- Demographics of Germany
-
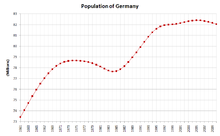 Population from 1961–2010. In years before 1990, the figures of the FRG and the GDR are combined
Population from 1961–2010. In years before 1990, the figures of the FRG and the GDR are combined
The Demographics of Germany were determined also by a series of full Census in Germany, with the most recent held in 1987. Since reunification, German authorities rely on a micro census.
The demography of the Federal Republic of Germany is monitored by the "Statistisches Bundesamt" (Federal Statistical Office of Germany). The population of Germany is approximately 81,880,000, making it the 14th most populous country in the world. Germany's population is characterized by zero or declining growth,[1] with an aging population and smaller cohort of youths. The total fertility rate was 1.4 in 2011.[2] Fertility was closely linked to educational achievement (with the less educated women having more children than the educated ones).[3] Persons, who adhere to no religion, have fewer children than Christians, also studies found that among Christians the more conservative ones had more children than the more liberal ones.[4][5]
While most child-births in Germany happen within marriage, a growing number of children is born out-of-wedlock. In 2010 the out-of-wedlock-rate was 33 percent, more than twice of what it was in 1990.[6]
More than 16 million people are of foreign/immigrant descent (first and second generation, including mixed heritage and ethnic German repatriates and their descendants). 96,1% of those reside in western Germany and Berlin.[7]
About seven million of them are foreign residents, which is defined as those not having German citizenship. The largest ethnic group of non-German origin are the Turkish. Since the 1960s, West and later reunified Germany has been attracting migrants primarily from Southern and Eastern Europe as well as Turkey, many of whom (or their children) over time acquired German citizenship. While most of these migrations had an economic background, Germany has also been a prime destination for refugees from many developing countries, in part because its constitution long had a clause giving a 'right' to political asylum, but restrictions over the years have since made it less attractive.
Within Germany, there is a long history of East-to-West migrations, starting with the 19th century Ostflucht. After the World War II border shifts and expulsions, the Germans from Eastern Europe and the former eastern territories moved westward to post-war Germany. During the partition of Germany, many Germans from East Germany fled to West Germany for political and also economic reasons. Since Germany's reunification, there are ongoing migrations from the eastern New Länder to the western Old Länder for economic reasons.
Germany has one of the world's highest levels of education, technological development, and economic productivity. Since the end of World War II, the number of students entering universities has more than tripled, and the trade and technical schools are among the world's best. With a per capita income of about $36.850 Purchasing power parity (in 2009),[2] Germany is a broadly middle class society. However there has been a strong increase in the children living in poverty in Germany. While in 1965 one in 75 children was on the welfare rolls in 2007 one in 6 was.[8] Those children live in relative poverty, but not in absolute poverty however. Germans also are very mobile; millions travel abroad each year. The social welfare system provides for universal health care, unemployment compensation, child benefits and other social programmes. Due to Germany's aging population and struggling economy, the welfare system came under a lot of strain in the 1990s. This led the government to adopt a wide-ranging programme of belt-tightening reforms, Agenda 2010, including the labour market reforms known as Hartz I - IV.
Contents
Major metropolitan regions
Main article: Metropolitan regions in GermanyGermany officially has eleven metropolitan regions. In 2005 Germany had 82 cities with more than 100,000 inhabitants.
City name Location Description Population (2004) Largest German ethnic groups Largest non-German ethnic groups Rhine-Ruhr Metropolitan Region 
Cologne is the largest city of the Rhineland, the very Western part of Germany. Particularly among young Germans, Cologne and Düsseldorf are known for their nightlife and open-minded atmosphere. 11.7 million Rhinelanders, Westfalians and others Turks, Poles, Italians, Dutch, French, Arabs, Iranians, South Asians like Indians, and Japanese (large Japanese community in Düsseldorf).[citation needed] Frankfurt Rhine-Main Region 
Frankfurt is the economic and financial center both for Germany and the continental European Union. It boasts a large airport and numerous skyscrapers. Within Germany, the city has a reputation of being very business-oriented, perhaps at the expense of other pursuits. 5.8 million Hessians and others Turks, Italians, Dutch, Arabs, Iranians, Greeks, Russians, Poles, Israelis, Koreans, Afghans, and Pakistanis (mostly Pashtun & Panjabi ethnic groups).[citation needed] Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region 
Berlin is the capital of Germany and its largest city. Berlin lies in the eastern part of the country and is regarded as one of Europe's most vibrant and ever changing capitals. It is also the 3rd most visited city in Europe. Additionally, it is Germany's most ethnically and culturally diverse city. 4.9 million Berliners, Prussians, Swabians, Bavarians etc. Turks, Arabs, Poles, Russians, Albanians, Serbs, Kurds, Vietnamese, Israelis, Chinese, rising number of Africans, Chileans, Brazilians and other Latin Americans.[citation needed] Munich Metropolitan Region 
