- Spina bifida
-
Spina bifida Classification and external resources 
ICD-10 Q05, Q76.0 ICD-9 741, 756.17 OMIM 182940 DiseasesDB 12306 eMedicine orthoped/557 MeSH C10.500.680.800 Spina bifida (Latin: "split spine") is a developmental congenital disorder caused by the incomplete closing of the embryonic neural tube. Some vertebrae overlying the spinal cord are not fully formed and remain unfused and open. If the opening is large enough, this allows a portion of the spinal cord to protrude through the opening in the bones. There may or may not be a fluid-filled sac surrounding the spinal cord. Other neural tube defects include anencephaly, a condition in which the portion of the neural tube which will become the cerebrum does not close, and encephalocele, which results when other parts of the brain remain unfused.
Spina bifida malformations fall into three categories: spina bifida occulta, spina bifida cystica (myelomeningocele), and meningocele. The most common location of the malformations is the lumbar and sacral areas. Myelomeningocele is the most significant form and it is this that leads to disability in most affected individuals. The terms spina bifida and myelomeningocele are usually used interchangeably.
Spina bifida can be surgically closed after birth, but this does not restore normal function to the affected part of the spinal cord. Intrauterine surgery for spina bifida has also been performed and the safety and efficacy of this procedure is currently being investigated. The incidence of spina bifida can be decreased by up to 70% when daily folic acid supplements are taken prior to conception.
Contents
Classification
Spina bifida occulta
Occulta is Latin for "hidden". This is the mildest forms of spina bifida.[1]
In occulta, the outer part of some of the vertebrae are not completely closed.[2] The split in the vertebrae is so small that the spinal cord does not protrude. The skin at the site of the lesion may be normal, or it may have some hair growing from it; there may be a dimple in the skin, or a birthmark.[3]
Many people with the mildest form of this type of spina bifida do not even know they have it, as the condition is asymptomatic in most cases.[3] The incidence of spina bifida occulta is approximately 10% of the population,[4] and most people are diagnosed incidentally from spinal X-rays. A systematic review of radiographic research studies found no relationship between spina bifida occulta and back pain.[5] More recent studies not included in the review support the negative findings.[6][7][8]
However, other studies suggest spina bifida occulta is not always harmless. One study found that among patients with back pain, severity is worse if spina bifida occulta is present.[9][10]
Meningocele
The least common form of spina bifida is a posterior meningocele (or meningeal cyst).
In a posterior meningocele, the vertebrae develop normally, however the meninges are forced into the gaps between the vertebrae. As the nervous system remains undamaged, individuals with meningocele are unlikely to suffer long-term health problems, although there are reports of tethered cord. Causes of meningocele include teratoma and other tumors of the sacrococcyx and of the presacral space, and Currarino syndrome, Bony defect with outpouching of meninges.[11]
A meningocele may also form through dehiscences in the base of skull. These may be classified by their localisation to occipital, frontoethmoidal, or nasal. Endonasal meningoceles lie at the roof of the nasal cavity and may be mistaken for a nasal polyp. They are treated surgically. Encephalomeningoceles are classified in the same way and also contain brain tissue.
Myelomeningocele
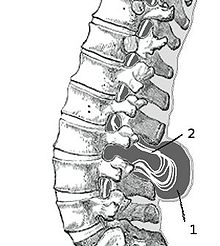 Myelomeningocele in the lumbar area.
Myelomeningocele in the lumbar area.
(1) External sac with cerebrospinal fluid.
