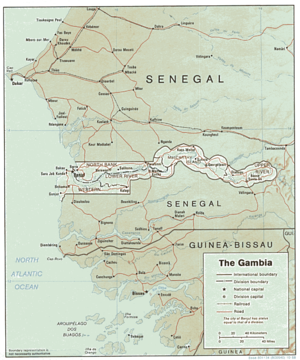
- Geography of the Gambia
-
The Gambia is a very small and narrow country with the border based on the Gambia River. The country is less than 48 km wide at its greatest width. The country's present boundaries were defined in 1889 after an agreement between the United Kingdom and France. It is often claimed by Gambians that the distance of the borders from the Gambia River correspond to the area that British naval cannon of the time could reach from the river's channel. However, there is no historical evidence to support the story, and the border was actually delineated using careful surveying methods by the Franco-British boundary commission.[1][2] Apart from its coastline, where The Gambia borders the Atlantic Ocean, it is an enclave of Senegal and is by far the smallest country on the continent of Africa.
Contents
Climate
The Gambia has a subtropical climate with distinct cool and hot seasons. From November to mid-May there is uninterrupted dry weather, with temperatures as low as 16 °C (60.8 °F) in Banjul and surrounding areas. Hot, humid weather predominates the rest of the year, with a rainy season from June to October; during this period, temperatures may rise as high as 43 °C (109.4 °F) but are usually lower near the sea. Mean temperatures range from 23 °C (73.4 °F) in January to 27 °C (80.6 °F) in June along the coast, and from 24 °C (75.2 °F) in January to 32 °C (89.6 °F) in May inland. The average annual rainfall ranges from 920 mm (36.2 in) in the interior to 1,450 mm (57.1 in) along the coast.
Terrain
The grassy flood plain of the Gambia river, which contains Guinean mangroves near the coast, with West Sudanian savanna upriver inland.
Statistics
Location: Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean and Senegal.
Geographic coordinates: 13°28′N 16°34′W / 13.467°N 16.567°W
Map references: Africa
Area:
total: 11,300 km²
land: 10,000 km²
water: 1,300 km²Area - comparative: slightly less than Jamaica; slightly less than the size of Delaware.
Land boundaries:
total: 740 km
border countries: Senegal 740 kmCoastline: 80 km
Maritime claims:
contiguous zone: 18 nmi (33.3 km; 20.7 mi)
continental shelf: not specified
exclusive fishing zone: 200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi)
territorial sea: 12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)Climate: tropical; hot, rainy season (June to November); cooler, dry season (November to May)
Terrain: flood plain of the Gambia river flanked by some low hills
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point: Red Rock 53 mNatural resources: fish, groundnuts (peanuts), titanium, tin, zircon, silica sand, clay, petroleum
Land use:
arable land: 27.88%
permanent crops: 0.44%
other: 71.68% (2005 est.)Irrigated land: 20 km² (2003)
Natural hazards: drought (rainfall has dropped by 30% in the last 30 years)
Environment - current issues: deforestation; desertification; water-borne diseases prevalent
Environment - international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsExtreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of The Gambia, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northern-most point – unnamed location on the border with Senegal immediatelysouth of the Senegalese village of Keur Mali Makham, Central River Division
- Eastern-most point – unnamed point on the border with Senegal near the village of Sembagne, Upper River Division
- Southern-most point – the point at which the border with Senegal enters the Atlantic Ocean at the mouth of the Allahein River, Western Division
- Western-most point - Bijol Islands, Western Division
- Western-most point (mainland) - Solifor Point, Western Division
Gallery
-
The Spotted hyena is part of The Gambia's fauna.
See also
Notes
Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
Climate of Africa Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.