Munich has Germany's highest standard of living. Countless sporting and leisure opportunities - both in the city and in its picturesque region. Munich is a powerhouse of the German economy and rich in Bavarian culture. 4.7 million Bavarians, Franconians and others Turks, Croats, Serbs, Dutch, Afghans, Greeks, Albanians, Macedonians, Italians, Bosnians, Hungarians, Spaniards and Romanians.[citation needed] Hamburg Metropolitan Region 
Hamburg is a free city state and the second largest city in Germany. It has a long tradition for sea trade and civil establishment and is home to Europe's 2nd largest port. The city is proud of its diverse nightlife and music scene centered in and around the famous St. Pauli district. According to European Union Statistics (EUROSTAT) it is Germany's richest city. 4.3 million Hamburgers, Schleswiger, Holsteiner, Lower Saxons and others Turks, Russians, Albanians, Dutch, Poles, Pakistanis, Iranians, Macedonians, Chinese, Portuguese, Afghans, Africans[citation needed] Southern Lower Saxony: Hannover–Braunschweig–Göttingen–Wolfsburg Metropolitan Region The relatively urban south of Lower Saxony, located on route between the Ruhr area and Berlin, and the route form Hamburg to the south, has been important for logistics, industry, but also developed a strong standing in the service industries. 3.9 million Lower Saxons, Eastphalians and others Turks, Poles, Kurds (especially around Celle), Serbs, Ukrainians, Greeks, Russians, Italians (especially in Wolfsburg) and Spanish (Especially in Hanover).[citation needed] Leipzig-Halle-Dresden (Saxon Triangle) 
Also dubbed "City of Heroes", Leipzig is where the 1989 revolution that brought down the Berlin Wall started. Today totally refurbished, it sports Europe's highest density of Art Nouveau architecture.[citation needed] Very lively bar scene, fastest growing economy in Germany. 3.5 million Saxons and others Vietnamese, Indians, Poles, Russians, Portuguese, Italians, Iranians, Turks, Dutch, Arabs and Pakistanis.[citation needed] Stuttgart Metropolitan Region 
Stuttgart has a reputation for research, inventions and industry. The German headquarters of many international enterprises are in Stuttgart. This contrasts with the strong rural, down-to-earth attitude of the Stuttgarters throughout the classes. A popular slogan is "We are good at everything. Except speaking High (standard) German." 3.5 million Swabians and others Turks, Greeks, Dutch, Italians, Croats, Serbs, French, Chinese, Romanians, Americans and Spaniards.[citation needed] Bremen/Oldenburg Metropolitan Region 
Located in the northwestern part of Germany, the main axis contains the cities of Bremen, Delmenhorst and Oldenburg, with the cities of Wilhelmshaven and Bremerhaven being the northern corners at the north sea. Major rural areas are covered in between these cities. There is a smooth transition to the Hamburg metropolitan area to the east. 2.4 million Lower Saxons, Frisians and others Turks, Russians, Poles, Albanians, Serbs, Portuguese, Iranians, Dutch, Americans and Britons.[citation needed] Ethnic groups
 Turkish parade in Berlin
Turkish parade in Berlin
 A guest worker from Cuba, working in an East German factory (Chemiefaserkombinat "Wilhelm Pieck"), 1986
A guest worker from Cuba, working in an East German factory (Chemiefaserkombinat "Wilhelm Pieck"), 1986 A person like Simone Hauswald, who has a German and a Korean parent, is considered a "persons with immigrant background" in German statistics even if they themselves are born in Germany. Another statistical term that is used to classify person with one German and one Asian parent is Eurasian
A person like Simone Hauswald, who has a German and a Korean parent, is considered a "persons with immigrant background" in German statistics even if they themselves are born in Germany. Another statistical term that is used to classify person with one German and one Asian parent is Eurasian
In 2005: Total population = 82 million[9]
In 2009 3.0 million of the persons of immigrant background had Turkish roots, 2.9 million had their roots in the successor states of the former Soviet Union, 1.5 million had their roots in the successor states of former Yugoslavia and 1.5 million had Polish roots.[11]
In 2008 18.4% of Germans of any age group and 30% of German children had at least one parent born abroad. Median age for Germans with at least one parent born abroad was 33.8 years, while that for Germans, who had two parents born in Germany was 44.6 years.[12]
Four other sizable groups of people are referred to as "national minorities" (nationale Minderheiten) because they have lived in their respective regions for centuries: Danes, Frisians, Roma and Sinti, and Sorbs. There is a Danish minority (about 50,000, according to government sources) in the northern-most state of Schleswig-Holstein. Eastern and Northern Frisians live at Schleswig-Holstein's western coast, and in the north-western part of Lower Saxony. They are part of a wider community (Frisia) stretching from Germany to the northern Netherlands. The Sorbs, a Slavic people with about 60,000 members (according to government sources), are in the Lusatia region of Saxony and Brandenburg. They are the last remnants of the Slavs that lived in central and eastern Germany since the 7th century.
