- Geography of Swaziland
-
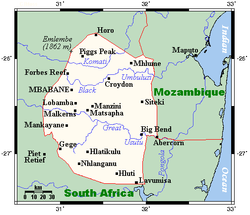
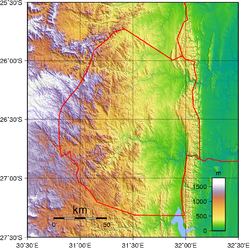
Swaziland is a country in Southern Africa, lying between Mozambique and South Africa. The country is located at the geographic coordinates 26°30′S 31°30′E / 26.5°S 31.5°E. Swaziland has an area of 17,363 square kilometres, of which 160 are water. The major regions of the country are Lowveld, Midveld and Highveld.
Contents
Climate
The climate of Swaziland varies from tropical to near temperate. The seasons are the reverse of those in the Northern Hemisphere with December being mid-summer and June mid-winter. Generally speaking, rain falls mostly during the summer months, often in the form of thunderstorms. Winter is the dry season. Annual rainfall is highest on the Highveld in the West, between 1,000 and 2,000 mm (39.4 and 78.7 in) depending on the year. The further East, the less rain, with the Lowveld recording 500 to 900 mm (19.7 to 35.4 in) per annum. Variations in temperature are also related to the altitude of the different regions. The Highveld temperature is temperate and, seldom, uncomfortably hot while the Lowveld may record temperatures around 40 °C (104 °F) in summer.
The average temperatures at Mbabane, according to seasons:
Spring September – October 18 °C (64.4 °F) Summer November – March 20 °C (68 °F) Autumn April – May 17 °C (62.6 °F) Winter June – August 13 °C (55.4 °F) Physical geography
The terrain largely consists of mountains and hills, with some moderately sloping plains. The lowest point is the Great Usutu River, at 21 metres, and the highest is Emlembe, at 1,862 m.
As a landlocked country, Swaziland has neither coastline nor maritime claims. In terms of land boundaries, Swaziland borders Mozambique for 105 kilometres, and South Africa for 430, giving a total land boundary length of 535 km.
Natural resources
Swaziland possesses the following natural resources: asbestos, coal, clay, cassiterite, hydropower, forests, small gold and diamond deposits, quarry stone, and talc
670 km² of the country's land is irrigated. The following table describes land use in Swaziland.
Land use Use Percentage of Area arable land 9.77 permanent crops 0.7 other 89.53 Environment
The kingdom of Swaziland is prone to floods and drought. Soil erosion as a result of overgrazing is a growing problem.
Swaziland is party to the following international agreements: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Endangered Species, Nuclear Test Ban and Ozone Layer Protection. The country has signed, but not ratified the agreement on desertification, and the law of the sea.
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of Swaziland, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northern-most point - unnamed location of the border with South Africa immediately north of the village of Horo, Hhohho District
- Eastern-most point - the tripoint with South Africa and Mozambique, Lubombo District
- Southern-most point - unnamed location on the border with South Africa, Shiselweni District
- Western-most point - a section of the border with South Africa, Manzini District*
- Note: Swaziland does not have a western-most point as the western-most section of the border is formed by the 31° longitude
External links
- European Digital Archive on the Soil Maps of the world - soil maps of Swaziland
Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
Climate of Africa Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.