- Ontario Highway 77
-
Highway 77 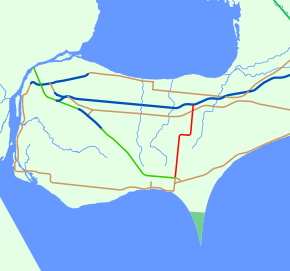
Highway 77 Limited-access King's Highway Former highwaysRoute information Maintained by the Ministry of Transportation Length: 22.1 km[2] (13.7 mi) Existed: April 1, 1963[1] – present Major junctions South end:  Highway 3 – Leamington
Highway 3 – Leamington County Road 8
County Road 8
 County Road 46 (Middle Road) – Comber
County Road 46 (Middle Road) – ComberNorth end:  Highway 401
Highway 401Location Major cities: Leamington Towns: Blytheswood, Staples, Comber Highway system Ontario provincial highways
400-series • Former←  Highway 72
Highway 72Highway 85  →
→King's Highway 77, also known as Highway 77, is a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. One of three highways within Essex County, Highway 77 serves to interconnect Highway 3 near Leamington with Highway 401 near Tilbury. Prior to 1998, the highway extended south into Leamington, ending at the former routing of Highway 3 and Highway 18. This section was turned over to Essex County and renamed Erie Street. The speed limit on Highway 77 is 80 km/h (50 mph) in most places, dropping to 50 km/h in built-up areas. It is patrolled by the Ontario Provincial Police.
Contents
Route description
Due to the flat topography of Essex County, the land use surrounding Highway 77 is almost entirely agricultural. Soil conditions in Essex are ideal for farming, and as a result very few natural areas can be found in the county.[3] Many streams have been diverted to irrigate the endless farmland to either side of the highway. Relief from the plain is provided only by the few hamlets along the route. In addition, Lake Erie and Lake Huron are both a short distance from Highway 77.[4]
Highway 77 begins at the Leamington Bypass, north of the city of the same name. The western section of Highway 3 shares its eastern terminus with Highway 77;[5] from there it travels west towards Windsor.[4] Several greenhouses are visible near the southern end of the highway, a small percentage of the 610 hectares (1,500 acres) of land occupied by them in the Leamington area.[6] Point Pelee National Park, the southernmost point in Canada, is also nearby.[5]
The highway runs 11.5 km (7.1 mi) north through Mount Carmel and Blytheswood to the village of Staples before turning to the east. It continues in this direction for 2 km (1.2 mi) before returning to its northward orientation.[4] North of there, the highway passes to the east of the Comber and District Historical Society Museum. The museum, which focuses on the history of agriculture, was established in the former Maple Grove Schoolhouse, which was built in 1894.[7] Pressing north to Highway 401, it passes Middle Road (once Highway 98) in the centre of Comber.[8] Highway 401 provides access to Windsor and the United States to the west, and to the town of Tilbury and city of Chatham–Kent to the east. To the north, the road continues as Essex County Road 35 to Stoney Point on the shores of Lake Huron.[4]
Traffic levels along Highway 77 vary, but are generally low. The busiest section of the highway lies at the southern end between Leamington and Blythesville, with an average of 6,000 vehicles travelling it per day. North of that, traffic drops considerably to 3,000 vehicles, but increases approaching Comber and Highway 401 to around 4,500.[2]
History
The Highway 77 designation was first applied on August 5, 1936 to a road running southeast from Rodney, Ontario to Highway 3 at New Glasgow. On December 5, 1957, the highway was transferred to Elgin County and is now known as Elgin County Road 103.[9][10] The current Highway 77 was designated between Leamington and Highway 401 on April 1, 1963.[1] The southern end followed present-day Erie Street south through the city to Talbot Road. At the time, Highway 3 travelled along that road; Highway 77 continued south of Talbot Road as Highway 18.[11] In early December 1999, the Leamington Bypass of Highway 3 opened.[12] The southern terminus of Highway 77 was subsequently truncated by 1.7 km (1.1 mi) to end at the new bypass.[4]
Major intersections
The following table lists the major junctions along Highway 77. In addition, it includes some minor junctions that are noted by the Ministry of Transportation of Ontario.[2] The entirety of Highway 77 is located within Essex County.
