- Geography of Djibouti
-
 Satellite image of Djibouti
Satellite image of Djibouti
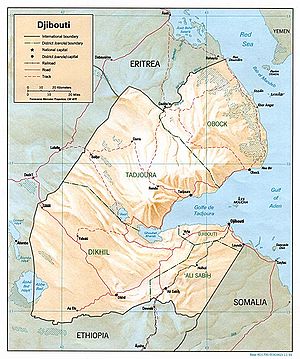
Djibouti is a country in Eastern Africa, bordering the Gulf of Aden and the Red Sea, between Eritrea and Somalia. Its coordinates are 11°30′N 43°00′E / 11.5°N 43°E.
Contents
Location
Djibouti shares 113 kilometres (70 mi) of border with Eritrea, 337 kilometres (209 mi) with Ethiopia and 58 kilometres (36 mi) with Somalia (total 506 km or 314 mi). It also has 314 kilometres (195 mi) of coastline.
It has a strategic location near the world's busiest shipping lanes and close to Arabian oilfields. Djibouti is also terminus of rail traffic into Ethiopia.
Climate
Its climate is mostly warm, dry desert.
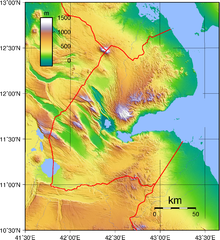
Terrain
Mountains in the center of the country separate a coastal plain and a plateau. The lowest point is Lac Assal (−155 m or −508.5 ft) and the highest is Moussa Ali (2,028 m or 6,654 ft). There is no arable land, irrigation, permanent crops, and negligible forest cover. (What little forest, is in the Goda Mountains, especially in the Day Forest National Park.) 9% of the country is permanent pastureland (1993 est). Therefore most of Djibouti has been described as part of the Ethiopian xeric grasslands and shrublands ecoregion except for a strip along the Red Sea coast is part of the Eritrean coastal desert, noted as an important migration route for birds of prey.[1]
Environment
Natural hazards include earthquakes, droughts, and occasional cyclonic disturbances from the Indian Ocean, which bring heavy rains and flash floods. Natural resources include geothermal energy. Inadequate supplies of potable water and desertification are current issues. Djibouti is a party to international agreements on Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution.
Area
- total: 23,000 km2 (8,880 sq mi)
- land: 22,980 km2 (8,873 sq mi)
- water: 20 km2 (8 sq mi)
Maritime claims
- contiguous zone: 24 nautical miles (44.4 km; 27.6 mi)
- exclusive economic zone: 200 nautical miles (370.4 km; 230.2 mi)
- territorial sea: 12 nautical miles (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of Djibouti, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northern-most point - Ras Doumera, Obock Region
- Northern-most point (mainland) - the point at which the border with Eritrea enters the Red Sea, Obock Region
- Eastern-most point - unnamed section of the Red Sea coast north of Ras Bir, Obock Region
- Southern-most point - unnamed location on the border with Ethiopia west of the town of As Ela, Dikhil Region
- Western-most point - unnamed location on the border with Ethiopia immediately east of the Ethiopian town of Afambo, Dikhil Region
References
 Djibouti topics
Djibouti topicsHistory Politics Constitution · Elections · Flag · Foreign relations · Law enforcement · Military · Political parties · President · Prime MinisterGeography Economy and infrastructure Culture and society Communications · Demographics · Education · Ethnic groups · Health · Holidays · Languages · Media · Music · Olympics · ReligionPortal Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
Climate of Africa Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
Categories:- Geography of Djibouti
- Afrotropic
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.