(2) Spinal cord wedged between the vertebrae.This type of spina bifida is the most common and often results in the most severe complications.[12] In individuals with myelomeningocele, the unfused portion of the spinal column allows the spinal cord to protrude through an opening. The meningeal membranes that cover the spinal cord form a sac enclosing the spinal elements. Spina bifida with myeloschisis is the most severe form of myelomeninocele. In this type, the involved area is represented by a flattened, plate-like mass of nervous tissue with no overlying membrane. The exposure of these nerves and tissues make the baby more prone to life-threatening infections.[13]
The protruded portion of the spinal cord and the nerves which originate at that level of the cord are damaged or not properly developed. As a result, there is usually some degree of paralysis and loss of sensation below the level of the spinal cord defect. Thus, the higher the level of the defect, the more severe the associated nerve dysfunction and resultant paralysis. People may have ambulatory problems, loss of sensation, deformities of the hips, knees or feet and loss of muscle tone. Depending on the location of the lesion, intense pain may occur originating in the lower back, and continuing down the leg to the back of the knee.[citation needed]
Signs and symptoms
Physical Complications
Physical signs of spina bifida may include:
- Leg weakness and paralysis [14]
- Orthopedic abnormalities (i.e., club foot, hip dislocation, scoliosis) [14]
- Bladder and bowel control problems, including incontinence, urinary tract infections, and poor renal function [14]
- Latex allergy
- Pressure sores and skin irritations [14]
- Abnormal eye movement[15]
According to the Spina Bifida Association of America (SBAA), over 73 percent of people with spina bifida develop an allergy to latex, ranging from mild to life-threatening. The common use of latex in medical facilities makes this a particularly serious concern. The most common approach to avoid developing an allergy is to avoid contact with latex-containing products such as examination gloves, condoms, catheters, and many of the products used by dentists.[2]
The spinal cord lesion or the scarring due to surgery may result in a tethered spinal cord. In some individuals, this causes significant traction and stress on the spinal cord and can lead to a worsening of associated paralysis, scoliosis, back pain, and worsening bowel and/or bladder function.[16]
Neurological Complications
Many individuals with spina bifida will have an associated abnormality of the cerebellum, called the Arnold Chiari II malformation. In affected individuals, the back portion of the brain is displaced from the back of the skull down into the upper neck. In approximately 90 percent of the people with myelomeningocele, hydrocephalus will also occur because the displaced cerebellum interferes with the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid, causing an excess of the fluid to accumulate.[17] In fact, the cerebellum also tends to be smaller in individuals with spina bifida, especially for those with higher lesion levels.[15]
The corpus callosum is abnormally developed in 70-90% of individuals with spina bifida myelomeningocele; this impacts the communication processes between the left and right brain hemispheres.[18] Further, white matter tracts connecting posterior brain regions with anterior regions appear less-organized. White matter tracts between frontal regions have also been found to be impaired.[15]
Cortex abnormalities may also be present. For example, frontal regions of the brain tend to be thicker than expected while posterior and parietal regions are thinner. Thinner sections of the brain are also associated with increased cortical folding. [15] Neurons within the cortex may also be displaced.[19]
Executive Function
Several studies have demonstrated difficulties with executive functions in youth with spina bifida,[20][21] with greater deficits observed in youth with shunted hydrocephalus.[22][22] Unlike typically developing children, youth with spina bifida do not tend to improve in their executive functioning as they grow older.[21] Specific areas of difficulty in some individuals include planning, organizing, initiating, and working memory. Problem-solving, abstraction, and visual planning may also be impaired.[23] Further, children with spina bifida may have poor cognitive flexibility. Although executive functions are often attributed to the frontal lobes of the brain, individuals with spina bifida have intact frontal lobes; therefore, other areas of the brain may be implicated.[22]
Individuals with spina bifida, especially those with shunted hydrocephalus, often have attention problems. Children with spina bifida and shunted hydrocephalus have higher rates of ADHD than typically developing children (31% vs. 17%).[20] Deficits have been observed for selective attention and focused attention, although poor motor speed may contribute to poor scores on tests of attention.[22][24] Attention deficits may be evident at a very early age, as infants with spina bifida lag behind their peers in orienting to faces.[25]
Academic Skills
Individuals with spina bifida may struggle academically, especially in the subjects of mathematics and reading. In one study, 60% of children with spina bifida were diagnosed with a learning disability.[26] In addition to brain abnormalities directly related to various academic skills, achievement is likely affected by impaired attentional control and executive functioning.[19] Children with spina bifida may perform well in elementary school, but begin to struggle as academic demands increase.
