- White blood cell
-
"White Blood Cells" redirects here. For the album by The White Stripes, see White Blood Cells (album).
White blood cell 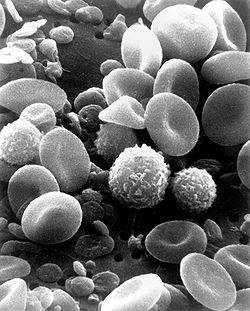
A scanning electron microscope image of normal circulating human blood. In addition to the irregularly shaped leukocytes, both red blood cells and many small disc-shaped platelets are visible. Latin leucocytus Code TH H2.00.04.1.02001 White blood cells, or leukocytes (also spelled "leucocytes", leuco- Ancient Greek "white"), are cells of the immune system involved in defending the body against both infectious disease and foreign materials. Five[1] different and diverse types of leukocytes exist, but they are all produced and derived from a multipotent cell in the bone marrow known as a hematopoietic stem cell. They live for about 3 to 4 days in the average human body. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system.[2]
The number of leukocytes in the blood is often an indicator of disease. There are normally between 4×109 and 1.1×1010 white blood cells in a litre of blood, and ranging from 7 and 21 micrometres in diameter, they make up approximately 1% of blood in a healthy adult.[3] An increase in the number of leukocytes over the upper limits is called leukocytosis, and a decrease below the lower limit is called leukopenia. The physical properties of leukocytes, such as volume, conductivity, and granularity, may change due to activation, the presence of immature cells, or the presence of malignant leukocytes in leukemia.
Contents
Etymology
The name "white blood cell" derives from the fact that after centrifugation of a blood sample, the white cells are found in the buffy coat, a thin, typically white layer of nucleated cells between the sedimented red blood cells and the blood plasma. The scientific term leukocyte directly reflects this description, derived from Ancient Greek λευκό (white), and κύτταρο (cell). Blood plasma may sometimes be green if there are large amounts of neutrophils in the sample, due to the heme-containing enzyme myeloperoxidase that they produce.
Types
There are several different types of white blood cells. They all have many things in common, but are all distinct in form and function. A major distinguishing feature of some leukocytes is the presence of granules; white blood cells are often characterized as granulocytes or agranulocytes:
- Granulocytes (polymorphonuclear leukocytes): leukocytes characterised by the presence of differently staining granules in their cytoplasm when viewed under light microscopy. These granules are membrane-bound enzymes which primarily act in the digestion of endocytosed particles. There are three types of granulocytes: neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils, which are named according to their staining properties.
- Agranulocytes (mononuclear leukocytes): leukocytes characterized by the apparent absence of granules in their cytoplasm. Although the name implies a lack of granules these cells do contain non-specific azurophilic granules, which are lysosomes.[4] The cells include lymphocytes, monocytes, and macrophages.[5]
Overview table
Type Microscopic Appearance Diagram Approx. %
in adults[6]
See also:
Blood valuesDiameter (μm)[6] Main targets[3] Nucleus[3] Granules[3] Lifetime[6] Neutrophil 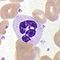

54–62%[5] 10–12 - bacteria
- fungi
multilobed fine, faintly pink (H&E Stain) 6 hours–few days
(days in spleen and other tissue)Eosinophil 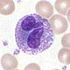
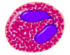
1–6% 10–12 - larger parasites
- modulate allergic inflammatory responses
bi-lobed full of pink-orange (H&E Stain) 8–12 days (circulate for 4–5 hours) Basophil 
<1% 12–15 - release histamine for inflammatory responses
bi-lobed or tri-lobed large blue a few hours to a few days Lymphocyte 

28–33% 7–8 - B cells: releases antibodies and assists activation of T cells
- T cells:
- Th (T helper) cells: activate and regulate T and B cells
- CD8+ cytotoxic T cells: virus-infected and tumor cells.