Until World War II the Poles were recognized as one of the national minorities. In 1924 the Union of Poles in Germany had initiated cooperation between all national minorities in Germany under the umbrella organization Association of National Minorities in Germany. Some of the union members wanted the Polish communities in easternmost Germany (now Poland) to join the newly established Polish nation after World War I.[citation needed] Even before the German invasion of Poland, leading anti-Nazi members of the Polish minority were deported to concentration camps; some were executed at the Piaśnica murder site. Minority rights for Poles in Germany were revoked by Hermann Göring's World War II decree of 27 February 1940, and their property was confiscated. Adolf Hitler was known to also disliked Polish and Slavic peoples and even considered Polish-Germans alike to be Untermenschen along side with Jews and Roma people.[citation needed] Despite the war ended in 1945, the German government never cancelled the Nazi regulations outlawing the union and denying Poles living in Germany their minority rights, and despite being now a signatory to the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities, continues to deny them. In contrast, Germans living in Poland are recognized as national minority and have granted seats in Polish Parliament.[13][14]
Roma people have been in Germany since the Middle Ages. They were persecuted by the Nazis, and thousands of Roma living in Germany were killed by the Nazi regime. Nowadays, they are spread all over Germany, mostly living in major cities. It is difficult to estimate their exact number, as the German government counts them as "persons without immigration background" in their statistics. There are also many assimilated Sinti and Roma. A vague figure given by the German Department of the Interior is about 70,000. In the late 1990s, many Roma moved to Germany from Kosovo. In contrast to the old-established Roma population, the majority of them do not have German citizenship, they are classified as immigrants or refugees.
After World War II, 14 million ethnic Germans were expelled from the eastern territories of Germany and homelands outside former German Empire. The accommodation and integration of these Heimatvertriebene in the remaining part of Germany, in which many cities and millions of apartments had been destroyed, was a major effort in the post-war occupation zones and later states of Germany.
Since the 1960s, ethnic Germans from the People's Republic of Poland and Soviet Union (especially from Kazakhstan, Russia, and Ukraine), have come to Germany. During the time of Perestroika, and after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the number of immigrants increased heavily. Some of these immigrants are of mixed ancestry. During the 10 year period between 1987 and 2001, a total of 1,981,732 ethnic Germans from the FSU immigrated to Germany, along with more than a million of their non-German relatives. After 1997, however Ethnic Slavs or those belonging to Slavic-Germanic mixed origins outnumbered these with only Germanic descent amongst the immigrants. The total number of people currently living in Germany having FSU connection is around 4 to 4.5 million (Including Germans, Slavs, Jews and those of mixed origins), out of that more than 50% is of German descent.[15][16]
Germany now has Europe's third-largest Jewish population. In 2004, twice as many Jews from former Soviet republics settled in Germany as in Israel, bringing the total inflow to more than 200,000 since 1991. Jews have a voice in German public life through the Zentralrat der Juden in Deutschland. Some Jews from the former Soviet Union are of mixed heritage.
In the year 2000 there were also around 300,000-500,000 Afro-Germans (those who have German citizenship)[17] and 150,000+ African nationals. Most of them live in Berlin and Hamburg. Numerous persons from Tunisia and Morocco live in Germany, which in most cases do not considers themselve "Afro-Germans" and are not considered "Afro-Germans" by the German public despite the fact they come from Northern Africa, because they look different and have a different culture. However, Germany does not keep any statistics regarding ethnicity or race. Hence, the exact number of Blacks or Afro-Germans in particular, is unknown.
Germany's biggest East Asian minority are the Vietnamese people in Germany. About 40,000 Vietnamese live in Berlin and surroundings. Also there are about 20,000 to 25,000 Japanese people residing in Germany. Some South Asian and Southeast Asian immigration has took place. Nearly 50,000 Indians live in Germany. As of 2008, there were 68,000 Filipino residents and an unknown number of Indonesians residing in Germany.[18]
Numerous descedants of the so called Gastarbeiter live in Germany. The Gastarbeiter mostly came from Chile, Greece, Italy, Morocco, Portugal, Spain, Tunisia, Turkey (the most numerous non-European and non-Western nationality) and the former Yugoslavia. Also included were Vietnam, Mongolia, North Korea, Angola, Mozambique and Cuba when the former East Germany existed until reunification in 1990.[19] The (socialist) German democratic republic (East Germany) however had their guest-worker stay in single sex dormitories[20] Female guest workers had to sign treaties saying that they were not allowed to fall pregnant during their stay in. If they fell pregnant nevertheless they faced forced abortion or deportion.[21] This is one of the reasons why the vast majority of ethnic minorities today lives in western Germany and also one of the reasons why minorities such as the Vietnamese have the most unusual population pyramid, with nearly all second generation Vietnamese Germans born after 1989.
In German statistics a person, who has at least one parent born abroad will be counted as a person with immigrant background. That is also the case if the other parent is German and the person himself or herself has been born in Germany and holds the German citizenship.[22] If a person born in Germany holding the German citizenship, for example, has one German and one Korean parent, he or she will be counted "German with Korean immigrant background", "German with (East-)Asian immigrant background" or "Eurasian". Another category used is "East Asian including Eurasian".
