- Ontario Highway 404
-
"The 404" redirects here. For other uses, see The 404 (disambiguation).
Highway 404 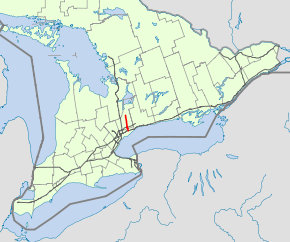
Route information Length: 36.6 km[1] (22.7 mi) Existed: 1977 – present Major junctions South end:  Highway 401 / DVP – Toronto
Highway 401 / DVP – Toronto Highway 407 – Markham
Highway 407 – Markham
 Regional Road 7 (Highway 7) – Richmond Hill, Markham
Regional Road 7 (Highway 7) – Richmond Hill, MarkhamNorth end:  Regional Road 19 (Green Lane) – East Gwillimbury
Regional Road 19 (Green Lane) – East GwillimburyHighway system Ontario provincial highways
400-series • Former←  Highway 403
Highway 403Highway 405  →
→King's Highway 404, also known as Highway 404 and colloquially as the four-oh-four, is a 400-series highway in the Canadian province of Ontario connecting Highway 401 and the Don Valley Parkway in Toronto with Newmarket. The controlled-access highway also connects with Highway 407 in Richmond Hill.
Construction on the freeway began soon after the completion of the Don Valley Parkway, with the first section south of Steeles Avenue opening in 1977. Over the next twelve years, the Ministry of Transportation of Ontario (MTO) undertook a continuous construction program to build the freeway to Davis Drive in Newmarket. This was completed on October 24, 1989. Since then, the route has been expanded in width and extended by 2 km (1.2 mi) to Green Lane, an east-west road in the town of East Gwillimbury. A northward extension to Ravenshoe Road is currently under construction, with completion tentatively scheduled for December, 2012. This 13.5 km (8.4 mi) route is the first part of a proposed extension to southeast of Beaverton.
Highway 404 is one of several freeways in the Greater Toronto Area (GTA) with High-Occupancy Vehicle (HOV) lanes; the southbound lane was one of the initial projects in the province and opened on December 13, 2005. The northbound lane opened on July 23, 2007.
Contents
Route description
Running parallel to Highway 400 approximately 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) to the east, Highway 404 extends 36 km (22 mi) on a north–south orientation between Highway 401 and Green Lane. There are 14 interchanges along its length, mostly of the Parclo A4 configuration. Exit numbers on the freeway start at 17, suggesting that the length of the Don Valley Parkway was considered in distance calculations; there are no exit numbers posted on the parkway.[2]
Officially, the Ministry of Transportation of Ontario (MTO) jurisdiction over the freeway begins as the opposing directions of travel diverge south of the Highway 401 interchange.[note 1] Northbound, two lanes from the DVP are joined by a third from the eastbound collectors of Highway 401. These narrow to two lanes before merging with a single lane from westbound Highway 401 immediately south of Sheppard Avenue. An additional two lanes from westbound Highway 401 converge and form a separate carriageway with no access to Sheppard.[3] Southbound, the freeway is divided into two carriageways, both of which provide access to the DVP. The outer carriageway also provides access from Sheppard and to Highway 401, including the westbound express lanes, while the inner carriageway is intended for DVP-bound traffic. The HOV lane also provides access to westbound Highway 401 via a dedicated tunnel, which passes beneath the other southbound lanes.[4] To the east of Highway 404 is the Consumers Road office park. To the west and north of Sheppard Avenue is Fairview Mall, which has its own connection with the southbound lanes.[2]
The highway continues directly north along the old Woodbine Avenue right-of-way to just south of Steeles Avenue, where it diverges to the west before continuing north. From just north of Sheppard, a northbound HOV lane is present alongside the central median. Southbound, the HOV lane continues as far as Highway 401. Alongside the 404 to the east is an industrial warehouse and commercial office area, while on the west is a suburban subdivision of North York. Northbound, the freeway is six lanes wide from Sheppard Avenue to Finch Avenue, where one diverges onto an off-ramp, re-emerging north of Finch. Southbound, it is six lanes wide from Steeles south to Sheppard.[2]