- γδ T cells:
- Regulatory (suppressor) T cells: Returns the functioning of the immune system to normal operation after infection; prevents autoimmunity
- Natural killer cells: virus-infected and tumor cells.
deeply staining, eccentric NK-cells and Cytotoxic (CD8+) T-cells years for memory cells, weeks for all else. Monocyte 

2–10% 7.72–9.99[7] Monocytes migrate from the bloodstream to other tissues and differentiate into tissue resident macrophages, Kupffer cells in the liver. kidney shaped none hours to days Macrophage 

21 (human)[8] Phagocytosis (engulfment and digestion) of cellular debris and pathogens, and stimulation of lymphocytes and other immune cells that respond to the pathogen. activated: days
immature: months to yearsDendritic cells 
Main function is as an antigen-presenting cell (APC) that activates T lymphocytes. similar to macrophages Neutrophil
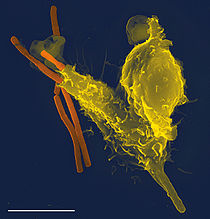 Neutrophil engulfing anthrax bacteria.
Neutrophil engulfing anthrax bacteria. Main article: Neutrophil granulocyte
Main article: Neutrophil granulocyteNeutrophils defend against bacterial or fungal infection and other very small inflammatory processes that are usually first responders to microbial infection; their activity and death in large numbers forms pus. They are commonly referred to as polymorphonuclear (PMN) leukocytes, although technically PMN refers to all granulocytes. They have a multi-lobed nucleus which may appear like multiple nuclei, hence the name polymorphonuclear leukocyte. The cytoplasm may look transparent because of fine granules that are pale lilac. Neutrophils are very active in phagocytosing bacteria and are present in large amount in the pus of wounds. These cells are not able to renew their lysosomes (used in digesting microbes) and die after having phagocytosed a few pathogens.[9] Neutrophils are the most common cell type seen in the early stages of acute inflammation, and make up 60-70% of total leukocyte count in human blood.[3] The life span of a circulating human neutrophil is about 5.4 days.[10]
Eosinophil
Main article: Eosinophil granulocyteEosinophils primarily deal with parasitic infections. Eosinophils are also the predominant inflammatory cells in allergic reactions. The most important causes of eosinophilia include allergies such as asthma, hay fever, and hives; and also parasitic infections. Generally their nucleus is bi-lobed. The cytoplasm is full of granules which assume a characteristic pink-orange color with eosin stain.
Basophil
Main article: Basophil granulocyteBasophils are chiefly responsible for allergic and antigen response by releasing the chemical histamine causing vasodilation. The nucleus is bi- or tri-lobed, but it is hard to see because of the number of coarse granules which hide it. They are characterized by their large blue granules.
Lymphocyte
Main article: LymphocyteLymphocytes are much more common in the lymphatic system. Lymphocytes are distinguished by having a deeply staining nucleus which may be eccentric in location, and a relatively small amount of cytoplasm. The blood has three types of lymphocytes:
- B cells: B cells make antibodies that bind to pathogens to enable their destruction. (B cells not only make antibodies that bind to pathogens, but after an attack, some B cells will retain the ability to produce an antibody to serve as a 'memory' system.)
- T cells:
- CD4+ (helper) T cells having co-receptor CD4 is known as CD4+ T cells.These cells binds with the antigen having MHC II receptor on its surface. Then it presents this antigen to B cells. B cells produce antibodies to destroy antigen. Thus CD4+ T cell is also known as antigen presenting cells.T cells co-ordinate the immune response and are important in the defense against intracellular bacteria. In acute HIV infection, these T cells are the main index to identify the individual's immune system activity. Research has shown[11] that CD8+ cells are also another index to identify human's immune activity.
- CD8+ cytotoxic T cells are able to kill virus-infected and tumor cells.T cells having co-receptor CD8 are known as CD8+ T cells. These cells kills damaged or cancerous cells. CD8 binds with MHC I receptor of damaged cells(carrying antigen). All nucleated cells possess MHC I on its surface.
