- Cholescintigraphy
-
Cholescintigraphy Intervention 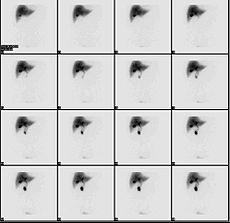
Normal hepatobiliary scan (HIDA scan). The nuclear medicine hepatobiliary scan is clinically useful in the detection of the gallbladder disease.ICD-9-CM 92.02 OPS-301 code: 3-707.6 A cholescintigraphy or Hepatobiliary Imino-Diacetic Acid scan, (HIDA scan) is a nuclear imaging procedure to evaluate the health and function of the gallbladder. A radioactive tracer, usually technetium-99m, is injected through any accessible vein, then allowed to circulate to the liver, where it is excreted into the biliary system and stored by the gallbladder and biliary system.[1]
In the absence of disease, the gallbladder is visualized within 1 hour of the injection of the radioactive tracer. If the gallbladder is not visualized within 4 hours after the injection, this indicates either cholecystitis or cystic duct obstruction. This investigation is usually conducted after an ultrasound examination of the abdominal right upper quadrant for pain. If the non-invasive ultrasound examination fails to demonstrate gall stones (or other obstruction to the gall bladder or biliary tree) in an attempt to establish a cause of right upper quadrant pain, this HIDA scan can be performed as a more sensitive and specific test. HIDA scans are not generally done first line due to their increased cost and invasiveness.
Cholescintigraphy for acute cholecystitis has sensitivity of 97%, Specificity of 94%.[2][citation needed]
Imino-Diacetic Acid is rarely used currently, as better contrast materials have replaced it, but the term HIDA remains.
See also
- Iminodiacetic acid
References
- ^ Michael, Picco, M.D.. "HIDA scan (cholescintigraphy): Why is it performed?". Mayo Clinic. http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/hida-scan/AN00424. Retrieved 2007-12-11.
- ^ Harvey A. Ziessman. Nuclear Medicine Hepatobiliary Imaging. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. Volume 8, Issue 2, February 2010, Pages 111-116.
Medical testing : Medical imaging · Radiology · (ICD-9-CM V3 87-88, ICD-10-PCS B, CPT 70010-79999) X-ray/
medical radiography/
Industrial radiographyMedical: Pneumoencephalography · Dental radiography · Sialography · Myelography · CXR (Bronchography) · AXR / KUB · DXA/DXR · Upper gastrointestinal series/Small bowel follow-through/Lower gastrointestinal series · Cholangiography/Cholecystography · Mammography · Pyelogram · Cystography · Arthrogram · Hysterosalpingography · Skeletal survey · Angiography (Angiocardiography, Aortography) · Venography · Lymphogram
Industrial: Radiographic testingMedical: CT pulmonary angiogram · Cardiac CT · Abdominal and pelvic CT (Virtual colonoscopy) · CT angiography · CT head · pQCT · Spiral computed tomography · High resolution CT · Whole body imaging (Full-body CT scan) · Electron beam tomography
Industrial: Industrial CT ScanningOtherMRI MRI of brain and brain stem · MR neurography · Cardiac MRI/Cardiac MRI perfusion · MR angiography · MR cholangiopancreatography · Breast MRI
Functional MRI · Diffusion MRIUltrasound Echocardiography / Doppler echocardiography (TTE · TEE) · Intravascular · Gynecologic · Obstetric · Echoencephalography · Transcranial doppler · Abdominal ultrasonography · Transrectal · Breast ultrasound · Transscrotal ultrasound · Carotid ultrasonography
Contrast-enhanced · 3D ultrasound · Endoscopic ultrasound · Emergency ultrasound (FAST) · DuplexRadionuclide 2D / scintigraphyCholescintigraphy · Scintimammography · Ventilation/perfusion scan · Radionuclide ventriculography · Radionuclide angiography · Radioisotope renography · Sestamibi parathyroid scintigraphy · Radioactive iodine uptake test · Bone scintigraphy · Immunoscintigraphy
full body: Octreotide scan · Gallium 67 scan · Indium 111 WBC scan3D / ECTSPECT (gamma ray): SPECT of brain, Myocardial perfusion imaging
PET (positron): Brain PET, Cardiac PET, PET mammography, PET-CTOptical laser Thermography Breast thermographyCategories:- 2d nuclear medical imaging
- Digestive system imaging
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
