- Esophageal motility study
-
Esophageal motility study Intervention 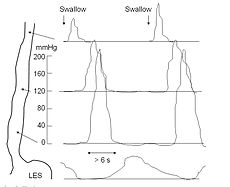
Diagram of esophageal motility study in nutcracker esophagus. The disorder shows peristalsis with high pressure esophageal contractions exceeding 180 mmHg and contractile waves with a long duration exceeding 6 seconds.ICD-9-CM 89.32 OPS-301 code: 1-313 An esophageal motility study (EMS) or esophageal manometry is a test to assess motor function of the Upper Esophageal Sphincter (UES), Esophageal body and Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES).
Contents
Indications
An EMS is typically done to evaluate suspected disorders of motility or peristalsis of the esophagus. These include achalasia, diffuse esophageal spasm, nutcracker esophagus and hypertensive lower esophageal sphincter. These disorders typically present with dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, usually to both solids and liquids even initially. Other patients with spasm disorders may have the test done to diagnose chest pain thought not to be of cardiac cause. The test is not useful for anatomical disorders of the esophagus (that is, disorders that distort the anatomy of the esophagus), such as peptic strictures and esophageal cancer.
Procedure
A technician places a catheter into the nose and guides it into the stomach. Once placed, the catheter is slowly withdrawn, allowing it to detect pressure changes and to record information for later review. The patient will be asked at various times to take a deep breath or to take some swallows of water. The degree of discomfort varies among patients. Patients are not sedated because sedatives would alter the functioning of the esophageal muscles. Overall the procedure takes about 45 minutes. After the procedure is complete, patients can usually resume their normal daily activities.
Recent advances in esophageal motility testing
Recently, high resolution manometry (HRM) has been developed that significantly reduces the procedure time (10 minutes vs. 45 mins with conventional manometry) and provides enhanced patient comfort. Newer catheters also incorporate concurrent impedance with HRM.
External links
http://www.hrmconsensus.org/files/Pandolfino%20Fox_NGM09_HRM%20Consensus.pdf High Resolution Oesophageal Manometry systmems
Categories:- Medicine stubs
- Medical tests
- Diagnostic gastroenterology
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