- γδ T cells possess an alternative T cell receptor as opposed to CD4+ and CD8+ αβ T cells and share characteristics of helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells.
- Natural killer cells: Natural killer cells are able to kill cells of the body which are displaying a signal to kill them, as they have been infected by a virus or have become cancerous.
Monocyte
Main article: MonocyteMonocytes share the "vacuum cleaner" (phagocytosis) function of neutrophils, but are much longer lived as they have an additional role: they present pieces of pathogens to T cells so that the pathogens may be recognized again and killed, or so that an antibody response may be mounted. Monocytes eventually leave the bloodstream to become tissue macrophages which remove dead cell debris as well as attacking microorganisms. Neither of these can be dealt with effectively by the neutrophils. Unlike neutrophils, monocytes are able to replace their lysosomal contents and are thought to have a much longer active life. They have the kidney shaped nucleus and are typically agranulated. They also possess abundant cytoplasm.
Once monocytes move from the bloodstream out into the body tissues, they undergo changes (differentiate) allowing phagocytosis and are then known as macrophages.
Medication causing leukopenia
Some medications can have an impact on the number and function of white blood cells. Leukopenia is the reduction in the number of white blood cells, which may affect the overall white cell count or one of the specific populations of white blood cells. For example, if the number of neutrophils is low, the condition is known as neutropenia. Likewise, low lymphocyte levels are termed lymphopenia. Medications which can cause leukopenia include clozapine, an antipsychotic medication with a rare adverse effect leading to the total absence of all granulocytes (neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils). Other medications include immunosuppressive drugs, such as sirolimus, mycophenolate mofetil, tacrolimus, and cyclosporine. Interferons used to treat multiple sclerosis, like Rebif, Avonex, and Betaseron, can also cause leukopenia.
Fixed leukocytes
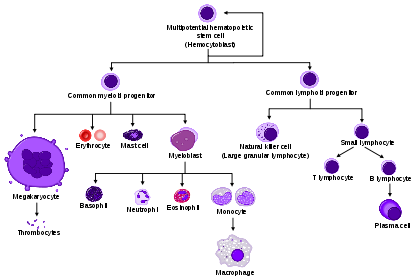 HSC=Hematopoietic stem cell, Progenitor=Progenitor cell, L-blast=Lymphoblast, Lymphocyte, Mo-blast=Monoblast, Monocyte, Myeloblast, Pro-M=Promyelocyte, Myelocyte, Meta-M=Metamyelocyte, Neutrophil, Eosinophil, Basophil, Pro-E=Proerythroblast, Baso-E=Basophilic erythroblast, poly-E=Polychromatic erythroblast, Ortho-E=Orthochromatic erythroblast, Erythrocyte, Promegakaryocyte, Megakaryocyte, Platelet
HSC=Hematopoietic stem cell, Progenitor=Progenitor cell, L-blast=Lymphoblast, Lymphocyte, Mo-blast=Monoblast, Monocyte, Myeloblast, Pro-M=Promyelocyte, Myelocyte, Meta-M=Metamyelocyte, Neutrophil, Eosinophil, Basophil, Pro-E=Proerythroblast, Baso-E=Basophilic erythroblast, poly-E=Polychromatic erythroblast, Ortho-E=Orthochromatic erythroblast, Erythrocyte, Promegakaryocyte, Megakaryocyte, Platelet
Some leukocytes migrate into the tissues of the body to take up a permanent residence at that location rather than remaining in the blood. Often these cells have specific names depending upon which tissue they settle in, such as fixed macrophages in the liver which become known as Kupffer cells. These cells still serve a role in the immune system.
