- Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub
-
 Eucalyptus forest.
Eucalyptus forest. A Mediterranean forest, the Upper Galilee
A Mediterranean forest, the Upper Galilee
Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome, defined by the World Wildlife Fund, characterized by dry summers and rainy winters. Summers are typically hot in low-lying inland locations but can be cool near some seas, as near San Francisco, which have a sea of cool waters. Winters are typically mild to cool in low-lying locations but can be cold in inland and higher locations.
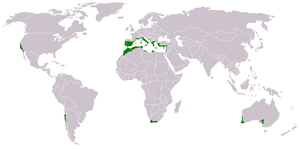
The Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome can be found around the world. More specifically, it occurs in the world's five Mediterranean climate zones, on the west coast of continents in the mid-latitudes:[1]
- the Mediterranean Basin
- the Chilean Matorral
- the California chaparral and woodlands ecoregion of California and the Baja California Peninsula
- the Cape Province-Western Cape of South Africa
- the Southwest Australia corner area
Contents
Diversity
These regions are home to a tremendous diversity of habitats and species. Vegetation types can range from forests to woodlands, savannas, shrublands, and grasslands; "mosaic habitat" landscapes are common, where differing vegetation types are interleaved with one another in complex patterns created by variations in soil, topography, exposure to wind and sun, and fire history. Much of the woody vegetation in Mediterranean-climate regions is sclerophyll, which means 'hard-leaved' in Greek. Sclerophyll vegetation generally has small, dark leaves covered with a waxy outer layer to retain moisture in the dry summer months.
All these ecoregions are highly distinctive, collectively harboring 10% of the Earth’s plant species.[2]Phytogeographers consider the Fynbos (South-Africa) as a separate floral kingdom because 68% of the 8,600 vascular plant species crowded into its 90,000 square kilometres (35,000 sq mi) are endemic and highly distinctive at several taxonomic levels).[1][3]
In terms of species densities, this is equivalent to about 40% of the plant species of the United States and Canada combined, found within an area the size of the state of Maine. The Fynbos and Southwest Australia shrublands have flora that are significantly more diverse than the other ecoregions, although any Mediterranean shrubland is still rich in species and endemics relative to other non-forest ecoregions.[1][3]
Biome Plant Groups
Major plant communities in this biome include:
- Forest: Mediterranean forests are generally composed of broadleaf trees, such as the oak and mixed sclerophyll forests of California and the Mediterranean region, the Eucalyptus forests of Southwest Australia, and the Nothofagus forests of central Chile. Forests are often found in riparian areas, where they receive more summer water. Coniferous forests also occur, especially around the Mediterranean. Pine and Deciduous Oak forest are widespread across California
- Woodland: Oak woodlands are characteristic of the Mediterranean Basin and in California. Pine woodlands are also present in the Mediterranean Basin. California additionally has walnut woodlands.
- Savanna and grassland: The California Central Valley grasslands are the largest Mediterranean grassland eco-region, although these grasslands have mostly been converted to agriculture. Small Woodland area occur mainly oak, walnut, or pine woodlands.
- Shrubland: Shrublands are dense thickets of evergreen sclerophyll shrubs and small trees, called chaparral (California), matorral (Chile and southern Spain), maquis (France and elsewhere around the Mediterranean), macchia (Italy), fynbos (South Africa), or kwongan (Southwest Australia). In some places shrublands are the mature vegetation type, and in other places the result of degradation of former forest or woodland by logging or overgrazing, or disturbance by major fires.
- Scrubland: Scrublands are most common near the seacoast, and are often adapted to wind and salt air from the ocean. Low, soft-leaved scrublands around the Mediterranean are known as garrigue in France, gariga in Italy, phrygana in Greece, tomillares in Spain, and batha in Israel. Northern coastal scrub and coastal sage scrub, also known as soft chaparral, occur near the California coast; strandveld in the Western Cape of South Africa; coastal matorral in the central Chile, and sand-heath and kwongan in Southwest Australia.The warm temperature allows the growth of delicate citrus fruits, including oranges, limes, and lemons.
Fire as a medium of change
Further information: Fire ecologyFire, both natural and human-caused, has played a large role in shaping the ecology of Mediterranean ecoregions. The hot, dry summers make much of the region prone to fires, and lightning-caused fires occur with some frequency. Many of the plants are pyrophytes, or fire-loving, adapted or even depending on fire for reproduction, recycling of nutrients, and the removal of dead or senescent vegetation. In both the Australian and Californian Mediterranean-climate eco-regions, native peoples used fire extensively to clear brush and trees, making way for the grasses and herbaceous vegetation that supported game animals and useful plants. The plant communities in these areas adapted to the frequent human-caused fires, and pyrophyte species grew more common and more fire-loving, while plants that were poorly adapted to fire retreated. After European colonization of these regions, fires were suppressed, which has caused some unintended consequences in these ecoregions; fuel builds up, so that when fires do come they are much more devastating, and some species dependent on fire for their reproduction are now threatened. The European shrublands have also been shaped by anthropogenic fire, historically associated with transhumance herding of sheep and goats.
Geography
Mediterranean eco-regions are semi-arid, and often have poor soils, so they are vulnerable to degradation by human activities such as logging, overgrazing, and the introduction of exotic species. These regions are also some of the most endangered on the planet, and many eco-regions have suffered tremendous degradation and habitat loss through logging, overgrazing, conversion to agriculture, urbanization, and introduction of exotic and invasive species. The eco-regions around the Mediterranean basin and in California have been particularly affected by degradation due to human activity, suffering extensive loss of forests and soil erosion, and many native plants and animals have become extinct or endangered.
References
- ^ a b c "Mediterranean Forests, Woodlands, and Scrub Ecoregions". WWF. http://www.panda.org/about_our_earth/ecoregions/about/habitat_types/selecting_terrestrial_ecoregions/habitat12.cfm. Retrieved 2010-05-27. (included verbatim material: licensed under CC-BY-SA-3.0)
- ^ Cody, M.L. (1986). "Diversity, rarity, and conservation in Mediterranean-climate regions". In Soulé, M.E.. Conservation biology: the science of scarcity and diversity. Sunderland, Massachusetts, USA.: Sinauer. pp. 122–152.
- ^ a b Cowling, R.M.; MacDonald, I.A.W.; Simmons, M.T. (1996). "The Cape Peninsula, South Africa: Physiographical, biological and historical background to an extraordinary hot-spot of biodiversity". Biodiversity and Conservation 5: 527–550.
External links
- National Geographic Global 200 Ecoregions: Mediterranean Forest, Woodland and Scrub. Part of National Geographic's Wild World Terrestrial Ecoregions of the World mapping project.
Biomes and Ecozones Terrestrial
biomesPolar/montaneTemperate(Sub)tropicalDryMediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub · Deserts and xeric shrublandsWetAquatic
biomesOther biomes Ecozones Categories:- Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub
- Terrestrial biomes
- Environment of the Mediterranean
- Flora of the Mediterranean
- Conifers
- Plant communities of California
- California chaparral and woodlands
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.