- Geography of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
-
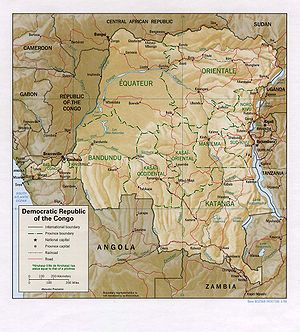
The Democratic Republic of the Congo includes the greater part of the Congo River Basin, which covers an area of almost 1,000,000 square kilometres (390,000 sq mi). The country's only outlet to the Atlantic Ocean is a narrow strip of land on the north bank of the Congo River.
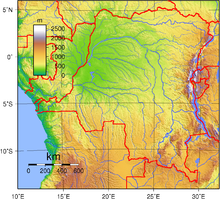
The vast, low-lying central area is a basin-shaped plateau sloping toward the west, covered by tropical rainforest and criss-crossed by rivers, a large area of this has been categorised by the World Wildlife Fund as the Central Congolian lowland forests ecoregion. The forest centre is surrounded by mountainous terraces in the west, plateaus merging into savannas in the south and southwest, and dense grasslands extending beyond the Congo River in the north. High mountains of the Ruwenzori Range (some above 5,000 m/16,000 ft) are found on the eastern borders with Rwanda and Uganda (see Albertine Rift montane forests for a description of this area).
Contents
Climate
The DRC lies on the Equator, with one-third of the country to the north and two-thirds to the south. The climate is hot and humid in the river basin and cool and dry in the southern highlands, with a cold, alpine climate in the Ruwenzori Range. There is a South of the Equator, the rainy season lasts from October to May and north of the Equator, from April to November. Along the Equator, rainfall is fairly regular throughout the year. During the wet season, thunderstorms often are violent but seldom last more than a few hours. The average rainfall for the entire country is about 1,070 mm (42 in).
Data
Location: Central Africa, northeast of Angola
Geographic coordinates: 0°00′N 25°00′E / 0°N 25°E
Map references: Africa
Area:
total: 2,345,410 km2
land: 2,267,600 km2
water: 77,810 km2Area - comparative: slightly less than one-fourth the size of the US
Land boundaries:
total: 10,744 km
border countries: Angola 2,511 km, Burundi 233 km, Central African Republic 1,577 km, Republic of the Congo 2,410 km, Rwanda 217 km, South Sudan 628 km, Tanzania 473 km, Uganda 765 km, Zambia 1,930 kmCoastline: 37 km (23 mi).
Maritime claims:
exclusive economic zone: boundaries with neighbors
territorial sea: 12 nmi (22 km)Climate: tropical; hot and humid in equatorial river basin; cooler and drier in southern highlands; cooler-cold and wetter in eastern highlands and the Ruwenzori Range; north of Equator - wet season April to October, dry season December to February; south of Equator - wet season November to March, dry season April to October
Terrain: vast central plateau covered by tropical rainforest, surrounded by mountains in the west, plains and savanna in the south/southwest, and grasslands in the north. The high mountains of the Ruwenzori Range on the eastern borders.
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point: Pic Marguerite on Mont Ngaliema (Mount Stanley) 5,110 mNatural resources: cobalt, copper, cadmium, petroleum, industrial and gem diamonds, gold, silver, zinc, manganese, tin, germanium, uranium, radium, bauxite, iron ore, coal, hydropower, timber
Land use:
arable land: 2.96% (1998 est), 3% (1993 est.)
permanent crops: 0.52% (1998 est.), 0% (1993 est.)
permanent pastures: 7% (1993 est.)
forests and woodland: 77% (1993 est.)
other: 96.52 (1998 est.), 13% (1993 est.)Irrigated land: 110 km2 (1998 est.), 100 km2 (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: periodic droughts in south; Congo River floods (seasonal); in the east, in the Great Rift Valley, there are active volcanoes
Environment - current issues: poaching threatens wildlife populations (for example, the Painted Hunting Dog, Lycaon pictus is now considered extinct in the Congo[1] due to human overpopulation and poaching); water pollution; deforestation (chiefly due to land conversion to agriculture by indigenous farmers[2]); refugees responsible for significant deforestation, soil erosion, and wildlife poaching; mining of minerals (coltan — a mineral used in creating capacitors, diamonds, and gold) causing environmental damage
Environment - international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Environmental ModificationGeography: straddles Equator; very narrow strip of land that controls the lower Congo River and is the only outlet to South Atlantic Ocean; dense tropical rainforest in central river basin and eastern highlands
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northern-most point - unnamed location on the border with the Central African Republic in the Bomu river immediately west of the town of Mbaga in CAR, Orientale Province
- Eastern-most point - at the point where the northern section of the border with Uganda enters Lake Albert immediately west of Mahagi Port, Oritentale Province
- Southern-most point - unnamed location on the border with Zambia immediately to north-west of the Zambian town of Ndabala, Katanga province
- Western-most point - the point at which the border with Cabinda enters the Atlantic Ocean, Bas-Congo province
See also
Line Notes
References
- C. Michael Hogan. 2009. Painted Hunting Dog: Lycaon pictus, GlobalTwitcher.com, ed. N. Stromberg
- Anne Welsbacher. 2008. Protecting Earth's Rain Forests, page 36
Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
Climate of Africa Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
 Democratic Republic of the Congo topics
Democratic Republic of the Congo topicsPolitics and law History Early history · Colonisation (1867–85) · Congo Free State (1885–1908) · Belgian Congo (1908–60) · Congo-Léopoldville (1960–65) · Congo Crisis (1960–65) · Zaire (1965–97) · First Congo War (1996–98) · Second Congo War (1998–2003) · 2000sGeography Economy and infrastructure Agriculture · Airports · Central Bank · Communications · Energy · Franc · Health · Mining · Resource extraction · TransportCulture and society
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.