Vital statistics since 1900[23]
Note: territorial changes occurred in 1918/1919, 1921/1922 and 1945/1946.
Average population (x 1000) Live births Deaths Natural change Crude birth rate (per 1000) Crude death rate (per 1000) Natural change (per 1000) 1900 54 326 1944 139 1199 382 744 757 35.8 22.1 13.7 1901 55 144 1980 313 1140 489 839 824 35.9 20.7 15.2 1902 56 017 1971 735 1088 492 883 243 35.2 19.4 15.8 1903 56 869 1931 078 1135 905 795 173 34.0 20.0 14.0 1904 57 695 1972 847 1128 183 844 664 34.2 19.6 14.6 1905 58 514 1935 153 1158 314 776 839 33.1 19.8 13.3 1906 59 343 1970 477 1078 202 892 275 33.2 18.2 15.0 1907 60 183 1948 933 1084 309 864 624 32.4 18.0 14.4 1908 61 023 1964 052 1100 490 863 562 32.2 18.0 14.2 1909 61 857 1929 278 1062 217 867 061 31.2 17.2 14.0 1910 62 698 1876 778 1016 665 860 113 29.9 16.2 13.7 1911 63 469 1824 729 1097 784 726 945 28.7 17.3 11.5 1912 64 236 1823 636 1000 749 822 887 28.4 15.6 12.8 1913 65 058 1794 750 975 950 818 800 27.6 15.0 12.6 1914 65 860 1775 596 1246 310 529 286 27.0 18.9 8.0 1915 65 953 1353 546 1410 420 -56 874 20.5 21.4 -0.9 1916 65 795 1005 484 1258 054 -252 570 15.3 19.1 -3.8 1917 65 450 912 109 1345 424 -433 315 13.9 20.6 -6.6 1918 64 800 926 813 1606 475 -679 662 14.3 24.8 -10.5 1919 62 897 1260 500 978 380 282 120 20.0 15.6 4.5 1920 61 794 1599 287 932 929 666 358 25.9 15.1 10.8 1921 62 473 1581 130 869 555 711 575 25.3 13.9 11.4 1922 61 890 1425 000 890 000 535 000 23.0 14.4 8.6 1923 62 250 1318 000 867 000 451 000 21.2 13.9 7.2 1924 62 740 1291 000 767 000 524 000 20.6 12.2 8.4 1925 63 110 1311 000 753 000 558 000 20.8 11.9 8.8 1926 63 510 1245 000 743 000 502 000 19.6 11.7 7.9 1927 63 940 1179 000 765 000 414 000 18.4 12.0 6.5 1928 64 470 1200 000 747 000 453 000 18.6 11.6 7.0 1929 64 670 1164 000 815 000 349 000 18.0 12.6 5.4 1930 65 130 1144 000 719 000 425 000 17.6 11.0 6.5 1931 65 510 1048 000 734 000 314 000 16.0 11.2 4.8 1932 65 716 993 000 708 000 285 000 15.1 10.8 4.3 1933 66 027 971 000 738 000 233 000 14.7 11.2 3.5 1934 66 409 1198 350 725 000 473 000 18.0 10.9 7.1 1935 66 871 1263 976 792 018 471 958 18.9 11.8 7.1 1936 67 349 1278 583 795 793 482 790 19.0 11.8 7.2 1937 67 831 1277 046 794 367 482 679 18.8 11.7 7.1 1938 68 424 1348 534 799 220 549 314 19.7 11.7 8.0 1939 69 314 1413 230 854 348 558 882 20.4 12.3 8.1 1940 69 838 1402 258 885 591 516 667 20.1 12.7 7.4 1941 70 244 1308 232 844 435 463 797 18.6 12.0 6.6 1942 70 834 1055 915 847 861 208 054 14.9 12.0 2.9 1943 70 411 1124 718 853 246 271 472 16.0 12.1 3.9 1944 69 000 1215 000 915 000 300 000 17.6 13.3 4.3 1945 66 000 1060 000 1210 000 -150 000 16.1 18.3 -2.3 1946 64 260 921 998 1001 331 -79 333 14.3 15.6 -1.2 1947 65 842 1028 421 932 628 95 793 15.6 14.2 1.5 1948 67 365 1049 074 804 839 244 235 15.6 11.9 3.6 1949 68 080 1106 803 770 852 335 951 16.3 11.3 4.9 1950 68 374 1116 835 748 329 368 506 16.3 10.9 5.4 1951 68 882 1106 608 752 697 353 911 16.1 10.9 5.1 1952 69 171 1105 080 767 637 337 443 16.0 11.1 4.9 1953 69 564 1095 096 790 654 304 442 15.7 11.4 4.4 1954 69 934 1110 028 775 291 334 737 15.9 11.1 4.8 1955 70 307 1113 128 795 938 317 190 15.8 11.3 4.5 1956 70 711 1137 169 812 111 325 058 16.1 11.5 4.6 1957 71 166 1165 555 840 195 325 360 16.4 11.8 4.6 1958 71 637 1175 870 818 418 357 452 16.4 11.4 5.0 1959 72 180 1243 922 835 402 408 520 17.2 11.6 5.7 1960 72 664 1261 614 876 721 384 893 17.4 12.1 5.3 1961 73 352 1313 505 850 300 463 205 17.9 11.6 6.3 1962 74 049 1316 534 878 814 437 720 17.8 11.9 5.9 1963 75 019 1355 595 895 070 460 525 18.1 11.9 6.1 1964 75 273 1357 304 870 319 486 985 18.0 11.6 6.5 1965 76 061 1325 386 907 882 417 504 17.4 11.9 5.5 1966 76 734 1318 303 911 984 406 319 