At Steeles Avenue, the freeway enters the Regional Municipality of York. To the east are industrial units, while on the west are residential suburbs. This land-use persists north to the Highway 407 ETR interchange, a multi-level stack interchange with two flyovers. North of Highway 407, the freeway crosses Highway 7, where the HOV lanes transition to standard through lanes. The freeway passes west of Buttonville Airport and interchanges with 16th Avenue. It narrows and the central barrier ends; a grass median taking its place between the opposing lanes. The land-use density continues to drop, with the appearance of some open spaces and farms interspersed with industrial and commercial buildings. By 19th Avenue, the land-use is agricultural on both sides of Highway 404. Immediately south of Stouffville Road, the freeway curves to the east before proceeding north.[2]
North of Bethesda Road, the freeway crosses through a green space area. Two small lakes are present to either side. The larger, to the east, is Simeon Lake. North of Aurora Road, the highway reduces in width to four lanes, which is its configuration north to East Gwillumbury,[5] where the highway terminates at Green Lane (York Regional Road 19).[2]
History
Initial construction
A freeway east of Highway 11 was in the works as early as 1954, when the province extended Highway 48 south from Port Bolster. A large cloverleaf interchange was constructed with the Toronto Bypass, and plans formulated for a dual highway around the east side of Lake Simcoe, connecting with Highway 11 near Orillia or Gravenhurst. This route was dropped when Metropolitan Toronto began planning for the northern extension of the DVP in 1957, as subdivisions encroached upon Woodbine Avenue north of Highway 401. The six-lane expressway was to follow the alignment of Woodbine from its southern terminus at Lawrence Avenue to north of Steeles Avenue, where the Department of Highways (DOH) would continue the road as a "new King's Highway".[6]
In 1959, the DOH announced that they would construct and maintain the new route once the DVP was completed to Highway 401 and designate it Highway 404.[7] The proposed route of the freeway was presented at a special delegation on December 13, 1960 by Harold Barry, a representative of the department.[8] Design work started in 1973[9], the first contract was awarded in early 1976,[10] and construction began in March 1976 with the awarding of a C$6.9 million contract. This contract included construction of the Finch Avenue interchange, overpasses at McNicoll and Van Horne Avenues and 4.5 km (2.8 mi) of six-lane freeway between Sheppard and Steeles Avenues.[11][12] Shortly thereafter, on April 20, Ernest Avenue and Van Horne Avenue were closed to traffic at Woodbine.[13] The first section of Highway 404 between Highway 401 and Steeles Avenue opened in late 1977, including the flyover ramp from southbound Woodbine Avenue.[10] The freeway was separated by a grass median with a steel beam acting as a barrier between the lanes. Construction north of Toronto proceeded quickly, with the contract for the section from Steeles to Highway 7 being awarded in 1976[10] and the section opening in mid-1980. By the end of 1980, the freeway reached as far north as Major Mackenzie Drive; the segment north of Highway 7 was four lanes wide. The next extension to Stouffville Road (then known as the Gormley Side Road) was opened during the second week of December, 1981.[14]
 Highway 404 looking southbound from Finch Avenue. Note the HOV lane on the left side of the carriageway.
Highway 404 looking southbound from Finch Avenue. Note the HOV lane on the left side of the carriageway.