Location km[2] Destinations Notes Leamington 0.0  Highway 3 east – Windsor
Highway 3 east – WindsorLeamington Bypass 
Blytheswood 6.0 Mersea Concession Road 8 
 County Road 14 – Albuna
County Road 14 – Albuna
8.8 Mersea Concession Road 10 
Staples 11.7  County Road 8 west
County Road 8 west
 County Road 8 east
County Road 8 east
Comber 21.0  County Road 46 (Middle Road)
County Road 46 (Middle Road)
22.6  Highway 401 – Windsor, London, Chatham, Tilbury
Highway 401 – Windsor, London, Chatham, Tilbury
1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi See also
- List of numbered roads in Elgin County
- List of numbered roads in Essex County
References
- ^ a b AADT Traffic Volumes 1955–1969 And Traffic Collision Data 1967–1969. Ontario Department of Highways. 1969. p. 98.
- ^ a b c d Ministry of Transportation of Ontario (2004). "Annual Average Daily Traffic (AADT) counts". http://www.raqsb.mto.gov.on.ca/techpubs/TrafficVolumes.nsf/tvweb?OpenForm&Seq=5. Retrieved February 26, 2010.
- ^ Canada Centre for Remote Sensing (January 17, 2008). "Tour Canada from space, Essex County, Southern Ontario". Natural Resources Canada. http://www.ccrs.nrcan.gc.ca/resource/tour/07/07scene2_e.php. Retrieved August 13, 2010.
- ^ a b c d e Peter Heiler Ltd (2008). Southwestern Ontario (Map). Cartography by MapArt. Section C5–E6. ISBN 978-1-55368-220-2.
- ^ a b Peter Heiler Ltd (2008). Windsor and Essex County (Map). Cartography by MapArt. Essex County overview inset. ISBN 978-1-55368-285-1.
- ^ "Leamington's Thriving Greenhouse Industry". Municipality of Leamington. http://www.leamington.ca/municipal/edo_demographics.asp. Retrieved August 11, 2010.
- ^ IBI Group (September 2007). "Community Cultural Master Plan". Town of Lakeshore. p. 5.14. http://www.townoflakeshore.on.ca/media/CSCulturalMasterPlanSept28_000.pdf. Retrieved August 13, 2010.
- ^ Peter Heiler Ltd (2008). Windsor and Essex County (Map). Cartography by MapArt. Section Comber, X44–Z45. ISBN 978-1-55368-285-1.
- ^ Annual Report (Report). Department of Highways. March 31, 1958. p. 237.
- ^ Peter Heiler Ltd (2010). Ontario Back Road Atlas (Map). Cartography by MapArt. ISBN 978-1-55198-226-7.
- ^ Ministry of Transportation of Ontario (January 1, 1990). Ontario Road Map (Map). Cartography by Cartography Section. Section P2.
- ^ "Official Records for 21 December 1999". Legislative Assembly of Ontario. December 21, 1999. http://www.ontla.on.ca/web/house-proceedings/house_detail.do?locale=en&Date=1999-12-21&detailPage=/house-proceedings/transcripts/files_html/1999-12-21_L032A.htm#P19_3772. Retrieved December 9, 2010.
External links
The King's Highways of Ontario Current highwaysFormer highways- 2A
- 2B
- 2S
- 3B
- 4A
- 5A
- 7B
- 8A
- 12B
- 14
- 15A
- 18
- 18A
- 22
- 24A
- 25
- 27
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 35A
- 35B
- 36
- 38
- 39
- 40B
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48B
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 59
- 68
- 70
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 103
- 104
- 106
- 107
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 114
- 116
- 117
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 126
- 128
- 131
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 169
- 400A
- 401A
County roads in Ontario · Ontario numbered highways · Expressways and 400-series highways · King's Highways · Secondary highways · Tertiary and 7000-series highways · List of Ontario provincial highways · List of former provincial highways in Ontario · Highways in Ontario · List of Ontario expressways · Trans-Canada Highway · Connecting Link · Emergency Detour RouteCategories:- Ontario provincial highways
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