17.2 11.9 5.3 1967 76 954 1272 276 914 417 357 859 16.5 11.9 4.7 1968 77 249 1214 968 976 521 238 447 15.7 12.6 3.1 1969 77 918 1142 368 988 092 154 276 14.7 12.7 2.0 1970 77 772 1047 737 975 664 72 073 13.5 12.5 0.9 1971 78 355 1013 396 965 623 47 773 12.9 12.3 0.6 1972 78 717 901 657 965 689 -64 032 11.5 12.3 -0.8 1973 78 951 815 969 963 034 -147 065 10.3 12.2 -1.9 1974 78 966 805 500 956 573 -151 073 10.2 12.1 -1.9 1975 78 862 782 310 989 649 -207 339 9.9 12.5 -2.6 1976 78 299 798 334 966 873 -168 539 10.2 12.3 -2.2 1977 78 161 805 496 931 155 -125 659 10.3 11.9 -1.6 1978 78 066 808 619 955 550 -146 931 10.4 12.2 -1.9 1979 78 082 817 217 944 474 -127 257 10.5 12.1 -1.6 1980 78 295 865 789 952 371 -86 582 11.1 12.2 -1.1 1981 78 399 862 100 954 436 -92 336 11.0 12.2 -1.2 1982 78 293 861 275 943 832 -82 557 11.0 12.1 -1.1 1983 78 082 827 933 941 032 -113 099 10.6 12.1 -1.4 1984 77 797 812 292 917 299 -105 007 10.4 11.8 -1.3 1985 77 619 813 803 929 649 -115 846 10.5 12.0 -1.5 1986 77 635 848 231 925 411 -77 180 10.9 11.9 -1.0 1987 77 718 867 969 901 291 -33 322 11.2 11.6 -0.4 1988 78 116 892 993 900 627 -7 634 11.4 11.5 -0.1 1989 78 677 880 459 903 441 -22 103 11.2 11.5 -0.3 1990 79 365 905 675 914 361 -15 800 11.4 11.5 -0.2 1991 79 984 830 019 911 245 -81 226 10.4 11.4 -1.0 1992 80 570 809 114 885 443 -76 329 10.0 11.0 -0.9 1993 81 187 798 447 897 270 -98 823 9.8 11.1 -1.2 1994 81 422 769 603 884 659 -115 056 9.5 10.9 -1.4 1995 81 661 765 221 884 588 -119 367 9.4 10.8 -1.5 1996 81 896 796 013 882 843 -86 830 9.7 10.8 -1.1 1997 82 061 812 173 860 389 -48 216 9.9 10.5 -0.6 1998 82 024 785 034 852 382 -67 348 9.6 10.4 -0.8 1999 82 101 770 744 846 330 -75 586 9.4 10.3 -0.9 2000 82 213 766 999 838 797 -71 798 9.3 10.2 -0.9 2001 82 350 734 475 828 541 -94 066 8.9 10.1 -1.1 2002 82 489 719 250 841 673 -122 423 8.7 10.2 -1.5 2003 82 541 706 721 853 946 -147 225 8.6 10.3 -1.8 2004 82 517 705 622 818 271 -112 649 8.6 9.9 -1.4 2005 82 470 685 795 830 227 -144 432 8.3 10.1 -1.8 2006 82 377 672 724 821 627 -148 903 8.2 10.0 -1.8 2007 82 267 684 862 827 155 -142 293 8.3 10.1 -1.7 2008 82 110 682 514 844 439 -161 925 8.3 10.3 -2.1 2009 81 901 665 126 854 544 -189 418 8.1 10.4 -2.3 2010[24] 677 947 858 768 -180 821 8.3 10.5 New federal states
See also: New federal statesAbout 1.7 million people have left the new federal states since the fall of the Berlin Wall, or 12% of the population,[25] a disproportionately high number of them were women under 35.[26]
After 1990, the fertility rate in the East dropped to 0.77. In 2006, the rates in the new states (1.30) are approaching those in the West (1.37).[27] Since 1989, about 2,000 schools have closed because of a scarcity of children.[25]
In some regions the number of women between the ages of 20 and 30 has dropped by more than 30 percent.[25] In 2004, in the age group 18-29 (statistically important for starting families) there were only 90 women for every 100 men in the new federal states (including Berlin).[27]
Immigration
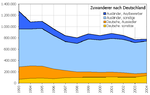
Main article: Immigration to GermanyFurther information: Germans AbroadIn its State of World Population 2006 report, the United Nations Population Fund lists Germany with hosting the third-highest percentage of the main international migrants worldwide, about 5% or 10 million of all 191 million migrants.[28]
Agreements
Germany had previously signed special visa agreements with several countries in times of severe labour shortages or when particular skills were deficient within the country. During the 60s & 70s, agreements were signed with the governments of Turkey, Yugoslavia and Spain to help Germany overcome its severe labour shortage.
