the diaphragm, posterolateral (in Bochdalek's triangle, resulting in Bochdalek's hernia), or anteromedial-retrosternal (in the cleft of Larrey/Morgagni's foramen, resulting in Morgagni-Larrey hernia, or Morgagni's hernia).
Other hernias
Since many organs or parts of organs can herniate through many orifices, it is very difficult to give an exhaustive list of hernias, with all synonyms and eponyms. The above article deals mostly with "visceral hernias", where the herniating tissue arises within the abdominal cavity. Other hernia types and unusual types of visceral hernias are listed below, in alphabetical order:
- Cooper's hernia: a femoral hernia with two sacs, the first being in the femoral canal, and the second passing through a defect in the superficial fascia and appearing almost immediately beneath the skin.
- Epigastric hernia: a hernia through the linea alba above the umbilicus.
- Hiatal hernia: a hernia due to "short oesophagus" - insufficient elongation - stomach is displaced into the thorax
- Littre's hernia: a hernia involving a Meckel's diverticulum. It is named after the French anatomist Alexis Littre (1658–1726).
- Lumbar hernia (Bleichner's Hernia): a hernia in the lumbar region (not to be confused with a lumbar disc hernia), contains the following entities:
- Petit's hernia: a hernia through Petit's triangle (inferior lumbar triangle). It is named after French surgeon Jean Louis Petit (1674–1750).
- Grynfeltt's hernia: a hernia through Grynfeltt-Lesshaft triangle (superior lumbar triangle). It is named after physician Joseph Grynfeltt (1840–1913).
- Maydl's hernia: two adjacent loops of small intestine are within a hernial sac with a tight neck. The intervening portion of bowel within the abdomen is deprived of its blood supply and eventually becomes necrotic.
- Obturator hernia: hernia through obturator canal
- Pantaloon hernia/ Saddle Bag hernia: a combined direct and indirect hernia, when the hernial sac protrudes on either side of the inferior epigastric vessels
- Paraesophageal hernia
- Paraumbilical hernia: a type of umbilical hernia occurring in adults
- Perineal hernia: a perineal hernia protrudes through the muscles and fascia of the perineal floor. It may be primary but usually is acquired following perineal prostatectomy, abdominoperineal resection of the rectum, or pelvic exenteration.
- Properitoneal hernia: rare hernia located directly above the peritoneum, for example, when part of an inguinal hernia projects from the deep inguinal ring to the preperitoneal space.
- Richter's hernia: a hernia involving only one sidewall of the bowel, which can result in bowel strangulation leading to perforation through ischaemia without causing bowel obstruction or any of its warning signs. It is named after German surgeon August Gottlieb Richter (1742–1812).
- Sliding hernia: occurs when an organ drags along part of the peritoneum, or, in other words, the organ is part of the hernia sac. The colon and the urinary bladder are often involved. The term also frequently refers to sliding hernias of the stomach.
- Sciatic hernia: this hernia in the greater sciatic foramen most commonly presents as an uncomfortable mass in the gluteal area. Bowel obstruction may also occur. This type of hernia is only a rare cause of sciatic neuralgia.
- Spigelian hernia, also known as spontaneous lateral ventral hernia
- Sports hernia: a hernia characterized by chronic groin pain in athletes and a dilated superficial ring of the inguinal canal.
- Velpeau hernia: a hernia in the groin in front of the femoral blood vessels
- Amyand's Hernia: containing the appendix vermiformis within the hernia sac
- Busse's Hernia: a testicle within the hernia sac
Characteristics
Hernias can be classified according to their anatomical location:
Examples include:
- abdominal hernias
- diaphragmatic hernias and hiatal hernias (for example, paraesophageal hernia of the stomach)
- pelvic hernias, for example, obturator hernia
- anal hernias
- hernias of the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral discs
- intracranial hernias
- Spigelian hernia [9]
Each of the above hernias may be characterized by several aspects:
- congenital or acquired: congenital hernias occur prenatally or in the first year(s) of life, and are caused by a congenital defect, whereas acquired hernias develop later on in life. However, this may be on the basis of a locus minoris resistantiae (Lat. place of least resistance) that is congenital, but only becomes symptomatic later in life, when degeneration and increased stress (for example, increased abdominal pressure from coughing in COPD) provoke the hernia.
- complete or incomplete: for example, the stomach may partially or completely herniate into the chest.
- internal or external: external ones herniate to the outside world, whereas internal hernias protrude from their normal compartment to another (for example, mesenteric hernias).
- intraparietal hernia: hernia that does not reach all the way to the subcutis, but only to the musculoaponeurotic layer. An example is a Spigelian hernia. Intraparietal hernias may produce less obvious bulging, and may be less easily detected on clinical examination.
- bilateral: in this case, simultaneous repair may be considered, sometimes even with a giant prosthetic reinforcement.
- irreducible (also known as incarcerated): the hernial contents cannot be returned to their normal site with simple manipulation.
If irreducible, hernias can develop several complications (hence, they can be complicated or uncomplicated):
- strangulation: pressure on the hernial contents may compromise blood supply (especially veins, with their low pressure, are sensitive, and venous congestion often results) and cause ischemia, and later necrosis and gangrene, which may become fatal.
- obstruction: for example, when a part of the bowel herniates, bowel contents can no longer pass the obstruction. This results in cramps, and later on vomiting, ileus, absence of flatus and absence of defecation.
- dysfunction: another complication arises when the herniated organ itself, or surrounding organs, start to malfunction (for example, sliding hernia of the stomach causing heartburn, lumbar disc hernia causing sciatic nerve pain, etc.).
