- Demographics of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
-
This article is about the demographic features of the population of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
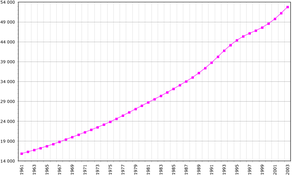 Demographics of Democratic Republic of the Congo, Data of FAO, year 2005 ; Number of inhabitants in thousands.
Demographics of Democratic Republic of the Congo, Data of FAO, year 2005 ; Number of inhabitants in thousands.
 Young women preparing fufu
Young women preparing fufu
As many as 250 ethnic groups have been distinguished and named. The most numerous people are the Bakongo, Luba, and Mongo.
Although 700 local languages and dialects are spoken, the linguistic variety is bridged both by the use of French and the intermediary languages Kikongo, Tshiluba, Swahili, and Lingala.
Christianity is the majority religion in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, followed by about 95.1% of the population. Denominations include Protestant (including Kimbanguism) 46.5%, Roman Catholic 41.5%, Orthodox 0.1%, other Christian 6.9%, Indigenous 2.8%, Muslim 0.9%, Non-religious 0.7%, Hindu 0.1%, and other 0.5%.[1] Kimbanguism was seen as a threat to the colonial regime and was banned by the Belgians. Kimbanguism, officially "the church of Christ on Earth by the prophet Simon Kimbangu", now has about three million members,[2] primarily among the Bakongo of Bas-Congo and Kinshasa. The largest concentration of Christians following William Branham is in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, where it is estimated that there are up to 2,000,000 followers.[citation needed]
Congolese diaspora
The table below shows DRC born people who have emigrated abroad (although it excludes their descendants).[3]
Rank Country Region DRC born population 1  France
FranceWestern Europe 19,080 2  Canada
CanadaNorth America 14,125 3  Belgium
BelgiumWestern Europe 9,911 4  United Kingdom
United KingdomNorthern Europe 8,569 5  United States
United StatesNorth America 3,455 6  Switzerland
SwitzerlandCentral Europe 2,570 7  Norway
NorwayNorthern Europe 1,759 8  Portugal
PortugalSouthern Europe 1,453 9  Netherlands
NetherlandsWestern Europe 1,314 10  Italy
ItalySouthern Europe 1,302 These are only estimates and do not account for Congolese migrants residing illegally in these countries. Among African countries, Congo's diaspora is second only to Nigeria in size.
CIA World Factbook demographic statistics
The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.
Population
- 71,712,867
- Note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population and growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and gender than would otherwise be expected (July 2011 est.)
Median age
- Total: 17.4 years
- Male: 17.2 years
- Female: 17.6 years (2011 est.)
Population growth rate
- 2.614% (2011)
Birth rate
- 37.74 births/1,000 population (2011 est.)
per day
Death rate
- 11.06 deaths/1,000 population (2011 est.)
per day
Net migration rate
-0.54 migrant(s)/1,000 population note: fighting between the Congolese Government and Uganda- and Rwanda-backed Congolese rebels spawned a regional war in DRC in August 1998, which left 2.33 million Congolese internally displaced and caused 412,000 Congolese refugees to flee to surrounding countries (2011 est.)
Given the situation in the country and the condition of state structures, it is extremely difficult to obtain reliable data however evidence suggests that DRC continues to be a destination country for immigrants in spite of recent declines. Immigration is seen to be very diverse in nature, with refugees and asylum-seekers - products of the numerous and violent conflicts in the Great Lakes Region - constituting an important subset of the population in the country. Additionally, the country’s large mine operations attract migrant workers from Africa and beyond and there is considerable migration for commercial activities from other African countries and the rest of the world, but these movements are not well studied. Transit migration towards South Africa and Europe also plays a role. Immigration in the DRC has decreased steadily over the past two decades, most likely as a result of the armed violence that the country has experienced. According to the International Organization for Migration, the number of immigrants in the DRC has declined from just over 1 million in 1960, to 754,000 in 1990, to 480,000 in 2005, to an estimated 445,000 in 2010. Valid figures are not available on migrant workers in particular, partly due to the predominance of the informal economy in the DRC. Data are also lacking on irregular immigrants, however given neighbouring country ethnic links to nationals of the DRC, irregular migration is assumed to be a significant phenomenon in the country.[4]
Figures on the number of Congolese nationals abroad vary greatly depending on the source, from 3 to 6 million. This discrepancy is due to a lack of official, reliable data. Emigrants from the DRC are above all long-term emigrants, the majority of which live within Africa and to a lesser extent in Europe; 79.7% and 15.3% respectively, according to estimates on 2000 data. Most Congolese emigrants however, remain in Africa, with new destination countries including South Africa and various points en route to Europe. In addition to being a host country, the DRC has also produced a considerable number of refugees and asylum-seekers located in the region and beyond. These numbers peaked in 2004 when, according to UNHCR, there were more than 460,000 refugees from the DRC; in 2008, Congolese refugees numbered 367,995 in total, 68% of which were living in other African countries.[4]
gender ratio
- At birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
- Under 15 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
- 15–64 years: 0.99 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over: 0.69 male(s)/female
- Total population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
Infant mortality rate
- Total: 78.43 deaths/1,000 live births
- Male: 82.20 deaths/1,000 live births
- Female: 74.55 deaths/1,000 live births (2011 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
- Total population: 55.33 years
- Male: 53.9 years
- Female: 56.8 years (2011 est.)