Religions
Main article: Religion in GermanyRoman Catholic 31.4%, Evangelical Church in Germany 30.8%, Nonreligious 29.6%, Muslim 5.4%, Orthodox 2%[29] Roman Catholic is mainly in the South East (Southern Bavaria) and the Far West (Rheinland & Cologne). Strongholds of Protestants are in all Northern States. Muslim, Orthodox and Jewish minority communities are mainly in the big cities.
Languages
Main article: Languages of GermanyGerman is the only official and most widely spoken language. Standard German is understood throughout the country.
Minority languages
Danish, Low German, the Sorbian languages (Lower Sorbian and Upper Sorbian), and the two Frisian languages, Saterfrisian and North Frisian, are officially recognized and protected as minority languages by the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages in their respective regions. With speakers of Romany are living in all parts of Germany, the federal government has promised to take action to protect the language. Until now, only Hesse has followed Berlin's announcement, and agreed on implementing concrete measures to support Romany speakers.
Implementation of the Charter is poor. The monitoring reports on charter implementation in Germany show many provisions unfulfilled.[30]
Minority language recognition
Protected Minority Languages in Germany Language States Danish Schleswig-Holstein North Frisian Schleswig-Holstein Saterland Frisian Lower Saxony Low German Brandenburg, Bremen, Hamburg, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, Schleswig-Holstein, North Rhine-Westphalia Upper Sorbian Saxony Lower Sorbian Brandenburg Romany Hesse (see text) High German dialects
 City limits sign; this city is called Emlichheim in High German and Emmelkamp in Low German
City limits sign; this city is called Emlichheim in High German and Emmelkamp in Low German
German dialects — some quite distinct from the standard language — are used in everyday speech, especially in rural regions. Many dialects, for example the Upper German varieties, are to some degree cultivated as symbols of regional identity and have their own literature, theaters and some few TV programming. While someone speaking dialect outside his home area might be frowned upon, in their original area some dialects can be spoken throughout all social classes. Nevertheless, partly due to Standard German media prevalence, their use has declined over the past century, especially in the younger population.
The status of different German dialects can be very different. The Alemannic and Bavarian dialects of the south are positively valued by the speakers and can be used in almost all social circumstances. The Saxonian and Thuringian dialects have less prestige and are subject to derision. While Bavarian and Alemannic have kept much of their distinctiveness, the Middle German dialects, which are closer to Standard German, lost some of their distinctive lexical and grammatical features and tend to be only pronunciation variants of Standard German.
Low Saxon dialects
Low Saxon is officially recognized as a language on its own, but despite this fact, there's little official action taken on fostering the language. Historically one third of Germany's territory and population was Low Saxon speaking. No data was ever collected on the actual number of speakers, but today the number of speakers ranges around 5 million persons. Despite this relatively high number of speakers there is very little coverage in the media (mostly on NDR TV, no regular programming) and very little education in or on the language. The language is not fixed as part of the school curriculum and Low Saxon is used as a medium of instruction in one school only in the whole Germany (as a "model project" in primary school sided by education in Standard German). As a consequence the younger generation refused to adopt the native language of their parents. Language prevalence dropped from more than 90% (depending on the exact region) in the 1930s to less than 5% today. This accounts for a massive intergenerational gap in language use. Older people regularly use the language and take private initiative to maintain the language, but the lack of innovative potential of the younger generation hinders language maintenance. The language too has an own literature (around 150 published books every year) and there are many theatres (mostly lay stages, but some professional ones, like for example Ohnsorg-Theater).
Use of Low Saxon is mainly restricted to use under acquaintances, like family members, neighbours and friends. A meeting of a village council can be held almost completely in Low Saxon if all participants know each other (as long as written protocols are written in Standard German), but a single foreigner can make the whole switching to Standard German.
The Low Saxon dialects are different in their status too. There's a north-south gradient in language maintenance. The Southern dialects of Westfalian, Eastfalian and Brandenburgish have had much stronger speaker losses, than the northern coastal dialects of Northern Low Saxon. While Eastfalian has lost speakers to Standard German, Westfalian has lost speakers to Standard German and Standard German based regiolect of the Rhine-Ruhr area. Brandenburgish speakers mostly switched to the Standard German based regiolect of Berlin. Brandenburgish is almost completely replaced by the Berlin regiolect. Northern Low Saxon speakers switched mostly to pure Standard German.