Children with spina bifida are more likely than their typically-developing peers to have dyscalculia.[27] Individuals with spina bifida have demonstrated stable difficulties with arithmetic accuracy and speed, mathematical problem-solving, and general use and understanding of numbers in everyday life.[28] Mathematics difficulties may be directly related to the thinning of the parietal lobes (regions implicated in mathematical functioning) and indirectly associated with deformities of the cerebellum and midbrain that affect other functions involved in mathematical skills. Further, higher numbers of shunt revisions are associated with poorer mathematics abilities.[29] Working memory and inhibitory control deficiencies have been implicated for math difficulties,[30] although visual-spatial difficulties are not likely involved.[27] Early intervention to address mathematics difficulties and associated executive functions is crucial.[30]
Individuals with spina bifida tend to have better reading skills than mathematics skills.[29] Children and adults with spina bifida have stronger abilities in reading accuracy compared to reading comprehension.[31] Comprehension may be especially impaired for text that requires an abstract synthesis of information rather than a more literal understanding.[32] Individuals with spina bifida may have difficulty with writing due to deficits in fine motor control and working memory.[31]
Social Complications
Compared to typically developing children, youth with spina bifida may have fewer friends[33] and spend less time with peers.[34] They may be more socially immature and more passive in social situations.[34] Children with spina bifida have also reported feeling less close to their friends and feel they do not receive as much emotional support from their friendships.[35] Many social difficulties tend to be stable, lasting into adulthood.[36] Youth who encounter the most social difficulties tend to have lower executive functioning[37] and shunted hydrocephalus.[38] However, not all studies have found social difficulties in these youth compared with their typically developing peers.[39]
Pathophysiology
Spina bifida is caused by the failure of the neural tube to close during the first month of embryonic development (often before the mother knows she is pregnant).
Normally the closure of the neural tube occurs around the 23rd (rostral closure) and 27th (caudal closure) day after fertilization.[40] However, if something interferes and the tube fails to close properly, a neural tube defect will occur. Medications such as some anticonvulsants, diabetes, having a relative with spina bifida, obesity, and an increased body temperature from fever or external sources such as hot tubs and electric blankets may increase the chances of conception of a baby with a spina bifida. However, most women who give birth to babies with spina bifida have none of these risk factors, and so in spite of much research, it is still unknown what causes the majority of cases.[citation needed]
Extensive evidence from mouse strains with spina bifida indicates that there is sometimes a genetic basis for the condition. In human spina bifida, as with other human diseases such as cancer, hypertension and atherosclerosis (coronary artery disease), spina bifida likely results from the interaction of multiple genes and environmental factors.
Research has shown that lack of folic acid (folate) is a contributing factor in the pathogenesis of neural tube defects, including spina bifida. Supplementation of the mother's diet with folate can reduce the incidence of neural tube defects by about 70 percent, and can also decrease the severity of these defects when they occur.[41][42][43] It is unknown how or why folic acid has this effect.
Spina bifida does not follow direct patterns of heredity like muscular dystrophy or haemophilia. Studies show that a woman who has had one child with a neural tube defect such as spina bifida, has about a three percent risk of having another child with a neural tube defect. This risk can be reduced to about one percent if the woman takes high doses (4 mg/day) of folic acid before and during pregnancy. For the general population, low-dose folic acid supplements are advised (0.4 mg/day).[citation needed]
Prevention
There is no single cause of spina bifida nor any known way to prevent it entirely. However, dietary supplementation with folic acid has been shown to be helpful in preventing spina bifida (see above). Sources of folic acid include whole grains, fortified breakfast cereals, dried beans, leaf vegetables and fruits.[44]
Folate fortification of enriched grain products has been mandatory in the United States since 1998. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Public Health Agency of Canada[45] and UK recommended amount of folic acid for women of childbearing age and women planning to become pregnant is at least 0.4 mg/day of folic acid from at least three months before conception, and continued for the first 12 weeks of pregnancy.[46] Women who have already had a baby with spina bifida or other type of neural tube defect, or are taking anticonvulsant medication should take a higher dose of 4–5 mg/day.[46]
Certain mutations in the gene VANGL1 are implicated as a risk factor for spina bifida: these mutations have been linked with spina bifida in some families with a history of spina bifida.[47]
Pregnancy screening
Neural tube defects can usually be detected during pregnancy by testing the mother's blood (AFP screening) or a detailed fetal ultrasound. Increased levels of maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (MSAFP) should be followed up by two tests - an ultrasound of the fetal spine and amniocentesis of the mother's amniotic fluid (to test for alpha-fetoprotein and acetylcholinesterase). Spina bifida may be associated with other malformations as in dysmorphic syndromes, often resulting in spontaneous miscarriage. However, in the majority of cases spina bifida is an isolated malformation.
