- Normoblast
-
An erythroblast is a type of red blood cell which still retains a cell nucleus. It is the immediate precursor of a normal erythrocyte.
Contents
Nomenclature
The term normoblast is sometimes used as a synonym for erythroblast, but at other times it is considered a subcategory. In the latter context, there are two types of erythroblasts:
- "normoblasts" - develop as expected
- "megaloblasts" - unusually large erythroblasts that can be associated with pernicious anemia and folic acid deficiency (collectively called megaloblastic anemia)
Development
There are four stages in the development of a normoblast.
 HSC=Hematopoietic stem cell , Progenitor=Progenitor cell , L-blast=lymphoblast , Lymphocyte , Mo-blast=Monoblast , Monocyte , Myeloblast , Pro-M=Promyelocyte , Myelocyte , Meta-M=Metamyelocyte , Neutrophil , Eosinophil , Basophil , Pro-E=Proerythroblast , Baso-E=Basophilic erythroblast , poly-E=Polychromatic erythroblast , Ortho-E=orthochromatic erythroblast , Erythrocyte , Promegakaryocyte , megakaryocyte , Platlet
HSC=Hematopoietic stem cell , Progenitor=Progenitor cell , L-blast=lymphoblast , Lymphocyte , Mo-blast=Monoblast , Monocyte , Myeloblast , Pro-M=Promyelocyte , Myelocyte , Meta-M=Metamyelocyte , Neutrophil , Eosinophil , Basophil , Pro-E=Proerythroblast , Baso-E=Basophilic erythroblast , poly-E=Polychromatic erythroblast , Ortho-E=orthochromatic erythroblast , Erythrocyte , Promegakaryocyte , megakaryocyte , Platlet
Illustration Description Image 
Pronormoblast 
Basophilic normoblast 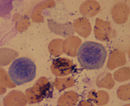

Polychromatic normoblast (also polychromatophilic) 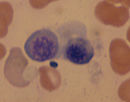

Orthochromatic normoblast (also orthochromatophilic) 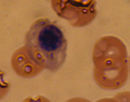
Additional images
See also
- Erythropoiesis
- Hemopoiesis
- Pluripotential hemopoietic stem cell
External links
- MeSH Normoblasts
- Histology at BU 01804loa - "Bone Marrow and Hemopoiesis bone marrow smear, erythroblast series with proerythroblast "
- Histology at uiowa.edu
Myeloid lineage - Blood (WBC and RBC) Cellular/
HSCsCFU-GMHistiocytes · Kupffer cells · Alveolar macrophage · Microglia · Osteoclasts · Epithelioid cells · giant cells (Langhans giant cells, Foreign-body giant cell, Touton giant cells)CFU-DLCommonCFU-BasoCFU-EosCFU-MegCFU-EReticulocyte · NormoblastCFU-MastNoncellular Myeloid physiology Hematopoiesis CFU-GMGranulopoiesis (Myeloblast, Promyelocyte, Myelocyte, Metamyelocyte, Band cell)
Monocytopoiesis (Monoblast, Promonocyte)Thrombopoiesis (Megakaryoblast, Promegakaryocyte)
Erythropoiesis (Proerythroblast, Normoblast, Reticulocyte)GeneralExtramedullary hematopoiesisHemostasis Other Erythrocyte aggregationCategories:- Blood
- Cell biology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