Foreign languages
English is the most common foreign language and almost universally taught by the secondary level, also taught at elementary level in some states. Other languages taught are French, Italian, Spanish, Portuguese, and Russian. Dutch is taught in states bordering the Netherlands and Polish in the case of the eastern states facing Poland. Latin and Ancient Greek are part of the classical education syllabus offered in many secondary schools.
According to a 2004 survey, two-thirds of Germany's citizens have at least basic knowledge of English. About 20% consider themselves to be speakers of French, followed by speakers of Russian (7%), Italian (6.1%), and Spanish (5.6%). The relatively high number of Russian speakers is a result of massive immigration from the former Soviet Union to Germany for almost 10 consecutive years — more than half of the Germans in the East learned Russian at school.
Literacy
Over 99% of those of age 15 and above are estimated to be able to read and write. However, a growing number of inhabitants are functionally illiterate. The young are much more likely to be functionally illiterate than the old. According to a study done by the University of Bremen in coorporation with the "Bundesverband Alphabetisierung e.V.", ten percent of youngsters living in Germany are illiterate and one quarter was able to understand only basic level texts.[31] Illiteracy rates of youngsters vary by ethnic group and parents' socioeconomic class.
Demographic statistics and policies
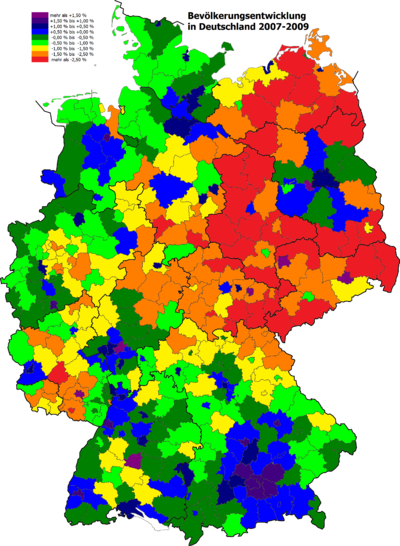 Change of population by districts between 2007 and 2009, highlighting the continued depopulation of the former East Germany and the growth of German suburbia
Change of population by districts between 2007 and 2009, highlighting the continued depopulation of the former East Germany and the growth of German suburbia
 two medical students and their triplets in the GDR in 1984; the GDR encouraged birth among college students
two medical students and their triplets in the GDR in 1984; the GDR encouraged birth among college students
The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.
- Population
82,329,758 (July 2010 est.)
- Age structure
- 0–14 years: 13.9% (male 5,894,724/female 5,590,373)
- 15–64 years: 66.3% (male 27,811,357/female 26,790,222)
- 65 years and over: 19.8% (male 6,771,972/female 9,542,348) (2007 est.)
- 0–14 years: 13.7% (male 5,768,366/female 5,470,516)
- 15–64 years: 66.1% (male 27,707,761/female 26,676,759)
- 65 years and over: 20.3% (male 7,004,805/female 9,701,551) (2010est.)
- Sex ratio
- at birth: 1.06 male(s)/female
- under 15 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
- 15–64 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over: 0.72 male(s)/female
- total population: 0.97 male(s)/female (2010 est.)
- Infant mortality rate
4.09 deaths per 1,000 live births (2007)
total: 3.99 deaths/1,000 live births (2010)
- Life expectancy at birth
total population: 79.26 years (2010)
- Total fertility rate
1.38 children born/woman (2008)
1.42 children born/woman (2010 est.)
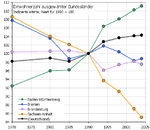
The Mikrozensus done in 2008 revealed that the number of children a German woman aged 40 to 75 had, was closely linked to her educational achievement.[3] In Western Germany the most educated women were the most likely to be childless. 26% of those groups stated they were childless, while only 16% of those having an intermediate education, and 11% of those having compulsory education stated the same. In Eastern Germany however, only 9% of the most educated women of that age group and only 7% of those who had a intermediary education were childless, while 12% of those having only compulsory education were childless. The reason for that east-western difference is the fact that the GDR had an "educated mother scheme" and actively tried to encourage first births among the more educated. It did so by propagandizing the opinion that every educated woman should "present at least one child to socialism" and also by financially rewarding its more educated citizen to become parents. The government especially tried to persuade students to become parents while still in college and it was quite successful in doing so. In 1986 38% of all women, who were about to graduate from college, were mothers of at least one child and additional 14% were pregnant and 43% of all men, who were about to graduate from college, were fathers of at least one child. There was a sharp decline in the birth rate and especially in the birth rate of the educated after the fall of the Berlin wall. Nowadays only 5% of those about to graduate from college are parents.
The more educated a Western German mother aged 40 to 75 is, the less likely she is to have a big family.
Percent of Western German mothers having 1, 2 and 3 and more children by educational attainment number of children compulsory education intermediary education highest education one child 22 30 31 two children 39 48 48 three or more children 39 22 21 [32] The same is true for a mother living in Eastern Germany.