The section of Highway 404 north of Stouffville Road was the subject of considerable controversy when work began to clear the route on May 15, 1981 before the completion of an environmental assessment. The Ministry of Transportation and Communications was charged with violating the newly enacted Environmental Assessment Act, which it contested came into effect after construction of the Highway 404 extension had begun.[15] Minister James Snow was charged with violating the act, and called upon to resign. The Minister did not resign, but paid a $3,500 fine. Despite the issues surrounding it, the extension between Stouffville Road and Bloomington Road was opened ceremoniously on the morning of August 10, 1982.[16]
Construction on the segment north of Bloomington to Aurora Sideroad was already in progress by this point. It was opened to traffic in late September 1985.[17] Construction on the 6.5 km (4.0 mi) section from Aurora Road to Davis Drive began in early 1986, and the section opened to traffic on October 24, 1989 at 8:30 am. This final segment cost $22.1 million, ending the continuous construction program undertaken since 1973 at a cost of $83.3 million.[9]
Expansion
Studies and environmental into various extensions began almost immediately, while Highway 404 ended at Davis Drive; it would take over a decade for any northward progression to take place. In the interim period, work went into expanding the six lane freeway through Toronto and Markham. In early 1998, the MTO announced plans for two contracts to widen Highway 404 south of Highway 7. The first contract converted the grass median into an additional lane in each direction with a central barrier between them. High-mast lighting was also installed, replacing the unique luminaires used on the freeway. The second contract resulted in an additional lane in each direction on the outside of the existing freeway south of Steeles Avenue, making it ten lanes wide. The proposal to eventually convert the inner lanes into HOV lanes was announced at the same time.[18] The next year, Highway 404 was widened to six lanes between Highway 7 and Major Mackenzie Drive.[5]
On June 23, 1998 the Minister of Transportation, Tony Clement, made a formal agreement with the Region of York to expand the route through the region. The MTO formally announced this on August 28, 2000: a three contract project to widen and extend Highway 404. The first contract added an additional lane in each direction in the grass median from Major Mackenzie Drive to Bloomington Road. A second contract then extended those two lanes north to Aurora Sideroad. These two projects both began in the summer of 2001 and were completed in December.[5] The third contract called for a four lane extension from Davis Drive to Green Lane and the reconstruction of Green Lane into a four-laned arterial road between Leslie Street and Woodbine Avenue.[19] This contract began shortly after the announcement in September 2000. The extension was opened to traffic on February 8, 2002 at a ceremony attended by York North MPP Julia Munro and York Regional Chair Bill Fisch.[20][21]
On June 19, 2003, Transportation Minister and Oak Ridges MPP Frank Klees opened a new interchange at Regional Road 73 (16th Avenue). Traffic was permitted onto the ramp following the ceremony, also attended by Thornhill MPP Tina Molinari.[22]
One of the three original HOV lanes in Ontario opened on Highway 404 in late 2005; the other two were the lanes on Highway 403. In early 2004, construction began on a new ramp to westbound Highway 401, curving beneath the southbound lanes of Highway 404. On December 13, 2005, the southbound HOV lane was opened to traffic.[23] Work on the northbound HOV lane began shortly thereafter, opening at 8:30 am on Monday, July 23, 2007.[24]
Future
On May 16, 2006 the MTO announced plans to extend Highway 404 by 15 kilometres from Green Lane to Ravenshoe Road at the south end of Keswick. The first contracts were awarded later that year for the construction of the northbound bridge over Green Lane,[25] followed by two structures over Mount Albert Road, west of Woodbine Avenue, begun in late 2008 and completed in 2009.[26][27] As of April 2011[update], the extension has been cleared and graded. Completion is planned for December 2012.[28]
Long term plans call for Highway 404 to be extended to Highway 12, between Sunderland and Beaverton. This extension would follow a new alignment to Port Bolster, east of which the freeway would incorporate the existing two lanes of Highway 48. The extension has drawn criticism from environmental groups who claim it will only serve to accelerate urban sprawl north of Toronto.[29]
Exit list
Division Location km Exit Destinations Notes  Highway 404 continues south as the Don Valley Parkway
Highway 404 continues south as the Don Valley Parkway 
Toronto 0.5 17  Highway 401
