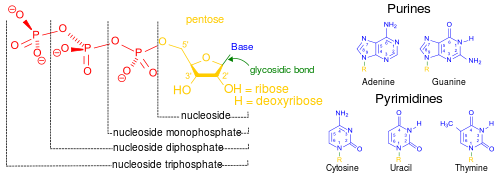
- Nucleoside
-
Nitrogenous base Nucleoside Deoxynucleoside 
Adenine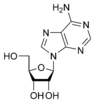
Adenosine
A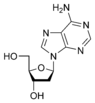
Deoxyadenosine
dA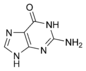
Guanine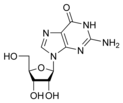
Guanosine
G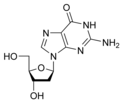
Deoxyguanosine
dG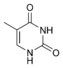
Thymine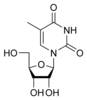
5-Methyluridine
m5U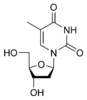
Thymidine
dT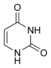
Uracil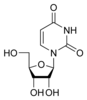
Uridine
U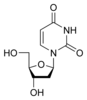
Deoxyuridine
dU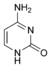
Cytosine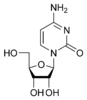
Cytidine
C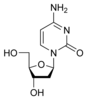
Deoxycytidine
dCNucleosides are glycosylamines consisting of a nucleobase (often referred to as simply base) bound to a ribose or deoxyribose sugar via a beta-glycosidic linkage. Examples of nucleosides include cytidine, uridine, adenosine, guanosine, thymidine and inosine.
Biological function
Nucleosides can be phosphorylated by specific kinases in the cell on the sugar's primary alcohol group (-CH2-OH), producing nucleotides, which are the molecular building-blocks of DNA and RNA.
Nucleosides can be produced by de novo synthesis pathways, in particular in the liver, but they are more abundantly supplied via ingestion and digestion of nucleic acids in the diet, whereby nucleotidases break down nucleotides (such as the thymidine monophosphate) into nucleosides (such as thymidine) and phosphate. The nucleosides, in turn, are subsequently broken down:
- in the lumen of the digestive system by nucleosidases into nucleobases and ribose or deoxyribose.
In addition, nucleotides can be broken down:
- inside the cell into nitrogenous bases, and ribose-1-phosphate or deoxyribose-1-phosphate.
Use in medicine and technology
In medicine several nucleoside analogues are used as antiviral or anticancer agents. The viral polymerase incorporates these compounds with non-canonical bases. These compounds are activated in the cells by being converted into nucleotides, they are administered as nucleosides since charged nucleotides cannot easily cross cell membranes.
In molecular biology, several analogues of the sugar backbone exist. Due to the low stability of RNA, which is prone to hydrolysis, several more stable alternative nucleoside/nucleotide analogues that correctly bind to RNA are used. This is achieved by using a different backbone sugar. These analogues include LNA, morpholino, PNA.
In sequencing, dideoxynucleotides are used. These nucleotides possess the non-canon sugar dideoxyribose, which lacks 3' hydroxyl group (which accepts the phosphate) and therefore cannot bond with the next base, terminating the chain, as DNA polymerases cannot distinguish between it and a regular deoxyribonucleotide.
See also
- Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
- Nucleotide
- Nucleobase
- Synthesis of nucleosides
Nucleic acid constituents Nucleobase Nucleoside Nucleotide
(Nucleoside monophosphate)Nucleoside diphosphate Nucleoside triphosphate biochemical families: prot · nucl · carb (glpr, alco, glys) · lipd (fata/i, phld, strd, gllp, eico) · amac/i · ncbs/i · ttpy/iCategories:- Nucleosides
- Biochemistry stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.