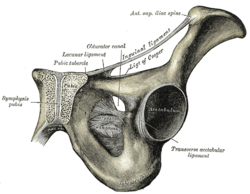
- Pectineal ligament
-
Ligament: Pectineal ligament The inguinal and lacunar ligaments. Latin ligamentum pectineum From lacunar ligament To pectineal line The pectineal ligament (sometimes known as the inguinal ligament of Cooper[1], after Astley Cooper) is an extension of the lacunar ligament that runs on the pectineal line of the pubic bone.
It was characterized by Cooper in 1804.[2][3] The structure is strong and holds suture well, facilitating reconstruction of the floor of the inguinal canal. This variant of non-prosthetic inguinal hernia repair, first used by Lotheissen in Austria [4], now bears his name.
See also
References
- ^ synd/911 at Who Named It?
- ^ Faure JP, Hauet T, Scepi M, Chansigaud JP, Kamina P, Richer JP (2001). "The pectineal ligament: anatomical study and surgical applications". Surg Radiol Anat 23 (4): 237–42. doi:10.1007/s00276-001-0237-1. PMID 11694967. http://www.springerlink.com/content/u0rt14667m10353k/.
- ^ Cooper, A. The Anatomy and Surgical Treatment of Internal and Congenital Hernia." London. 1804
- ^ http://www.medscape.org/viewarticle/420354_3
External links
List of muscles of abdominopelvic cavity (TA A04.5, GA 4.408) Abdomen/
wallAnterior/
lateralMuscleFasciaFascia/abdominal fascia: panniculus adiposus (Fascia of Camper) · stratum membranosum (Fascia of Scarpa) · Transversalis fascia (Interfoveolar ligament)
Linea alba · Linea semilunaris · Inguinal triangle
Inguinal canal (Deep inguinal ring, Superficial inguinal ring, Intercrural fibers, Crura of superficial inguinal ring)
Inguinal ligament (Pectineal ligament, Lacunar ligament, Reflected ligament)PosteriorMuscleFasciaPelvis MuscleFasciafascia/pelvic fascia visceral (Rectovaginal fascia, Rectoprostatic fascia) · parietal (Obturator fascia/Tendinous arch, Piriformis fascia)
floor/diaphragm: Superior fascia of pelvic diaphragm (Pubovesical ligament, Puboprostatic ligament) · Inferior fascia of pelvic diaphragm
Anococcygeal bodyCategories:- Ligament stubs
- Ligaments
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.