- Enoxaparin sodium
-
Enoxaparin sodium 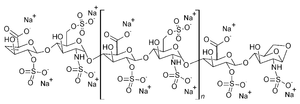
Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a696006 Pregnancy cat. B Legal status POM (UK) ℞-only (US) Routes Subcutaneous (SC) Injection and intervenous (IV) per package insert Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability 92% Protein binding 80% bound-albumin Metabolism primarily by kidneys Half-life 4.5 hours Identifiers CAS number 9005-49-6 
ATC code B01AB05 PubChem CID 772 DrugBank APRD00068 UNII 8NZ41MIK1O 
KEGG D07510 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1201685 
Chemical data Formula (C26H40N2O36S5)n Mol. mass 4500 daltons (average)  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Enoxaparin is a low molecular weight heparin marketed under the trade names Lovenox and Clexane, among others. It is an anticoagulant used to prevent and treat deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, and is given as a subcutaneous injection (by a health care provider or the patient). Its use is evolving in acute coronary syndromes (ACS).
Enoxaparin is manufactured by Sanofi and is derived from the intestinal mucosa of pigs.
Contents
Indications
- The treatment of unstable angina (UA) and non-Q-wave myocardial infarction (NQMI), administered concurrently with aspirin.
- Prophylaxis of DVT
- Total hip & knee replacement,
- Abdominal surgery.
- Treatment of DVT with or without PE.
- Treatment of DVT inpatient, with ACS, including STEMI.
Mechanism of action
Enoxaparin binds to and accelerates the activity of antithrombin III. By activating antithrombin III, enoxaparin preferentially potentiates the inhibition of coagulation factors Xa and IIa. The anticoagulant effect of enoxaparin can be directly correlated to its ability to inhibit factor Xa. Factor Xa catalyzes the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin, so enoxaparin’s inhibition of this process results in decreased thrombin and ultimately the prevention of fibrin clot formation.
Monitoring
- Enoxaparin does NOT affect PTT, international normalized ratio (INR), prothrombin time (PT)[citation needed]
- Anti-factor Xa levels can be measured, and are generally used to monitor enoxaparin activity in certain subgroups of patients. Anti-factor Xa levels may be recommended in underweight, obese, pregnant, or renally impaired patients. Anti-Xa levels should be checked at their peak at 4 hours after dosing (both q12 and q24 variations).
Pregnancy
Enoxaparin is an FDA pregnancy category B drug, and is not expected to harm an unborn baby. Enoxaparin does not cross the placenta. In animal models, there was no evidence of teratogenic effects or fetotoxicity due to enoxaparin. Pregnancy alone can raise a woman's risk of life threatening thromboembolic event. Enoxaparin can be used during all stages of pregnancy, however it should be closely monitored by a physician.
Dosing in patients with renal failure
Decreased dose is recommended in renal failure or ESRD patients. For DVT prophylaxis in a patient with GFR < 30, a dose of 30 mg daily is recommended. For DVT prophylaxis in a patient with GFR > 30, full dose (40 mg daily) can be given. For treatment of DVT/PE, the standard recommended dose is 1.5 mg/kg once daily or 1mg/kg every 12 hours. If the GFR < 30, the dose should be changed to 1 mg/kg daily.
Side effects
- Bleeding[1]
- Thrombocytopenia, i.e. can be associated with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (0.5-5.0% of patients treated for at least five days[2]
- Pain, bruising or irritation; hard, inflamed nodules or an itchy red rash at the injection site
- Symptoms similar to those of hayfever
- Abdominal/chest pain
- Headache
- Hyperkalemia
- Transaminitis
Reversal agent
- Protamine, although not as effective at reversal as it is for heparin due to more activity at the Xa clotting factor (enoxaparin); as heparin has both Xa and IIa. Protamine sulfate will reverse enoxaparin by 66% per package insert.
Availability
100 mg/mL concentration
- Prefilled Syringes: 30 mg/0.3mL, 40 mg/0.4mL
- Graduated Prefilled Syringes: 60 mg/0.6mL, 80 mg/0.8mL, 100 mg/1mL
- Multiple Dose Vials: 300 mg/3.0mL
150 mg/mL concentration
- Graduated Prefilled Syringes: 120 mg/0.8mL, 150 mg/1mL
- There are many L.M.W.H agonists, like Fragmin (dalteparin sodium).
Market
Annual sales approx $3.1bn. Enoxaparin is no longer protected by US patent due to inequitable conduct on the filing of Patent No. 5,389,618 (Fed. Cir. 2008 No. 2007-1280 Aventis Pharma v. Amphastar and Teva)
References
- ^ Warwick, D; Bannister, GC; Glew, D; Mitchelmore, A; Thornton, M; Peters, TJ; Brookes, S (1995). "Perioperative low-molecular-weight heparin. Is it effective and safe". The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume 77 (5): 715–9. PMID 7559695.
- ^ Levy, JH; Tanaka, KA; Hursting, MJ (2007). "Reducing thrombotic complications in the perioperative setting: an update on heparin-induced thrombocytopenia". Anesthesia and analgesia 105 (3): 570–82. doi:10.1213/01.ane.0000277497.70701.47. PMID 17717208.
External links
Categories:- Sanofi
- Heparins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