Genetic counseling and further genetic testing, such as amniocentesis, may be offered during the pregnancy as some neural tube defects are associated with genetic disorders such as trisomy 18. Ultrasound screening for spina bifida is partly responsible for the decline in new cases, because many pregnancies are terminated out of fear that a newborn might have a poor future quality of life. With modern medical care, the quality of life of patients has greatly improved.[40]
Treatment
There is no known cure for nerve damage due to spina bifida. To prevent further damage of the nervous tissue and to prevent infection, pediatric neurosurgeons operate to close the opening on the back. The spinal cord and its nerve roots are put back inside the spine and covered with meninges. In addition, a shunt may be surgically installed to provide a continuous drain for the excess cerebrospinal fluid produced in the brain, as happens with hydrocephalus. Shunts most commonly drain into the abdomen or chest wall. However, if spina bifida is detected during pregnancy, then open fetal surgery can be performed.[17]
Most individuals with myelomeningocele will need periodic evaluations by a variety of specialists[48] :
- Orthopedists to monitor growth and development of bones, muscles, and joints
- Neurosurgeons to perform surgeries at birth and manage complications associated with tethered cord and hydrocephalus
- Neurologists to treat and evaluate nervous system issues such as seizure disorders
- Urologists to address kidney, bladder, and bowel dysfunction. Many will need to manage their urinary system with a program of catheterization. Bowel management programs aimed at improving elimination are also designed.
- Opthamologists to evaluate and treat complications of the eyes.
- Orthotists to design and customize various types of assistive technology, including braces, crutchers, walkers, and wheelchairs to aid in mobility. As a general rule, the higher the level of the spina bifida defect the more severe the paralysis, but paralysis does not always occur. Thus, those with low levels may need only short leg braces while those with higher levels do best with a wheelchair, and some may be able to walk unaided.
- Physical therapists, occupational therapists, and speech/language pathologists to aid in rehabilitative therapies and increase independent living skills.
Such care is best begun immediately after birth.
Fetal surgery clinical trials
Management of Myelomeningocele Study (MOMS)[49] is a phase III clinical trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of fetal surgery to close a myelomeningocele. This involves surgically opening the pregnant mother's abdomen and uterus to operate on the fetus. This route of access to the fetus is called "open fetal surgery". Fetal skin grafts are used to cover the exposed spinal cord, to protect it from further damage caused by prolonged exposure to amniotic fluid. The fetal surgery may decrease some of the damaging effects of the spina bifida, but at some risk to both the fetus and the pregnant woman.
The MOMS trial was closed for efficacy in December 2010 based on comparing outcomes after prenatal and postnatal repair in 183 patients.
The trial demonstrated that outcomes after prenatal spina bifida treatment are improved to the degree that the benefits of the surgery outweigh the maternal risks. Results were reported in the New England Journal of Medicine by Adzick et al.[50]
Specifically, the study found that prenatal repair resulted in:
- Reversal of the hindbrain herniation component of the Chiari II malformation
- Reduced need for ventricular shunting (a procedure in which a thin tube is introduced into the brain’s ventricles to drain fluid and relieve hydrocephalus)
- Reduced incidence or severity of potentially devastating neurologic effects caused by the spine’s exposure to amniotic fluid, such as impaired motor function
In contrast to the open fetal operative approach tested in the MOMS, a minimally invasive approach is currently being tested by the German Center for Fetal Surgery & Minimally Invasive Therapy at the University of Giessen, Germany.[51] This minimally invasive approach uses three small tubes (trocars) with an external diameter of 5 mm that are directly placed via small needle punctures through the maternal abdominal wall into the uterine cavity. Via this route, the unborn can be postured and its spina bifida defect be closed using small instruments. In contrast to open fetal surgery for spina bifida, the fetoscopic approach results in less trauma to the mother as large incisions of her abdomen and uterus are not required. Early results indicate that the approach may maintain the fetal muscular and sensory function that is still present at the time of fetal surgery, regardless of lesion height.
