- Deep inguinal ring
-
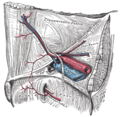
Deep inguinal ring 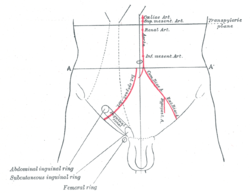
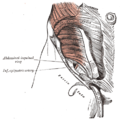
Front of abdomen, showing surface markings for arteries and inguinal canal. (Abdominal inguinal ring labeled at lower left.) Latin annulus inguinalis profundus Gray's subject #286 1315 The deep inguinal ring (internal or deep abdominal ring, abdominal inguinal ring, internal inguinal ring) is the entrance to the inguinal canal.
Contents
Location
The surface marking of the deep inguinal ring is classically described as the midpoint of the inguinal ligament (midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic tubercle).[1]
However, the surface anatomy of the point is disputed. In a recent study[2] it was found to be in a region between the mid-inguinal point (situated midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic symphysis) and the midpoint of the inguinal ligament (i.e. midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic tubercle). Traditionally, either one of these 2 sites was claimed as its location. However, this claim is based upon the study's dissection of 52 cadavers, and may not reflect the live in vivo anatomy.
Some sources state that it is at the layer of the transversalis fascia.[3]
Shape
It is of an oval form, the long axis of the oval being vertical; it varies in size in different subjects, and is much larger in the male than in the female.
Boundaries
It is bounded, above and laterally, by the arched lower margin of the transversalis fascia; below and medially, by the inferior epigastric vessels.
Transmission
It transmits the spermatic cord in the male and the round ligament of the uterus in the female.
Extensions
From its circumference a thin funnel-shaped membrane, the infundibuliform fascia, is continued around the cord and testis, enclosing them in a distinct covering.
Additional images
References
- ^ Susan Standring (2004). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Medicine and Surgery. Churchill-Livingstone. p. 1098. ISBN 0-443-07168-3.
- ^ Koliyadan S, Narayan G, Balasekran P (2004). "Surface marking of the deep inguinal ring". Clin Anat 17 (7): 554–7. doi:10.1002/ca.10257. PMID 15376291.
- ^ Kyung Won, PhD. Chung (2005). Gross Anatomy (Board Review). Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 198. ISBN 0-7817-5309-0.
See also
External links
- SUNY Figs 36:01-03 - "The inguinal canal and derivation of the layers of the spermatic cord."
- SUNY Anatomy Image 7362
- -261423027 at GPnotebook
- inguinalregion at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- Atlas of anatomy at UMich abdo_wall65 - "The Coverings of the Inguinal Canal, External & Internal Oblique & Transversus Abdominis Removed"
- The Inguinal Canal and Hernias (includes diagram at burrill.demon.co.uk)
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
List of muscles of abdominopelvic cavity (TA A04.5, GA 4.408) Abdomen/
wallAnterior/
lateralMuscleFasciaFascia/abdominal fascia: panniculus adiposus (Fascia of Camper) · stratum membranosum (Fascia of Scarpa) · Transversalis fascia (Interfoveolar ligament)
Linea alba · Linea semilunaris · Inguinal triangle
Inguinal canal (Deep inguinal ring, Superficial inguinal ring, Intercrural fibers, Crura of superficial inguinal ring)
Inguinal ligament (Pectineal ligament, Lacunar ligament, Reflected ligament)PosteriorMuscleFasciaPelvis MuscleFasciafascia/pelvic fascia visceral (Rectovaginal fascia, Rectoprostatic fascia) · parietal (Obturator fascia/Tendinous arch, Piriformis fascia)
floor/diaphragm: Superior fascia of pelvic diaphragm (Pubovesical ligament, Puboprostatic ligament) · Inferior fascia of pelvic diaphragm
Anococcygeal bodyCategories:- Abdomen
- Muscle stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.