- Cytidine
-
Cytidine 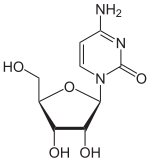 4-amino-1-[3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]pyrimidin-2-one
4-amino-1-[3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]pyrimidin-2-oneIdentifiers CAS number 65-46-3 
PubChem 6175 ChemSpider 5940 
UNII 5CSZ8459RP 
KEGG D07769 
MeSH Cytidine ChEBI CHEBI:17562 
ChEMBL CHEMBL95606 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C1/N=C(/N)\C=C/N1[C@@H]2O[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H]2O)CO
- InChI=1S/C9H13N3O5/c10-5-1-2-12(9(16)11-5)8-7(15)6(14)4(3-13)17-8/h1-2,4,6-8,13-15H,3H2,(H2,10,11,16)/t4-,6-,7-,8-/m1/s1

Key: UHDGCWIWMRVCDJ-XVFCMESISA-N
InChI=1/C9H13N3O5/c10-5-1-2-12(9(16)11-5)8-7(15)6(14)4(3-13)17-8/h1-2,4,6-8,13-15H,3H2,(H2,10,11,16)/t4-,6-,7-,8-/m1/s1
Key: UHDGCWIWMRVCDJ-XVFCMESIBD
Properties Molecular formula C9H13N3O5 Molar mass 243.22 g mol−1  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Cytidine is a nucleoside molecule that is formed when cytosine is attached to a ribose ring (also known as a ribofuranose) via a β-N1-glycosidic bond. Cytidine is a component of RNA.
If cytosine is attached to a deoxyribose ring, it is known as a deoxycytidine.
Dietary sources of cytidine
Dietary sources of cytidine include foods with high RNA (ribonucleic acid) content,[1] such as organ meats, Brewer's yeast, as well as pyrimidine-rich foods such as beer. During digestion, RNA-rich foods are broken-down into ribosyl pyrimidines (cytidine and uridine), which are absorbed intact.[1] In humans, dietary cytidine is converted into uridine, [2] which is probably the compound behind cytidine's metabolic effects.
References
- ^ a b Jonas DA, Elmadfa I, Engel KH, et al. (2001). "Safety considerations of DNA in food". Ann Nutr Metab. 45 (6): 235–54. doi:10.1159/000046734. PMID 11786646. http://content.karger.com/produktedb/produkte.asp?typ=fulltext&file=anm45235.
- ^ Wurtman RJ, Regan M, Ulus I, Yu L (Oct 2000). "Effect of oral CDP-choline on plasma choline and uridine levels in humans". Biochem Pharmacol. 60 (7): 989–92. doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(00)00436-6. PMID 10974208. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0006-2952(00)00436-6.
Nucleic acid constituents Nucleobase Nucleoside Nucleotide
(Nucleoside monophosphate)Nucleoside diphosphate Nucleoside triphosphate biochemical families: prot · nucl · carb (glpr, alco, glys) · lipd (fata/i, phld, strd, gllp, eico) · amac/i · ncbs/i · ttpy/iCategories:- Nucleosides
- Pyrimidones
- Ribosides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
