- Geography of Morocco
-
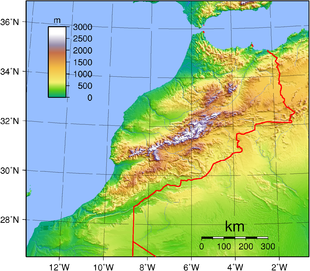
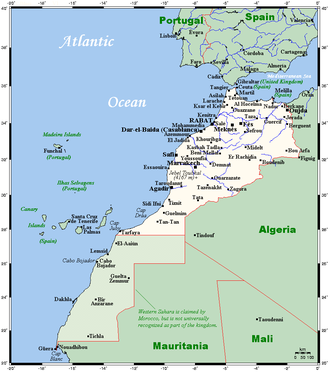
The geography of Morocco spans from the Atlantic Ocean, to mountainous areas, to the Sahara (desert). Morocco is a Northern African country, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
A large part of Morocco is mountainous. The Atlas Mountains are located mainly in the center and the south of the country. The Rif Mountains are located in the north of the country. Both ranges are mainly inhabited by the Berber people.
Geography statistics Coordinates: 32°00′N 5°00′W / 32°N 5°W
Map references: Africa
Area:
total: 446,550 km²
land: 446,550 km²
water: 250 km²Area - comparative: slightly larger than California
Land boundaries:
total: 2 017.9 km
border countries: Algeria 1 559 km, Mauritania 1561 km, Spain (Ceuta) 6.3 km, Spain (Melilla) 9.6 kmCoastline: 1 835 km
Maritime claims:
contiguous zone: 24 nmi (44.4 km; 27.6 mi)
continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
exclusive economic zone: 200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi)
territorial sea: 12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)Contents
Physical geography
Mediterranean, becoming more extreme in the interior
Terrain: northern coast and interior are mountainous with large areas of bordering plateaus, intermontane valleys, and rich coastal plains
Geography - note: strategic location along Strait of Gibraltar
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Sebkha Tah -55 m
highest point: Jbel Toubkal 4165 mClimate
Dry, hot, sandy summers and mild, wet winters.
Land use and natural resources
Natural resources: phosphates, iron ore, manganese, lead, zinc, fish, salt
Land use:
arable land: 21%
permanent crops: 1%
permanent pastures: 47%
forests and woodland: 20%
other: 11% (1993 est.)Irrigated land: 12 580 km² (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: northern mountains geologically unstable and subject to earthquakes; periodic droughts
Environment
Ecoregions
Terrestrial ecoregions
Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub
- Mediterranean dry woodlands and steppe
- Mediterranean woodlands and forests
- Mediterranean acacia-argania dry woodlands and succulent thickets
Temperate coniferous forests
Montane grasslands and shrublands
- Mediterranean High Atlas juniper steppe
Deserts and xeric shrublands
Freshwater ecoregions
- Permanent Maghreb
- Temporary Maghreb
Marine ecoregions
- Alboran Sea
- Saharan Upwelling
Current environmental issues
Land degradation/desertification (soil erosion resulting from farming of marginal areas, overgrazing, destruction of vegetation); water supplies contaminated by raw sewage; siltation of reservoirs; oil pollution of coastal waters
International environmental agreements
Morocco is party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution (MARPOL 73/78), Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Environmental Modification, Law of the SeaExtreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of Morocco, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location (excluding the disputed [[Western Sahara] area]).
- Northern-most point – Punta Cires, Tangier-Tétouan region
- Eastern-most point – unnamed point on the border with Algeria immediately east of the town of Iche, Oriental region
- Southern-most point – the border with Western Sahara, Guelmim-Es Semara region*
- Western-most point - the point at which the border with Western Sahara enters the Atlantic Ocean, Guelmim-Es Semara region
- *Note: Morocco does not have a southern-most point, the border being formed by a straight horizontal line
Gallery
-
Tanger by iboff.jpg
References
External links
- European Digital Archive on the Soil Maps of the world Soil Maps of Morocco
Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
Climate of Africa Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.