- Geography of Burundi
-
Geography of Burundi 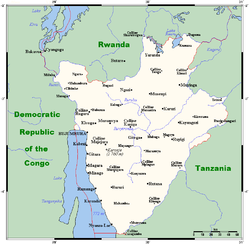
Continent Africa[1] Region Central Africa Coordinates 3°30′S 30°0′E / 3.5°S 30°E Area Ranked 153rd
27,830 km2 (10,750 sq mi)
92.2% land
12.8% waterBorders 974 km (DROC 233 km, Rwanda 290 km, Tanzania 451 km) Highest point Mount Heha 2670 m Lowest point Lake Tanganyika 772 m Largest lake Lake Tanganika Burundi is located in central Africa, to the east of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, at the co-ordinates 3°30′S 30°0′E / 3.5°S 30°E.
Contents
Physical geography
Burundi occupies an area equal to 27,830 square kilometres in size, of which 25,650 km² is land. The country has 974 kilometres of land border: 233 km of which is shared with the Democratic Republic of the Congo, 290 km with Rwanda and 451 km with Tanzania. As a landlocked country, Burundi possesses no coastline, although it straddles the crest of the Nile-Congo River watershed. The farthest headwaters of the Nile, the Ruvyironza River, has its source in Burundi.
Climate
Burundi in general has a tropical highland climate, with a considerable daily temperature range in many areas. Temperature also varies considerably from one region to another, chiefly as a result of differences in altitude. The central plateau enjoys pleasantly cool weather, with an average temperature of 20 °C (68 °F). The area around Lake Tanganyika is warmer, averaging 23 °C (73.4 °F); the highest mountain areas are cooler, averaging 16 °C (60.8 °F). Bujumbura’s average annual temperature is
23 °C (73.4 °F). Rain is irregular, falling most heavily in the northwest. Dry seasons vary in length, and there are sometimes long periods of drought. However, four seasons can be distinguished: the long dry season (June–August), the short wet season (September–November), the short dry season (December–January), and the long wet season (February–May). Most of Burundi receives between 1,300 and 1,600 mm (51.2 and 63.0 in) of rainfall a year. The Ruzizi Plain and the northeast receive between 750 and 1,000 mm (29.5 and 39.4 in).Terrain
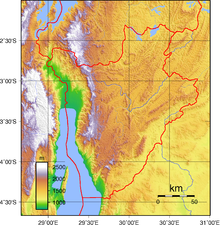
The terrain of Burundi is hilly and mountainous, dropping to a plateau in the east. The southern and eastern plains have been categorised by the World Wildlife Fund as part of the Central Zambezian Miombo woodlands ecoregion.
The lowest point in the country is at Lake Tanganyika, at 772 m, with the highest point being on Mount Heha, at 2,684 m.[2] Natural hazards are posed in Burundi by flooding and landslides.
Natural resources
Burundi possesses reserves of: nickel, uranium, rare earth oxides, peat, cobalt, copper, platinum (not yet exploited) and vanadium. There is also arable land and the potential for hydropower. 140 km² of land in Burundi is irrigated. The table below describes land use in Burundi.
Land use Use Percentage of Area arable land 35.57 permanent crops 13.12 other 51.31 Environment
Current issues
Soil erosion is an issue for Burundi, and is as a result of overgrazing and the expansion of agriculture into marginal lands. Other issues include: deforestation, due to the uncontrolled cutting-down of trees for fuel; and habitat loss threatens wildlife populations.
International agreements
Burundi is a party to the following international agreements that relate to the environment: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes and Ozone Layer Protection. The following have been signed but not yet ratified by Burundi: Law of the Sea and Nuclear Test Ban.
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of Burundi, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northernmost point - unnamed location on the border with Rwanda immediately south of the Rwandna town of Mbuye, Muyinga Province
- Easternmost point - unnamed location on the border with Tanzania immediately northwest of Mburi hill, Cankuzo Province
- Southernmost point - unnamed location on the border with Tanzania immediately north of the Tanzanian town of Mwenene, Makamba Province
- Westernmost point - unnamed location on the border the Democratic Republic of the Congo immediately east of the Congolese town of Kamanyola, Cibitoke Province
References
Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
Climate of Africa Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
 Burundi topics
Burundi topicsHistory Timeline · Burundi Civil War · Colonial heads · Genocide · German East Africa · Ruanda-Urundi · Monarchy · Second Congo WarPolitics Elections · Flag · Foreign relations · Human rights · Law enforcement · Military · Ministers · National Assembly · Political parties · Provincial governors · President · Prime Minister · SenateGeography Economy and infrastructure Culture and society List of Burundi-related topics Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.