- Hypertensive retinopathy
-
Hypertensive retinopathy Classification and external resources 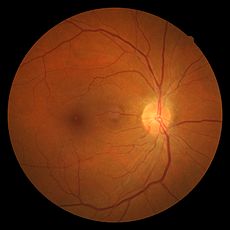
Hypertensive retinopathy with AV nicking and mild vascular tortuosityICD-10 H35.0 ICD-9 362.11 Hypertensive retinopathy is damage to the retina due to high blood pressure (i.e. hypertension).
Contents
Pathophysiology
The retina is one of the "target organs" that are damaged by sustained hypertension. Subjected to excessively high blood pressure over prolonged time, the small blood vessels that involve the eye are damaged, thickening, bulging and leaking.
Early signs of retinopathy correlate less well with mortality and morbidity than used to be thought, but signs of accelerated or "malignant" hypertension indicate severe illness.
Symptoms
Most patients with hypertensive retinopathy present without visual symptoms, however, some may report decreased vision or headaches.
Signs
Signs of damage to the retina caused by hypertension include:
- Arteriosclerotic changes
- Arteriolar narrowing that is almost always bilateral. (The following grading system is specific to the degree of the arteriolar narrowing only. See later for the grading of hypertensive retinopathy as a whole.)
- Grade I - 3/4 normal caliber
- Grade II - 1/2 normal caliber
- Grade III - 1/3 normal caliber
- Grade IV - thread-like or invisible
- Arterio-venous crossing changes (aka "AV nicking") with venous constriction and banking
- Arteriolar color changes
- Copper wire arterioles are those arterioles in which the central light reflex occupies most of the width of the arteriole
- Silver wire arterioles are those arterioles in which the central light reflex occupies all of the width of the arteriole
- Vessel sclerosis
- Arteriolar narrowing that is almost always bilateral. (The following grading system is specific to the degree of the arteriolar narrowing only. See later for the grading of hypertensive retinopathy as a whole.)
- Ischemic changes (e.g. "cotton wool spots")
- Hemorrhages, often flame shaped.
- Edema
- Papilledema, or optic disc edema, in patients with malignant hypertension
- Visual acuity loss, typically due to macular involvement
Grades
- Grade 1
- Generalised arteriolar constriction - seen as `silver wiring` and Vascular tortuosities.
- Grade 2
- As grade 1 + irregularly located, tight constrictions - Known as `AV nicking` or `AV Nipping`
- Grade 3
- As grade 2 + with cotton wool spots and flame-haemorrhages
- Grade 4
- As above but with swelling of the optic disk (papillodema)
There is an association between the grade of retinopathy and mortality. At 3 years 70% of those with grade 1 retinopathy will be alive whereas only 6% of those with grade 4 will survive.[1] Grading of the retinopathy is thus important as the hypertensive process will be affecting small vessels throughout the body in a similar manner. (The retina is simply the most visible area to assess.)
Differential Diagnoses
- Diabetic Retinopathy
- Collagen Vascular Disease
- Anemia
- Radiation Retinopathy
- Central Retinal Vein Occlusion
Treatment and management
A major aim of treatment is to prevent, limit, or reverse such target organ damage by lowering the patient's high blood pressure. Anti-hypertensive treatment plays a major role in reversing the retinal changes. The eye is an organ where damage is easily visible at an early stage, so regular eye examinations are important.
See also
- Hypertensive crisis
- List of eye diseases and disorders
- List of systemic diseases with ocular manifestations
- Ophthalmology
- Optometry
References
- The Wills Eye Manual: Office and Emergency Room Diagnosis and Treatment of Eye Disease, J.B. Lippincott, 1994.
- Hypertensive retinopathy
- ^ Wong TY, Mcintosh R (2005). "Hypertensive retinopathy signs as risk indicators of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality". British Medical Bulletin 73-74: 57–70. PMID 16148191.
Categories:- Disorders of choroid and retina
- Eye stubs
- Arteriosclerotic changes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