- Histiocytes
- Dendritic cells (Although these will often migrate to local lymph nodes upon ingesting antigens)
- Mast cells
- Microglia
See also
- Reference ranges for blood tests
- Leukocyte-promoting factor
Notes
- ^ LaFleur-Brooks, M. (2008). Exploring Medical Language: A Student-Directed Approach, 7th Edition. St. Louis, Missouri, USA: Mosby Elsevier. pp. 398. ISBN 978-0-323-04950-4.
- ^ Maton, D., Hopkins, J., McLaughlin, Ch. W., Johnson, S., Warner, M. Q., LaHart, D., & Wright, J. D., Deep V. Kulkarni (1000008). Human Biology and Health. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, USA: Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-981176-1.
- ^ a b c d e Alberts, B. (2005). "Leukocyte functions and percentage breakdown". Molecular Biology of the Cell. NCBI Bookshelf. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?highlight=leukocyte,functions&rid=mboc4.table.4143. Retrieved 2007-04-14.
- ^ Gartner, L. P., & Hiatt, J. L. (2007). Color Textbook of Histology (5rd ed.). Philadelphia, PA: SAUNDERS Elsevier. pp. 225. ISBN 978-1-4160-2945-8.
- ^ a b http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objID=AP14704
- ^ a b c Daniels, V. G., Wheater, P. R., & Burkitt, H. G. (1979). Functional histology: A text and colour atlas. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-01657-7.
- ^ Worthen, G. S., Downey, G. P.; Henson, P. M., Doherty, D. E.; Schwab b, 3rd; Elson, EL; Henson, PM; Worthen, GS (1990). "Retention of leukocytes in capillaries: role of cell size and deformability". Applied Physiology 69 (5): 1767–1778. PMID 2272970.
- ^ Krombach, F., Münzing, S., Allmeling, A. M., Gerlach, J. T., Behr, J., & Dörger, M. (1 September 1997). "Cell size of alveolar macrophages: an interspecies comparison". Environ. Health Perspect. (Brogan & Partners) 105 Suppl 5 (Suppl 5): 1261–1263. doi:10.2307/3433544. ISSN 00916765. JSTOR 3433544. PMC 1470168. PMID 9400735. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1470168.
- ^ Wheater, Paul R.; Stevens, Alan (2002). Wheater's basic histopathology: a colour atlas and text. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-07001-6. http://www.ecc-book.com/ACINFLMPDF1.pdf.
- ^ Pillay J, den Braber I, Vrisekoop N, Kwast LM, de Boer RJ, Borghans JA, Tesselaar K, Koenderman L. In vivo labeling with 2H2O reveals a human neutrophil lifespan of 5.4 days Blood. 2010 Jul 29;116(4):625-7.
- ^ Pantaleo, G., Demarest, J. F., Soudeyns, H., et. al. (August 1994). "Major expansion of CD8+ T cells with a predominant V beta usage during the primary immune response to HIV". Nature 370 (6489): 463–467. doi:10.1038/370463a0. PMID 8047166.
External links
Myeloid lineage - Blood (WBC and RBC) Cellular/
HSCsCFU-GMHistiocytes · Kupffer cells · Alveolar macrophage · Microglia · Osteoclasts · Epithelioid cells · giant cells (Langhans giant cells, Foreign-body giant cell, Touton giant cells)CFU-DLCommonCFU-BasoCFU-EosCFU-MegCFU-ECFU-MastNoncellular Blood: Lymphocytes Lymphoid/
HSC:CFU-LLymphopoiesis Immunology: Lymphocytic adaptive immune system and complement Lymphoid AntigensAntibodiesImmunity vs.
toleranceaction: Immunity · Autoimmunity · Alloimmunity · Allergy · Hypersensitivity · Inflammation · Cross-reactivity
inaction: Tolerance (Central, Peripheral, Clonal anergy, Clonal deletion, Tolerance in pregnancy) · ImmunodeficiencyLymphocytes Substances Complement Categories:- Hematology
- Immunology
- Immune system
- Leukocytes
- Human cells
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