Total fertility rate
- 5.24 children born/woman (2011 est.)
HIV/AIDS
Main article: HIV/AIDS in the Democratic Republic of the Congo- Adult prevalence rate: 4.2% (2003 est.)
- People living with HIV/AIDS: 1.1 million (2003 est.)
- Deaths: 100,000 (2003 est.)
Major infectious diseases
- Degree of risk: very high
- Food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
- Vectorborne diseases: malaria, plague, and African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) are high risks in some locations
- Water contact disease: schistosomiasis (2005)
Nationality
- Noun: Congolese (singular and plural)
- Adjective: Congolese or Congo
Ethnic groups
See also: Category:Ethnic groups in the Democratic Republic of the Congo- Over 200 African ethnic groups of which the majority are Bantu; the four largest groups - Mongo, Luba, Kongo (all Bantu), and the Mangbetu-Azande make up about 45% of the population. The country has also 60,000 Belgians, whose ancestors stepped out after it won independence.
Religions
- Protestant 46.5, Roman Catholic 41.5%, Muslim 0.9%, Non-religious 0.7%, Hindu 0.1% other syncretic sects and indigenous beliefs 2.8%
These values are estimates dating from a census that is at least a decade old as the religious landscape in the Congo has dramatically changed since the collapse of the economy during the 80s and the advent of American Pentecostal movement. For instance, with more than 10 millions people, Kinshasa, the largest and capital city accounts for a number of charismatic or evangelical churches known as églises de reveil (awakening churches), whose members come primarily from the Roman Catholic Church, and in number may rival the Roman Catholic. Mega churches are all over the country. These charismatic churches also have a strong number of young followers in Kinshasa, Mbuji Mayi, and Lubumbashi. Roman Catholic percentage maybe a little less than 45%, mainstream Protestant 15%, and Kimbanguist 10%. The Islamic religion is not practiced as much anymore and is mostly concentrated in the eastern provinces and may be a little less than 1%. Catholics and mainstream Protestants call evangelical churches "sects", a derogatory term in the Congo for non-denominational churches. Evangelicals (or non-denominational churches) may therefore account for a little over 15% and indigenous beliefs the remaining of the population. In the diaspora, most Congolese belong to evangelical churches.[citation needed]
Languages
Main article: Languages of the Democratic Republic of the Congo- French (official), Lingala (a lingua franca trade language), Kingwana (a dialect of Swahili), Kikongo, Tshiluba, over 200 ethnic languages
English is taught as a compulsory Foreign language in Secondary and High School around the country. It is a required subject in the Faculty of Economics at majors Universities around the country and there are countless language schools in major cities around the country that teach primarily English. In the town of Beni, for instance there is a Bilingual University that offer courses in both French and English. President Kabila himself is fluent in both English and French, as was his father.
Literacy
- Definition: age 15 and over can read and write French, Lingala, Kingwana, or Tshiluba
- Total population: 65.5%
- Male: 76.2%
- Female: 55.1% (2003 est.)
See also
References
- ^ Joshua Project - Congo, Democratic Republic of - Religions
- ^ "Zaire (Democratic Republic of Congo)", Adherents.com – Religion by Location. Sources quoted are CIA Factbook (1998), 'official government web site' of Democratic Republic of Congo. Retrieved 25 may 2007.
- ^ "Country-of-birth database". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/18/23/34792376.xls. Retrieved 2008-09-21.
- ^ a b Migration en République Démocratique du Congo: Profil national 2009, International Organization for Migration, 2009, http://publications.iom.int/bookstore/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=41_42&products_id=592, retrieved 2010-08-17
 This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook document "2007 edition".
This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook document "2007 edition".See also
- Health in the Democratic Republic of the Congo
External links
- Mortality in the Democratic Republic of the Congo: An Ongoing CrisisPDF (1.07 MB), International Rescue Committee, January 2008 (estimates 5.4 million excess deaths above sub-Saharan average from 1998 to 2007)
Demographics of Africa Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
 Democratic Republic of the Congo topics
Democratic Republic of the Congo topicsPolitics and law History Early history · Colonisation (1867–85) · Congo Free State (1885–1908) · Belgian Congo (1908–60) · Congo-Léopoldville (1960–65) · Congo Crisis (1960–65) · Zaire (1965–97) · First Congo War (1996–98) · Second Congo War (1998–2003) · 2000sGeography Economy and infrastructure Agriculture · Airports · Central Bank · Communications · Energy · Franc · Health · Mining · Resource extraction · TransportCulture and society Categories:- Demographics by country
- Democratic Republic of the Congo society
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
