- Barium swallow
-
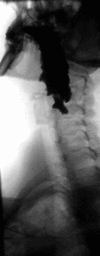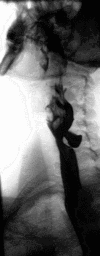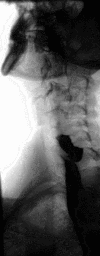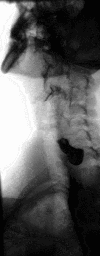
Barium swallow Diagnostics ICD-9-CM 87.61 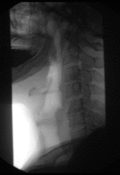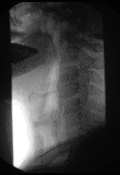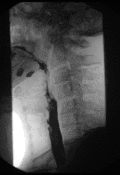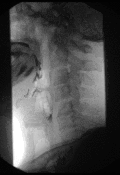 Normal barium swallow exam. Interactive version here.
Normal barium swallow exam. Interactive version here.
A barium swallow is a medical imaging procedure used to examine the upper GI (gastrointestinal) tract, which includes the esophagus and, to a lesser extent, the stomach.
Contents
Principle
Barium sulfate is a type of contrast medium that is visible to x-rays. As the patient swallows the barium suspension, it coats the esophagus with a thin layer of the barium. This enables the hollow structure to be imaged.
This is commonly used with baking soda (sodium bicarbonate crystals) to produce gas (see Reactions of sodium bicarbonate). As gas is low in density, and the X-rays pass through very easily, they will appear as black patches, as opposed to the white produced by relatively dense barium. As such, it is extremely useful in providing a contrast to the barium, to produce a double contrast image, to allow better visualisation of the contrasting features within the mucosal layer of the esophagus.
Barium sulfate is irritable outside the gastrointestinal tract. In cases where a leak is suspected or desired to be demonstrated, contrast imaging involving the use of water-soluble contrast media containing iodine is used.
As with all X-rays, the barium swallow technique employs radiation, and may irradiate the patient unnecessarily. The barium swallow should not be used unless required, and, although it cannot be replaced by endoscopy as for the barium enema, it should be avoided as much as possible for children and pregnant women.
Examination
The patient is asked to drink a suspension of barium sulfate. Fluoroscopy images are taken as the barium is swallowed. This is typically at a rate of 2 or 3 frames per second. The patient is asked to swallow the barium a number of times, whilst standing in different positions, i.e. AP, oblique and lateral, to assess the 3D structure as best as possible. This technique induces gas production in the esophagus, and can be uncomfortable to the subject.
Pathology
Pathologies detected on a Barium Swallow include:
- Achalasia
- Cancer of esophagus
- Tracheoesophageal fistula
- Schatzki ring
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD/GORD)
- Zenker's diverticulum
- Hiatus hernia
- Obstruction of esophagus
- Esophageal stenosis
See also
References
- Boon et al. Davidson's Principles & Practice of Medicine, 20th Edition, Chapter 22
- Harvard Health Publications - Diagnostic Tests - Barium Swallow - http://www.health.harvard.edu/diagnostic-tests/barium-swallow.htm
- Medline Plus Medical Encyclopedia - http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003816.htm
Medical testing : Medical imaging · Radiology · (ICD-9-CM V3 87-88, ICD-10-PCS B, CPT 70010-79999) X-ray/
medical radiography/
Industrial radiographyMedical: Pneumoencephalography · Dental radiography · Sialography · Myelography · CXR (Bronchography) · AXR / KUB · DXA/DXR · Upper gastrointestinal series/Small bowel follow-through/Lower gastrointestinal series · Cholangiography/Cholecystography · Mammography · Pyelogram · Cystography · Arthrogram · Hysterosalpingography · Skeletal survey · Angiography (Angiocardiography, Aortography) · Venography · Lymphogram
Industrial: Radiographic testingMedical: CT pulmonary angiogram · Cardiac CT · Abdominal and pelvic CT (Virtual colonoscopy) · CT angiography · CT head · pQCT · Spiral computed tomography · High resolution CT · Whole body imaging (Full-body CT scan) · Electron beam tomography
Industrial: Industrial CT ScanningOtherMRI MRI of brain and brain stem · MR neurography · Cardiac MRI/Cardiac MRI perfusion · MR angiography · MR cholangiopancreatography · Breast MRI
Functional MRI · Diffusion MRIUltrasound Echocardiography / Doppler echocardiography (TTE · TEE) · Intravascular · Gynecologic · Obstetric · Echoencephalography · Transcranial doppler · Abdominal ultrasonography · Transrectal · Breast ultrasound · Transscrotal ultrasound · Carotid ultrasonography
Contrast-enhanced · 3D ultrasound · Endoscopic ultrasound · Emergency ultrasound (FAST) · DuplexRadionuclide 2D / scintigraphyCholescintigraphy · Scintimammography · Ventilation/perfusion scan · Radionuclide ventriculography · Radionuclide angiography · Radioisotope renography · Sestamibi parathyroid scintigraphy · Radioactive iodine uptake test · Bone scintigraphy · Immunoscintigraphy
full body: Octreotide scan · Gallium 67 scan · Indium 111 WBC scan3D / ECTSPECT (gamma ray): SPECT of brain, Myocardial perfusion imaging
PET (positron): Brain PET, Cardiac PET, PET mammography, PET-CTOptical laser Thermography Breast thermographyCategories:- Fluoroscopy
- Digestive system imaging
- Barium
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.