Although fetoscopic techniques that involve making multiple puncture wounds in the uterus are theoretically appealing to potentially mitigate maternal morbidity, clinical reports on their use are limited and the results have been disappointing, primarily because of uterine membrane problems leading to premature birth 3 to 6 weeks after the procedure and delivery before 30 weeks of gestation.[52] As compared with the open fetal surgery technique, fetoscopic repair of myelomeningocele has resulted in higher rates of fetal death, premature rupture of membranes, chorioamnionitis, oligohydramnios, premature delivery, and persistent hindbrain herniation.[53][54] [55] If the problems of membrane rupture associated with fetoscopy can be solved, this minimally invasive approach to repairing myelomeningocele before birth should be tested clinically.
Epidemiology
Spina bifida is one of the most common birth defects, with an average worldwide incidence of 1–2 cases per 1000 births, but certain populations have a significantly greater risk.
In the United States, the average incidence is 0.7 per 1000 live births. The incidence is higher on the East Coast than on the West Coast, and higher in whites (1 case per 1000 live births) than in blacks (0.1–0.4 case per 1000 live births). Immigrants from Ireland have a higher incidence of spina bifida than do nonimmigrants.[56][57]
The highest incidence rates worldwide were found in Ireland and Wales, where 3–4 cases of myelomeningocele per 1000 population have been reported during the 1970s, along with more than six cases of anencephaly (both live births and stillbirths) per 1000 population. The reported overall incidence of myelomeningocele in the British Isles was 2–3.5 cases per 1000 births.[56][57] Since then, the rate has fallen dramatically with 0.15 per 1000 live births reported in 1998,[40] though this decline is partially accounted for by the fact that some fetuses are aborted when tests show signs of spina bifida (see Pregnancy screening above).
Parents of children with spina bifida have an increased risk of having a second child with a neural tube defect.[56][57]
This condition is more likely to appear in females; the cause for this is unknown.[citation needed]
Society and culture
Media
Nadia DeFranco, a young girl living with spina bifida was the subject of a Canadian short documentary I'll Find a Way, winner of the Academy Award for Best Live Action Short Film in 1977.[58]
The principal character in Stronger than Superman, an award winning theatre play by Roy Kift for audiences of 14 years and upwards, is a teenage boy with spina bifida. It premiered at the GRIPS Theater in Berlin in 1981 and has been performed all over the world, including Iceland, India and China. The play is a comedy with songs, whose humour derives from the reactions of the outside world to handicapped persons. It is published by Amber Lane Press in GB.[citation needed]
Notable people
Notable people that have spina bifida:
- Samuel Armas (an early recipient of open fetal surgery)
- Lucy Coleman, from the children's TV show Signing Time!
- Andy W. Clift,[59] British animator and film maker
- James Connelly, US Paralympian, 2006 Bronze Medal Winner, 2010 Gold Medal Winner; Sledge hockey
- Jean Driscoll, Paralympian and eight-time Boston Marathon winner
- Guro Fjellanger, Norwegian politician
- Aaron Fotheringham, American extreme wheelchair athlete
- Tanni Grey-Thompson, British Paralympian
- Lawrence Gwozdz, US saxophonist
- Adam Hall, New Zealand Paralympian, 2010 Gold Medal Winner
- Blaine Harrison,[60] lead singer, keyboards, rhythm guitarist and former drummer of the British band Mystery Jets
- Robert Hensel, Guinness record holder
- Rene Kirby,[61] US actor in films such as Shallow Hal and Stuck on You
- Matt Lloyd, British Paralympian
- John Mellencamp,[62] US rock and roll musician
- Karin Muraszko,[63] chair of Department of Neurosurgery at University of Michigan, first female appointed to such a position in the US
- Chandre Oram, an Indian man famous for his tail
- David Proud, British actor
- Jack Pryor, Professor of Developmental Neurology, University of Warwick
- Jesse Richards, American artist and filmmaker, founder of Remodernist film
- George Schappell, conjoined twin and country music musician
- Bobby Steele, US punk rock guitarist and songwriter
- Jeffrey Tate, British conductor
- Dale Tryon, Baroness Tryon, Australian socialite and friend of Prince Charles
- Hank Williams, US country music singer
- Lucinda Williams,[64] US country music singer/songwriter
- Miller Williams,[64] US poet
- Justin Yoder, US soap box racer
Popular Culture
At the end of Season 7 of Grey's Anatomy, Derek Shepherd and Meredith Grey attempt to adopt an African orphan, Zola, diagnosed with Spina Bifida.