Highway 4011.4 18 Sheppard Avenue Access from southbound 404 to Fairview Mall and from Fairview Mall to southbound 404 3.5 20 Finch Avenue 5.7 22 Steeles Avenue /  Regional Road 8 (Woodbine Avenue)
Regional Road 8 (Woodbine Avenue)Northbound exit and southbound entrance from Woodbine Avenue, full access interchange with Steeles Avenue York Region Markham 8.9 25  Highway 407
Highway 4079.8 27  Regional Road 7
Regional Road 7Formerly  Highway 7
Highway 7Markham – Richmond Hill boundary 11.8 29  Regional Road 73 (16th Avenue)
Regional Road 73 (16th Avenue)13.8 31  Regional Road 25 (Major Mackenzie Road)
Regional Road 25 (Major Mackenzie Road)15.7 33  Regional Road 49 (Elgin Mills Road)
Regional Road 49 (Elgin Mills Road)Richmond Hill – Whitchurch-Stouffville 20.1 37  Regional Road 14 (Stouffville Road)
Regional Road 14 (Stouffville Road)24.2 41  Regional Road 40 (Bloomington Road)
Regional Road 40 (Bloomington Road)Whitchurch-Stouffville – Aurora 28.4 45  Regional Road 15 (Aurora Road)
Regional Road 15 (Aurora Road)Whitchurch-Stouffville – Newmarket 32.4 49  Regional Road 74 (Vivian Road / Mulock Road)
Regional Road 74 (Vivian Road / Mulock Road)East Gwillimbury 34.5 51  Regional Road 31 (Davis Drive)
Regional Road 31 (Davis Drive)36.6 53  Regional Road 19 (Green Lane)
Regional Road 19 (Green Lane) Regional Road 77 (Queensville Sideroad)
Regional Road 77 (Queensville Sideroad)Bradford Bypass Possible interchange location for proposed freeway 50.1 
 Regional Road 8 / Regional Road 32 (Woodbine Avenue / Ravenshoe Road)
Regional Road 8 / Regional Road 32 (Woodbine Avenue / Ravenshoe Road)Closed • Under construction 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi External links
References
Notes
- ^ This demarcation line is visible on the highway as a change in pavement quality and the use of different high-mast lighting
Sources
- ^ Ministry of Transportation of Ontario (2007). "Annual Average Daily Traffic (AADT) counts". Government of Ontario. http://www.raqsb.mto.gov.on.ca/techpubs/TrafficVolumes.nsf/tvweb?OpenForm&Seq=5. Retrieved April 26, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e Peter Heiler Ltd (2011). Toronto & Area (Map). Cartography by MapArt. pp. 104, 320, 326, 332, 338, 344, 350, 355, section T26–F30. ISBN 978-1-55198-213-7.
- ^ Google, Inc. Google Maps – Highway 404 Northbound Lane Configuration Approaching Highway 401 Interchange (Map). Cartography by Google, Inc. http://maps.google.ca/?ie=UTF8&hq=&hnear=Toronto,+Toronto+Division,+Ontario&t=k&ll=43.769296,-79.337318&spn=0.007097,0.01929&z=16. Retrieved April 26, 2011.
- ^ Ministry of Transportation of Ontario. "Highway 404 Southbound HOV Lanes at Hwy 401/DVP". Government of Ontario. http://www.mto.gov.on.ca/english/traveller/hov/image/detail.pdf. Retrieved April 26, 2011.
- ^ a b c Ministry of Transportation of Ontario (February 8, 2002). "Backgrounder: Highway 404 Extension - Davis Drive to Green Lane". Government of Ontario. http://www.mto.gov.on.ca/english/news/regional/2002/020802b.shtml. Retrieved April 26, 2011.
- ^ Don Valley Parkway Extension, Highway 401 to Steeles Avenue (Report). Desjardines. 1957.
- ^ Annual Report (Report). Department of Highways. March 31, 1960. p. 7.
- ^ "New Highway Route Metro to Newmarket". The Globe and Mail (Toronto) 117 (34,636): p. 5. December 14, 1960. "Highway Department officials tonight outlined the proposed route the new No. 404 Highway will follow from Steeles Avenue to the Newmarket area."
- ^ a b Dexter, Brian (October 25, 1989). "Ontario Studies Plan to Extend Highway 404 Farther North". The Toronto Star: p. A8.
- ^ a b c Construction Program: King's and Secondary Highways (Report). Ministry of Transportation and Communications. 1976–77. p. XV.
- ^ "Headache on the 401". The Globe and Mail (Toronto): p. 5. May 4, 1976.
- ^ Construction Program: King's and Secondary Highways (Report). Ministry of Transportation and Communications. 1975–76. p. xvii.
- ^ "Road-Building Closes 2 Streets". The Toronto Star: p. B1. April 14, 1976.
- ^ Stevens, Victoria (January 21, 1981). "York Councillors Fly Over Their Region's Traffic Chaos". The Toronto Star: p. A29.
- ^ "Ministries at Loggerheads Over Extension of Highway". The Globe and Mail (Toronto): p. 5. May 26, 1981.
- ^ Keating, John (August 3, 1982). "404 extension opens Aug.10". The Toronto Star: p. 11. "The public is cordially invited to attend the OFFICIAL OPENING of Highway 404, from Gormley Road to Bloomington Side Road on Tuesday, August 10, 1982 at 11:00 a.m. on the southbound lanes of Highway 404 at Bloomington Side Road."
- ^ "New Stretch of 404 to Open". The Toronto Star: p. NR12. September 10, 1985. "Highway 404 should be open to the Aurora Sideroad by the end of September, a Ministry of Transportation official said last week.... Tenders for the next and final stage of the highway from the Aurora Sideroad to Davis Drive in Newmarket will be called in December and awarded in January the spokesman said."