Percent of Eastern German mothers having 1, 2 and 3 and more children by educational attainment number of children compulsory education intermediary education highest education one child 23 33 33 two children 37 46 51 three or more children 40 21 16 [32] References
- ^ "Population Handbook, 5th edition". Population Reference Bureau. http://www.prb.org/pdf/PopHandbook_Eng.pdf.
- ^ a b Länderdatenbank Deutschland
- ^ a b Statistisches Bundesamt. Mikrozensus 2008. Neue Daten zur Kinderlosigkeit in Deutschland. p. 27ff
- ^ Michael Blume, Carsten Ramsel, Sven Graupner: Religiosität als demografischer Faktor – Ein unterschätzter Zusammenhang?. Marburg Journal of Religion: Volume 11, No. 1 (June 2006) [www.blume-religionswissenschaft.de/pdf/blume_germ2006.pdf]
- ^ Michael Blume (2008) Homo religiosus, Gehirn und Geist 04/2009. S. 32–41.
- ^ Handelsblatt (August 12th 2011): "Familienplanung: Uneheliche Babys im Vormarsch" [1]
- ^ Bundeszentrale für politische Bildung: "Die soziale Situation in Deutschland: Bevölkerung mit Migrationshintergrund I
- ^ "Sozialhilfe: Kinderarmut nimmt zu". Focus. 15.11.2007
- ^ a b c d Germans and foreigners with an immigrant background by Federal Ministry of the Interior [2]
- ^ Federal Statistics Office - Foreign population
- ^ Bundeszentrale für politische Bildung: "Die soziale Situation in Deutschland - Bevölkerung mit Migrationshintergrund I"
- ^ Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland: "Leichter Anstieg der Bevölkerung mit Migrationshintergrund". Pressemitteilung Nr.105 vom 11.03.2008
- ^ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polish_minority_in_Germany
- ^ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Union_of_Poles_in_Germany#World_War_II_and_after
- ^ http://www.iza.org/iza/en/papers/transatlantic/1_locher.pdf
- ^ http://www.odessa3.org/journal/pohl.pdf
- ^ Nina Zimnik: Nicht jeder Deutsche ist automatisch weiß „Hamburger Abendblatt“ vom 15. August 2000
- ^ http://www.manilatimes.net/national/2008/mar/12/yehey/top_stories/20080312top6.html
- ^ http://www.migrationinformation.org/Profiles/display.cfm?id=235
- ^ Stephan Lanz: "Berlin aufgemischt - abendländisch - multikulturell - kosmopolitisch? Die politische Konstruktion einer Einwanderungsstadt". 2007. Bielefeld: transcript Verlag; p. 113
- ^ Karin Weiss: "Die Einbindung ehemaliger vietnamesischer Vertragsarbeiterinnen und Vertragsarbeiter in Strukturen der Selbstorganisation", In: Almut Zwengel: "Die "Gastarbeiter der DDR - politischer Kontext und Lebenswelt". Studien zur DDR Gesellschaft; p. 264
- ^ Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland: Bevölkerung und Erwerbstätigkeit. Bevölkerung mit Migrationshintergrund – Ergebnisse des Mikrozensus 2005. Erschienen am 4. Mai 2007
- ^ Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland
- ^ http://www.destatis.de/jetspeed/portal/cms/Sites/destatis/Internet/EN/Content/Statistics/Bevoelkerung/GeburtenSterbefaelle/Tabellen/Content75/BirthDeaths,templateId=renderPrint.psml
- ^ a b c Kulish (2009-06-19). "In East Germany, a Decline as Stark as a Wall". New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2009/06/19/world/europe/19germany.html. Retrieved October 11, 2009.
- ^ "Lack of Women in Eastern Germany Feeds Neo-Nazis". Spiegel International. 2007-05-31. http://www.spiegel.de/international/germany/0,1518,485942,00.html. Retrieved 2009-10-11.
- ^ a b "The Demographic State of the Nation". Berlin Institute for Population and Development. 2006. http://www.berlin-institut.org/fileadmin/user_upload/Studien/Kurzfassung_demografische_lage_englisch.pdf. Retrieved 2009-10-11.
- ^ United Nations Population Fund: State of World Population 2006
- ^ Religionen in Deutschland - Mitglieder und Anhänger .::. REMID
- ^ http://www.coe.int/t/e/legal_affairs/local_and_regional_democracy/regional_or_minority_languages/2_monitoring/2.3_Committee_of_Experts%27_Reports/Germany_2nd_report.pdf
- ^ Teachers News: "Funktionaler Analphabetismus"
- ^ a b Statistisches Bundesamt. Mikrozensus 2008. Neue Daten zur Kinderlosigkeit in Deutschland. p.29
External links
- Homepage of the Federal Statistical Office Germany (in English)
- German demographics in Online-Databank HISTAT (in German, Registration needed)
- Dossier "The Aging Society" of the Goethe-Institut
- Demographic Profile Germany: United in Decline Allianz Knowledge
Demographics of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territories- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jan Mayen
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
Other entities - European Union
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.