- Red eye (medicine)
-
For other uses, see Red eye (disambiguation).
Red eye (medicine) Classification and external resources
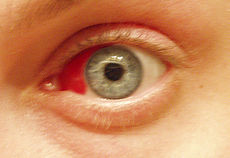
Subconjunctival hemorrhage causing red coloration as result of ruptured blood vessel in the eye.ICD-10 H57.9 ICD-9 379.93 DiseasesDB 18665 In medicine, red eye is a non-specific term to describe an eye that appears red due to illness, injury, or some other condition. Conjunctivitis and subconjunctival hemorrhage are two forms of a red eye.
Since it is a common affliction, primary care doctors often deal with patients with red eyes in their practices. The goal of the primary care doctor when presented with a red eye is to assess whether it is an emergency in need of referral and immediate action, or instead a benign condition that can be managed easily and effectively.
Red eye usually refers to hyperemia of the superficial blood vessels of the conjunctiva, sclera or episclera, and may be caused by diseases or disorders of these structures or adjacent structures that may affect them directly or indirectly.
Contents
Differential diagnosis
There are many causes of a red eye. The most common is conjunctivitis.[1] Others include blepharitis, acute glaucoma, injury, subconjunctival hemorrhage, keratitis, iritis, episcleritis, scleritis, inflamed pterygium, inflamed pinguecula, dry eye syndrome, airborne contaminants, a burst blood vessel, tick borne illnesses like Rocky Mountain spotted fever,[2] high stress levels and drug use including cannabis.
Diagnostic approach
Some signs and symptoms of red eye represent warnings that the underlying cause is serious and requires immediate attention. The person conducting a thorough eye examination should be attentive to the warning signs and symptoms during the eye exam.
There are six danger signs: conjunctival injection, ciliary flush (circumcorneal injection), corneal edema or opacities, corneal staining, abnormal pupil size, and abnormal intraocular pressure.
Visual acuity
Reduced visual acuity is indicative of serious ocular disease, such as corneal inflammation, iridocyclitis, and glaucoma, and never occurs in simple conjunctivitis without concurrent corneal involvement.
Ciliary flush
Ciliary flush is usually present in eyes with corneal inflammation, iridocyclitis or acute glaucoma, though not simple conjunctivitis. A ciliary flush is a ring of red or violet around the cornea of the eye.
Corneal opacification
Corneal opacities always indicate that a serious disease process is in progress. Opacification may be detected using an ophthalmoscope or, in more obvious cases, with a pen light. These opacities may be keratic, haze-like (usually from corneal edema), or they may be localized such as with ulcerated corneas or those affected by keratitis.
Corneal epithelial disruption
Corneal epithelial disruptions may be detected with fluorescein staining of the eye, and careful observation with cobalt-blue light. Corneal epithelial disruptions would stain green, which represents some injury of the corneal epithelium. These types of disruptions may be due to corneal inflammations or physical trauma to the cornea.
Pupillary abnormalities
An eye with iridocyclitis would have one pupil that is smaller than the other, which is caused by a reflex muscle spasm of the iris sphincter muscle. As is the general rule, conjunctivitis does not affect the pupils. With acute angle-closure glaucoma, the pupil would be partially dilated and oval.
Shallow anterior chamber depth
Shallow anterior chamber depth usually indicates some problem. If the eye is red, anterior chamber depth may indicate acute glaucoma, which requires immediate attention.
Abnormal intraocular pressure
Intraocular pressure should be measured as part of the routine eye examination. It is usually affected only by iridocyclitis or acute-closure glaucoma, but not by relatively benign conditions. In iritis and traumatic perforating ocular injuries, pressure is usually low.
Proptosis
Proptosis, or forward displacement of the globe, may be caused by an infection of the orbit, or a cavernous sinus disease. Most commonly, chronic proptosis is caused by thyroid diseases such as Graves disease.
Important warning symptoms
There are three main danger symptoms in a red eye: reduced visual acuity, severe ocular pain, and photophobia (light sensitivity).
Blurry vision
Blurry vision often indicates serious ocular disease. If the blurriness improves with blinking, it suggests ocular surface discharge of some variety. See a doctor if it gets worse.
Severe pain
Those suffering from conjunctivitis may report mild irritation or scratchiness, but never extreme pain. Severe pain is an indicator of keratitis, corneal ulceration, iridocyclitis, or acute glaucoma.
Photophobia
Photophobia (fear of light) is most characteristic of iritis, but may also depend on acute glaucoma.
Coloured halos
Coloured halos are an indication of corneal edema, and are a warning that acute glaucoma may be present.
References
- ^ Cronau, H; Kankanala, RR, Mauger, T (2010 Jan 15). "Diagnosis and management of red eye in primary care.". American family physician 81 (2): 137–44. PMID 20082509.
- ^ http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/pdf/rr/rr5504.pdf
See also
- List of eye diseases and disorders
Categories:- Medical emergencies
- Diseases of the eye and adnexa
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.