- ^ The Toronto Star.
- ^ Van Rijn, Nicholaas (August 29, 2000). "Longer, Wider Highway 404 In the Works". The Toronto Star: p. B3.
- ^ Ministry of Transportation of Ontario (February 8, 2002). "New Highway 404 Extension to Benefit Newmarket". Government of Ontario. http://www.mto.gov.on.ca/english/news/regional/2002/020802.shtml. Retrieved April 26, 2011.
- ^ Casey, Patrick (February 8, 2002). "Drivers have more options in northern York Region after improvements to Green Lane East and Highway 404". News (Regional Municipality of York). http://www.york.ca/Publications/News/2002/February+08,+2002,+Drivers+have+more+options+in+northern+York+Region+after+improvements+to+Green+Lan.htm. Retrieved April 26, 2011. "York Region drivers can now access Green Lane East between Leslie Street and Woodbine Avenue in the Town of East Gwillimbury. The Regional Municipality of York today opened the stretch of road in tandem with the completion of a 2.9 kilometre extension of Highway 404 from Davis Drive and Green Lane East."
- ^ Ministry of Transportation of Ontario (June 19, 2003). "Eves government to open Highway 404/16th Avenue interchange in Richmond Hill". Government of Ontario. Archived from the original on July 15, 2003. http://web.archive.org/web/20030715121539/http://ogov.newswire.ca/ontario/GONE/2003/06/19/c4986.html?lmatch=&lang=_e.html. Retrieved May 28, 2011. "Transportation Minster and Oak Ridges MPP Frank Klees and Associate Minister of Municipal Affairs and Housing and Thornhill MPP Tina Molinari will open the new Highway 404/16th Avenue interchange in Richmond Hill."
- ^ "New Southbound High Occupancy Vehicle Lane and Tunnel on Highway 404". Road Talk. Ministry of Transportation of Ontario. Winter 2006. http://www.mto.gov.on.ca/english/transtek/roadtalk/rt12-1/. Retrieved April 26, 2011.
- ^ CTV News (July 23, 2007). "HOV Lane Opens on Highway 404 Northbound". Bell Media. http://swo.ctv.ca/servlet/an/local/CTVNews/20070723/HOV_404_northbound-070723?hub=SWOHome. Retrieved April 26, 2011.
- ^ [1]
- ^ [2]
- ^ Mount Albert interchange bridge date stamp
- ^ Highway 404 Extension Status Update (Report). Government of Ontario. January 12, 2011. http://www.york.ca/NR/rdonlyres/udddjlyflzm2h4kzbbrszlbvzlaxcutsjr4ktjnyscae23nquep5jaimaw4eorzw5b3xvhu4deyt74coreqehqx4kg/rpt+1+pres+Kandiah.pdf. Retrieved April 26, 2011.
- ^ Winfield, Mark (April 13, 2006). "404 Extension a Highway to Sprawl, Environmental Groups Charge". The Pembina Institute. http://www.pembina.org/media-release/1220. Retrieved July 10, 2010.
Controlled-access highways of Ontario 400-series highways Other highways Current: 2A · 11 · 58 · 115 · 137 · Conestoga Pkwy. · Dougall Pkwy. · E.C. Row Expwy. · Hanlon Pkwy. · Queensway · Thunder Bay Expwy.
Municipal: Black Creek Dr. · Burlington St. · Cootes Dr. · Don Valley Pkwy. · Gardiner Expwy. · Harbour Expwy. · Highbury Ave. · Lincoln M. Alexander Pkwy. · Queensway · Red Hill Valley Pkwy. · Vets Mem. Pkwy. · W.R. Allen Rd.
Proposed: GTA West Corridor · Halton–Peel Freeway · Mid-Peninsula Highway · Bradford Bypass · West Durham Link · East Durham LinkCounty roads in Ontario · Ontario numbered highways · Expressways and 400-series highways · King's Highways · Secondary highways · Tertiary and 7000-series highways · List of Ontario provincial highways · List of former provincial highways in Ontario · Highways in Ontario · List of Ontario expressways · Trans-Canada Highway · Connecting Link · Emergency Detour RouteCategories:- 400-series highways in Ontario
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.




