- Laparotomy
-
Laparotomy Intervention 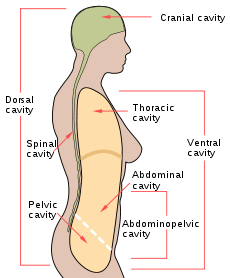
Abdominal cavityICD-9-CM 54.1 MeSH D007813 A laparotomy is a surgical procedure involving a large incision through the abdominal wall to gain access into the abdominal cavity. It is also known as coeliotomy.
Contents
Terminology
In diagnostic laparotomy (most often referred to as an exploratory laparotomy and abbreviated Ex-Lap), the nature of the disease is unknown, and laparotomy is deemed the best way to identify the cause.
In therapeutic laparotomy, a cause has been identified (e.g. peptic ulcer, colon cancer) and laparotomy is required for its therapy.
Usually, only exploratory laparotomy is considered a stand-alone surgical operation. When a specific operation is already planned, laparotomy is considered merely the first step of the procedure.
Spaces accessed
Depending on incision placement, laparotomy may give access to any abdominal organ or space, and is the first step in any major diagnostic or therapeutic surgical procedure of these organs, which include:
- the lower part of the digestive tract (the stomach, duodenum, jejunum, ileum and colon)
- the liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and spleen
- the bladder
- the female reproductive organs (the uterus and ovaries)
- the retroperitoneum (the kidneys, the aorta, abdominal lymph nodes)
- the appendix
Types of incisions
Main article: Surgical IncisionsMidline
The most common incision for laparotomy is the midline incision, a vertical incision which follows the linea alba.
- The upper midline incision usually extends from the xiphoid process to the umbilicus.
- A typical lower midline incision is limited by the umbilicus superiorly and by the pubic symphysis inferiorly.
- Sometimes a single incision extending from xiphoid process to pubic symphysis is employed, especially in trauma surgery.
Midline incisions are particularly favoured in diagnostic laparotomy, as they allow wide access to most of the abdominal cavity.
Other
Other common laparotomy incisions include:
- the Kocher (right subcostal) incision (after Emil Theodor Kocher); appropriate for certain operations on the liver, gallbladder and biliary tract.[1][2] This shares a name with the Kocher incision used for thyroid surgery: a transverse, slightly curved incision about 2 cm above the sternoclavicular joints;
- the Davis or Rockey-Davis "muscle-splitting" right lower quadrant incision for appendectomy;
- the Pfannenstiel incision, a transverse incision below the umbilicus and just above the pubic symphysis.[3][4] In the classic Pfannenstiel incision, the skin and subcutaneous tissue are incised transversally, but the linea alba is opened vertically. It is the incision of choice for Cesarean section and for abdominal hysterectomy for benign disease. A variation of this incision is the Maylard incision in which the rectus abdominis muscles are sectioned transversally to permit wider access to the pelvis.[5]
- Lumbotomy consists of a lumbar incision which permits access to the kidneys (which are retroperitoneal) without entering the peritoneal cavity. It is typically used only for benign renal lesions. It has also been proposed for surgery of the upper urological tract.[6]
- Cherney Incision
Related procedures
A related procedure is laparoscopy, where cameras and other instruments are inserted into the peritoneal cavity via small holes in the abdomen. For example, an appendectomy can be done either by a laparotomy or by a laparoscopic approach.
References
- ^ synd/1010 at Who Named It?
- ^ "Incisions". Archived from the original on 2007-11-01. http://web.archive.org/web/20071101054358/http://www.pdh-odp.co.uk/incisions.htm. Retrieved 2007-11-22.
- ^ synd/2500 at Who Named It?
- ^ H. J. Pfannenstiel. Ueber die Vortheile des suprasymphysären Fascienquerschnitts für die gynäkologischen Koeliotomien. (Volkmann’s) Sammlung klinischer Vorträge, Leipzig, 1900, n F. 268 (Gynäk. Nr. 97), 1735-1756.
- ^ Giacalone PL, Daures JP, Vignal J, Herisson C, Hedon B, Laffargue F (2002). "Pfannenstiel versus Maylard incision for cesarean delivery: A randomized controlled trial". Obstetrics and gynecology 99 (5 Pt 1): 745–50. doi:10.1016/S0029-7844(02)01957-9. PMID 11978282.
- ^ Bajpai M, Kumar A, Gupta AK, Pawar DK (2004). "Lumbotomy approach for upper urological tract surgery in children--an analysis of 68 consecutive lumbotomies". European Journal of Pediatric Surgery 14 (3): 163–7. doi:10.1055/s-2004-820903. PMID 15211405.
External links
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
