- Doppler echocardiography
-
Doppler echocardiography Intervention 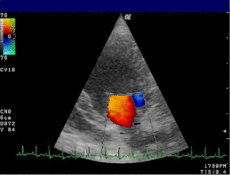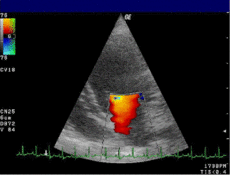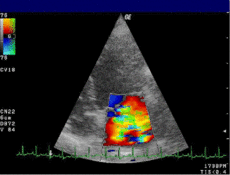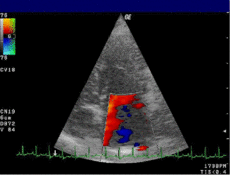
Mitral valveMeSH D015150 OPS-301 code: 3-052 Doppler echocardiography is a procedure which uses ultrasound technology to examine the heart.[1] An echocardiogram uses high frequency sound waves to create an image of the heart while the use of Doppler technology allows determination the speed and direction of blood flow by utilizing the Doppler effect.
An echocardiogram can, within certain limits, produce accurate assessment of the direction of blood flow and the velocity of blood and cardiac tissue at any arbitrary point using the Doppler effect. One of the limitations is that the ultrasound beam should be as parallel to the blood flow as possible. Velocity measurements allow assessment of cardiac valve areas and function, any abnormal communications between the left and right side of the heart, any leaking of blood through the valves (valvular regurgitation), calculation of the cardiac output and calculation of E/A ratio[2] (a measure of diastolic dysfunction). Contrast-enhanced ultrasound using gas-filled microbubble contrast media can be used to improve velocity or other flow-related medical measurements.
Although "Doppler" has become synonymous with "velocity measurement" in medical imaging, in many cases it is not the frequency shift (Doppler shift) of the received signal that is measured, but the phase shift (when the received signal arrives).
This procedure is frequently used to examine children's hearts for heart disease because there is no age or size requirement.
See also
- Medical ultrasonography section: Doppler sonography
- Echocardiography
- American Society of Echocardiography
- Christian Doppler
References
- ^ MeSH Doppler+Echocardiography
- ^ [1] Abdul Latif Mohamed, Jun Yong, Jamil Masiyati, Lee Lim, Sze Chec Tee. The Prevalence Of Diastolic Dysfunction In Patients With Hypertension Referred For Echocardiographic Assessment of Left Ventricular Function. Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 11, No. 1, January 2004, pp. 66-74
External links
- Echocardiography Textbook by Bonita Anderson
- Echocardiography (Ultrasound of the heart)
- Doppler Examination - Introduction
- The Doppler Principle and the Study of Cardiac Flows
MRI MRI of brain and brain stem · MR neurography · Cardiac MRI/Cardiac MRI perfusion · MR angiography · MR cholangiopancreatography · Breast MRI
Functional MRI · Diffusion MRIUltrasound Echocardiography / Doppler echocardiography (TTE · TEE) · Intravascular · Gynecologic · Obstetric · Echoencephalography · Transcranial doppler · Abdominal ultrasonography · Transrectal · Breast ultrasound · Transscrotal ultrasound · Carotid ultrasonography
Contrast-enhanced · 3D ultrasound · Endoscopic ultrasound · Emergency ultrasound (FAST) · DuplexRadionuclide 2D / scintigraphyCholescintigraphy · Scintimammography · Ventilation/perfusion scan · Radionuclide ventriculography · Radionuclide angiography · Radioisotope renography · Sestamibi parathyroid scintigraphy · Radioactive iodine uptake test · Bone scintigraphy · Immunoscintigraphy
full body: Octreotide scan · Gallium 67 scan · Indium 111 WBC scan3D / ECTSPECT (gamma ray): SPECT of brain, Myocardial perfusion imaging
PET (positron): Brain PET, Cardiac PET, PET mammography, PET-CTOptical laser Thermography Breast thermographyCategories:- Medical ultrasound
- Medical treatment stubs
- Health stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