Treatment
Main article: Hernia repairIt is generally advisable to repair hernias quickly in order to prevent complications such as organ dysfunction, gangrene and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Most abdominal hernias can be surgically repaired, and recovery rarely requires long-term changes in lifestyle. Time needed for recovery after treatment is greatly reduced if hernias are operated on laparoscopically, the minimally invasive operation most commonly used today.[10] Uncomplicated hernias are principally repaired by pushing back, or "reducing", the herniated tissue, and then mending the weakness in muscle tissue (an operation called herniorrhaphy). If complications have occurred, the surgeon will check the viability of the herniated organ, and resect it if necessary.
Modern muscle reinforcement techniques involve synthetic materials (a mesh prosthesis) that avoid over-stretching of already weakened tissue (as in older, but still useful methods). The mesh is placed either over the defect (anterior repair) or more preferably under the defect (posterior repair). At times staples are used to keep the mesh in place. These mesh repair methods are often called "Tension Free" repairs because, unlike older traditional methods, muscle is not pulled together under tension.
Evidence-based testing initially suggested that these Tension Free methods have the lowest percentage of recurrences and the fastest recovery period compared to older suture repair methods. However, prosthetic mesh usage seems to have a high incidence of infection with mesh usage becoming a study topic for the National Institutes of Health.[11]
One study attempted to identify the factors related to mesh infections and found that compromised immune systems (such as diabetes) was a factor.[12] Mesh has also become the subject of recalls and class action lawsuits.[13]
Laparoscopic surgery is also referred to as "minimally invasive" surgery, which requires one or more small incisions for the camera and instruments to be inserted, as opposed to traditional "open" or "microscopic" surgery, which requires an incision large enough for the surgeon's hands to be inserted into the patient. The term microscopic surgery refers to the magnifying devices used during open surgery.
Many patients are managed through day surgery centers, and are able to return to work within a week or two, while intensive activities are prohibited for a longer period. Patients who have their hernias repaired with mesh often recover in a number of days. Surgical complications have been estimated to be up to 10 percent, but most of them can be easily addressed. They include surgical site infections, nerve and blood vessel injuries, injury to nearby organs, and hernia recurrence.
Generally, the use of external devices to maintain reduction of the hernia without repairing the underlying defect (such as hernia trusses, trunks, belts, etc.), is not advised. Exceptions are uncomplicated incisional hernias that arise shortly after the operation (should only be operated after a few months), or inoperable patients.
It is essential that the hernia not be further irritated by carrying out strenuous labour
Complications
Complications may arise post-operation, including rejection of the mesh that is used to repair the hernia. In the event of a mesh rejection, the mesh will very likely need to be removed. Mesh rejection can be detected by obvious, sometimes localised swelling and pain around the mesh area. Continuous discharge from the scar is likely for a while after the mesh has been removed.
An untreated hernia may be complicated by:
- Inflammation
- Irreducibility
- Obstruction of any lumen, such as bowel obstruction in intestinal hernias
- Strangulation
- Hydrocele of the hernial sac
- Haemorrhage
- Autoimmune problems
- Incarceration, which is where it cannot be reduced, or pushed back into place,[14] at least not without very much external effort.[15] In intestinal hernias, this also substantially increases the risk of bowel obstruction and strangulation.
References
- ^ "hernia" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ "Symptoms". http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/inguinal-hernia/DS00364/DSECTION=symptoms.
- ^ "Hernia Symptoms and Signs". http://www.emedicinehealth.com/hernia/page4_em.htm. Retrieved 2010-05-24.
- ^ Lee HK, Park SJ, Yi BH. Multidetector CT reveals diverse variety of abdominal hernias. Diagnostic Imaging. 2010;32(5):27-31.
- ^ "Hiatal Hernia Symptoms, Causes And Relation To Acid Reflux And Heartburn". http://inguinalhernia.us/hiatal-hernia-causes.html. Retrieved 2010-05-24.[dead link]
- ^ "Hernia Causes". http://www.emedicinehealth.com/hernia/page2_em.htm. Retrieved 2010-05-24.
- ^ "Desarda MP. Surgical physiology of inguinal hernia repair. BMC Surgery 2003, 3:2". 2002-11-16. http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2482/3/2/.
- ^ "Risk Factors". http://www.herniainfo.com/herniainfo/content/what_hernia.aspx. Retrieved 2010-05-24.
- ^ 9. Bittner JG, Edwards MA, Shah MB, MacFadyen BV, Mellinger JD. Mesh-free laparoscopic Spigelian hernia repair. Am Surg 2008; 74(8):713-720.
- ^ "Hernia Surgery". Hernia Symptoms. http://herniasymptoms.blogsavy.com/hernia-surgery/. Retrieved 11 October 2011.
- ^ http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=427896
- ^ http://www.uptodate.com/patients/content/topic.do?topicKey=~AewAWy90g.DiQX
- ^ http://www.usdrugrecall.com/category/kugel-hernia-patch-recall
- ^ Trudie A Goers; Washington University School of Medicine Department of Surgery; Klingensmith, Mary E; Li Ern Chen; Sean C Glasgow (2008). The Washington manual of surgery. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-7447-0.
- ^ onlinedictionary.datasegment.com > incarcerated Citing: Webster 1913
External links
- Hernia Resources
- The Hernia Blog
- Hernia Symptoms
- Sports Hernia: Common Misdiagnosis
- Hernia:The World Journal of Hernia and Abdominal Wall Surgery
Pictures
Congenital diaphragm and abdominal wall defects, abdominopelvic cavity (Q79.0–Q79.5, 756.6–756.7) Thoracic diaphragm Abdominal wall Categories:- Diseases involving the fasciae
- Congenital disorders of musculoskeletal system
- Hernias
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.