See also
- Valproic acid
- Pseudomeningocele
- Malone antegrade continence enema (MACE)
- Meningohydroencephalocoele
- Mitrofanoff appendicovesicostomy
References
- ^ "What Is Spina Bifida?". ASBAH. http://www.asbah.org/Spina+Bifida/informationsheets/whatisspinabifida.htm. Retrieved 2009-02-14.
- ^ a b Foster, Mark R. "Spina Bifida". http://www.emedicine.com/orthoped/TOPIC557.HTM. Retrieved 2008-05-17.
- ^ a b "Spina Bifida Occulta". ASBAH. http://www.asbah.org/Spina+Bifida/informationsheets/spinabifidaocculta.htm. Retrieved 2009-02-14.
- ^ Saluja PG (1988). "The incidence of spina bifida occulta in a historic and a modern London population". J Anat. 158: 91–93. PMC 1261979. PMID 3066791. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1261979.
- ^ van Tulder MW, Assendelft WJ, Koes BW, Bouter LM (1997). "Spinal radiographic findings and nonspecific low back pain. A systematic review of observational studies". Spine 22 (4): 427–34. doi:10.1097/00007632-199702150-00015. PMID 9055372.
- ^ Iwamoto J, Abe H, Tsukimura Y, Wakano K (2005). "Relationship between radiographic abnormalities of lumbar spine and incidence of low back pain in high school rugby players: a prospective study". Scandinavian journal of medicine & science in sports 15 (3): 163–8. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0838.2004.00414.x. PMID 15885037.
- ^ Iwamoto J, Abe H, Tsukimura Y, Wakano K (2004). "Relationship between radiographic abnormalities of lumbar spine and incidence of low back pain in high school and college football players: a prospective study". The American journal of sports medicine 32 (3): 781–6. doi:10.1177/0363546503261721. PMID 15090397.
- ^ Steinberg EL, Luger E, Arbel R, Menachem A, Dekel S (2003). "A comparative roentgenographic analysis of the lumbar spine in male army recruits with and without lower back pain". Clinical radiology 58 (12): 985–9. doi:10.1016/S0009-9260(03)00296-4. PMID 14654032.
- ^ Taskaynatan MA, Izci Y, Ozgul A, Hazneci B, Dursun H, Kalyon TA (2005). "Clinical significance of congenital lumbosacral malformations in young male population with prolonged low back pain". Spine 30 (8): E210–3. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000158950.84470.2a. PMID 15834319.
- ^ Avrahami E, Frishman E, Fridman Z, Azor M (1994). "Spina bifida occulta of S1 is not an innocent finding". Spine 19 (1): 12–5. doi:10.1097/00007632-199401000-00003. PMID 8153797.
- ^ Kaplan hand book
- ^ "Myelomeningocele". NIH. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001558.htm. Retrieved 2008-06-06.
- ^ Mayo Clinic
- ^ a b c d Mitchell, L. E.; Adzick, N. S., Melchionne, J., Pasquariello, P. S., Sutton, L. N., & Whitehead, A. S. (2004). "Spina bifida". Lancet 364 (9448): 1885–1895. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17445-X. PMID 15555669.
- ^ a b c d Juranek, J; Salman MS (2010). "Anomalous development of brain structure and function in spina bifida myelomeningocele". Developmental Disabilities. 1 16: 23-30.
- ^ "Tethered Spinal Cord Syndrome". AANS. http://www.aans.org/Patient%20Information/Conditions%20and%20Treatments/Tethered%20Spinal%20Cord%20Syndrome.aspx. Retrieved 2011-10-23.
- ^ a b "Chiari Malformation Fact Sheet: National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)". Ninds.nih.gov. 2011-09-16. http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/chiari/detail_chiari.htm#186143087. Retrieved 2011-10-23.
- ^ Barkovich, J (2005). Pediatric Neuroimaging. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkens.
- ^ a b Wills, KE (1993). "Neuropsychological functioning in children with spina bifida and/or hydrocephalus". Journal of Clinical Child Psychology 22 (2): 247-265.
