- 5-Methyluridine
-
5-Methyluridine 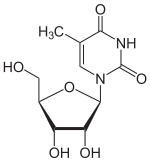 1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-5-methylpyrimidine-2,4-dioneOther namesRibothymidine, Ribosylthymine; Thymine riboside, m5u
1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-5-methylpyrimidine-2,4-dioneOther namesRibothymidine, Ribosylthymine; Thymine riboside, m5uIdentifiers CAS number 1463-10-1 PubChem 445408 ChemSpider 1363755 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C/1NC(=O)N(\C=C\1C)[C@H]2O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]2O)CO
- InChI=1S/C10H14N2O6/c1-4-2-12(10(17)11-8(4)16)9-7(15)6(14)5(3-13)18-9/h2,5-7,9,13-15H,3H2,1H3,(H,11,16,17)/t5-,6-,7-,9-/m0/s1

Key: DWRXFEITVBNRMK-AZRUVXNYSA-N
InChI=1/C10H14N2O6/c1-4-2-12(10(17)11-8(4)16)9-7(15)6(14)5(3-13)18-9/h2,5-7,9,13-15H,3H2,1H3,(H,11,16,17)/t5-,6-,7-,9-/m0/s1
Key: DWRXFEITVBNRMK-AZRUVXNYBS
Properties Molecular formula C10H14N2O6 Molar mass 258.23 g/mol Melting point 185 °C, 458 K, 365 °F
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references The chemical compound 5-methyluridine, also called ribothymidine, is a pyrimidine nucleoside. It is the ribonucleoside couterpart to the deoxyribonucleoside thymidine, which lacks a hydroxyl group at the 2' position. 5-Methyluridine contains a thymine base joined to a ribose pentose sugar.
It exists in solid form as small white crystals or white crystalline powder, has a molecular weight of 258.23 u, and has a melting point of 185 °C. The stability of 5-methyluridine under standard temperature and pressure (STP) is very high.
References
Nucleic acid constituents Nucleobase Nucleoside Nucleotide
(Nucleoside monophosphate)Nucleoside diphosphate Nucleoside triphosphate biochemical families: prot · nucl · carb (glpr, alco, glys) · lipd (fata/i, phld, strd, gllp, eico) · amac/i · ncbs/i · ttpy/iTypes of nucleic acids Constituents Nucleobases · Nucleosides · Nucleotides · DeoxynucleotidesRibonucleic acids
(coding and non-coding)translation: mRNA (pre-mRNA/hnRNA) · tRNA · rRNA · tmRNA
regulatory: miRNA · siRNA · piRNA · aRNA · RNAi ·
RNA processing: snRNA · snoRNA
other/ungrouped: gRNA · shRNA · stRNA · ta-siRNADeoxyribonucleic acids Nucleic acid analogues Cloning vectors biochemical families: prot · nucl · carb (glpr, alco, glys) · lipd (fata/i, phld, strd, gllp, eico) · amac/i · ncbs/i · ttpy/iCategories:- Nucleosides
- Pyrimidinediones
- Ribosides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
