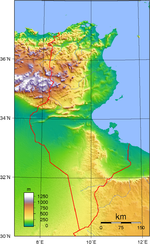
- Geography of Tunisia
-
Geography of Tunisia 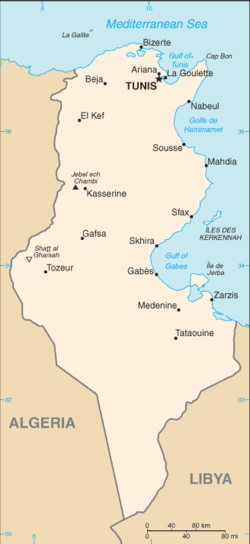
Continent Africa Region Northern Africa Coordinates 34°00′N 9°00′E / 34°N 9°E Area Ranked 92nd
163,610 km2 (63,170 sq mi)
95% land
5 % waterBorders Total land borders:
1,424 km
Algeria 965 km, Libya 459 kmHighest point Jebel ech Chambi
1,544 mLowest point Chott el Djerid
-17 mLongest river Medjerda River
450 kmTunisia is a country located in Northern Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Algeria and Libya. Its geographic coordinates are 34°00′N 9°00′E / 34°N 9°E. Tunisia occupies an area of 163,610 square kilometres, of which 8,250 are water. Tunisia borders Algeria for 965 km and Libya for 459 km.
Contents
Maritime claims
- Contiguous zone: 24 nmi (44.4 km; 27.6 mi)
- Territorial sea: 12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)
Physical geography
Tunisia is situated on the Mediterranean coast of North Africa, midway between the Atlantic Ocean and the Nile Delta. It is bordered by Algeria on the west and Libya on the south east. It lies between latitudes 30° and 38°N, and longitudes 7° and 12°E. An abrupt southward turn of the Mediterranean coast in northern Tunisia gives the country two distinctive Mediterranean coasts, west-east in the north, and north-south in the east. Tunisia is about the size of the American state of Wisconsin. Despite its relatively small size, Tunisia has great environmental diversity due to its north-south extent. Its east-west extent is limited. Differences in Tunisia, like the rest of the Maghreb, are largely north-south environmental differences defined by sharply decreasing rainfall southward from any point. The Dorsal, the eastern extension of the Atlas Mountains, runs across Tunisia in a northeasterly direction from the Algerian border in the west to the Cape Bon peninsula in the east. North of the Dorsal is the Tell, a region characterized by low, rolling hills and plains, again an extension of mountains to the west in Algeria. In the Khroumerie, the northwestern corner of the Tunisian Tell, elevations reach 1,050 metres (3,440 ft) and snow occurs in winter. The Sahel, a broadening coastal plain along Tunisia's eastern Mediterranean coast, is among the world's premier areas of olive cultivation. Inland from the Sahel, between the Dorsal and a range of hills south of Gafsa, are the Steppes. Much of the southern region is semi-arid and desert. Tunisia has a coastline 1,148 kilometres (713 mi) long. In maritime terms, the country claims a contiguous zone of 24 nautical miles (44.4 km; 27.6 mi), and a territorial sea of 12 nautical miles (22.2 km; 13.8 mi).
Climate
Tunisia's climate is temperate in the north, with mild rainy winters and hot, dry summers. Temperatures in July and August can exceed even up to 40°C. Winters are mild with temperatures rarely exceeding above 20°C (exception is the south-west of the country).[citation needed] The south of the country is desert. The terrain in the north is mountainous, which, moving south, gives way to a hot, dry central plain. The south is semiarid, and merges into the Sahara. A series of salt lakes, known as chotts or shatts, lie in an east-west line at the northern edge of the Sahara, extending from the Gulf of Gabes into Algeria. The lowest point is Chott el Djerid, at −17 m (−55.8 ft), and the highest is Jebel ech Chambi, at 1,544 metres (5,066 ft).
Largest cities
Cities in Tunisia Rank Name Population, 2006 Population, 2008 Governorate 1. Tunis 989,000 993,000 Tunis 2. Sfax 881,600 904,900 Sfax 3. Nabeul 714,500 733,500 Nabeul 4. Sousse 568,100 590,400 Sousse 5. Ben Arous 531,200 555,700 Ben Arous 6. Kairouan 550,300 553,800 Kairouan 7. Bizerte 532,900 538,900 Bizerte 8. Monastir 475,200 494,900 Monastir 9. Ariana 447,200 473,100 Ariana 10. Medenine 440,200 447,400 Medenine source: Institut National de la Statistique - Tunisie
Natural resources
Tunisia possesses petroleum, phosphates, iron ore, lead, zinc, salt and arable land. 3,850 km² of land is irrigated in Tunisia. The use of land in the country is demonstrated in the following table.
Land use Use Percentage of Area (1993) arable land 19 permanent crops 13 permanent pastures 20 forests and woodland 4 other 44 Environment
Current environmental issues for Tunisia include:
- Toxic and hazardous waste - disposal is ineffective and presents human health risks
- Water pollution from raw sewage
- Limited natural fresh water resources
- Deforestation
- Overgrazing
- Soil erosion
- Desertification
Tunisia is a party to the following international agreements: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution (MARPOL 73/78) and Wetlands. Tunisia has signed, but not ratified the Marine Life Conservation agreement.
Tunisia, like other North African countries, has lost much of its prehistoric biodiversity due to the ongoing expanding human population; for example, until historic times there was a population of the endangered primate Barbary Macaque, Macaca sylvanus.[1] The Monk Seal is now extirpated from Tunisia.[2]
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of Tunisia, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northern-most point - Iles des Chiens, Bizerte Governorate
- Northern-most point (mainland) – Ras ben Sakka (Ra's al Abyad), Bizerte Governorate*
- Eastern-most point – Bel Ahemer on the border with Libya, Medenine Governorate
- Southern-most point – the tripoint with Algeria and Libya, Tataouine Governorate
- Western-most point - unnamed location on the border with Algeria due west of Nefta, Tozeur Governorate
- *Note: this is also the northern-most point of the African continent
See also
References
- ^ C. Michael Hogan, (2008) Barbary Macaque: Macaca sylvanus, Globaltwitcher.com, ed. Nicklas Stromberg
- ^ Anthony Ham and Abigail Hole (2004) Tunisia, third ed., published by Lonely Planet, 312 pages, ISBN 1741041899
- Some material in this article is adapted from the CIA World Factbook 2008.
Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
Climate of Africa Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.