- ^ a b Burmeister, R; Hannay HJ, Copeland K, Fletcher JM, Boudousquie A, & Dennis M (2005). "Attention problems and executive functions in children with spina bifida and hydrocephalus". Child Neuropsychology 11 (3): 265–283. doi:10.1080/092970490911324. PMID 16036451.
- ^ a b Tarazi, RA; Zabel TA, & Mahone EM (2008). "Age-related changes in executive function among children with spina bifida/hydrocephalus based on parent behavior ratings". The Clinical Neuropsychologist 22 (4): 585–602. doi:10.1080/13854040701425940. PMC 2575658. PMID 17853154. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2575658.
- ^ a b c d Fletcher, JM, Brookshire BL, Landry SH, Bohan TP, Davidson KC et al. (1996). "Attentional skills and executive functions in children with early hydrocephalus". Developmental Neuropsychology 12: 53–76. doi:10.1080/87565649609540640.
- ^ Snow, JH (1999). "Executive processes for children with spina bifida". Children's Health Care 28 (3): 241–253. doi:10.1207/s15326888chc2803_3.
- ^ Rose, BM; Holmbeck GN (2007). "Attention and executive functions in adolescents with spina bifida". Journal of Pediatric Psychology 32 (8): 983–994. doi:10.1093/jpepsy/jsm042. PMID 17556398.
- ^ Landry, SH; Robinson SS, Copeland D, & Garner PW (1993). "Goal-directed behavior and perception of self-competence in children with spina bifida". Journal of Pediatric Psychology 18 (3): 389–396. doi:10.1093/jpepsy/18.3.389. PMID 8340846.
- ^ Mayes, SD; Calhoun, SL (2006). "Frequency of reading, math, and writing disabilities in children with clinical disorders". Learning and Individual Differences 16 (2): 145-157.
- ^ a b Barnes, MA; Wilkinson, M, Khemani, E, Boudesquie, A, Dennis, M, & Fletcher, JM (2006). "Arithmetic processing in children with spina bifida: Calculation accuracy, strategy use, and fact retrieval fluency". Journal of Learning Disabilities 39 (2): 174-187.
- ^ Dennis, M; Barnes, M (2002). "Math and numeracy in young adults with spina bifida and hydrocephalus". Developmental Neuropsychology 21 (2): 141-155.
- ^ a b Hetherington, R; Dennis M, Barnes M, Drake J, & Gentili J (2006). "Functional outcome in young adults with spina bifida and hydrocephalus". Child’s Nervous System 22 (2): 117-124. doi:10.1007/s00381-005-1231-4.
- ^ a b English,, LH; Barnes, MA, Taylor, HB, Landry, SH (2009). "Mathematical developmental development in spina bifida". Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews 15 (1): 28-34.
- ^ a b Barnes, M; Dennis M, & Hetherington R (2004). "Reading and writing skills in young adults with spina bifida and hydrocephalus". Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society 10 (5): 655-663. doi:10.10170S1355617704105055.
- ^ Fletcher, JM; Dennis M, Northrup H, Barnes AM, Hannay HJ...Francis, DF (2004). "Spina bifida: Genes, brain, and development". International Review of Research in Mental Retardation 29: 63-117. doi:10.1016/S0074-7750(04)29003-6.
- ^ Ellerton, M. L.; Stewart, M. J., Ritchie, J. A., & Hirth, A. M. (1996). "Social support in children with a chronic illness". The Canadian Journal of Nursing Research 28 (4): 15–36. PMID 9128474.
- ^ a b Holmbeck, G. N.; Westhoven, V. C., Phillips, W. S., Bowers, R., Gruse, C., Nikolopoulos, T.,...Davison, K. (2003). "A multimethod, multi-informant, and multidimensional perspective on psychosocial adjustment in preadolescents with spina bifida". Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 71 (4): 782–796. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.71.4.782. PMID 12924683.
- ^ Devine, K. A.; Gayes, L., Purnell, J., & Holmbeck, G. N. (in press). "Close friendships of children and adolescents with spina bifida: Reciprocity and social adjustment". Journal of Pediatric Psychology.
- ^ Holmbeck, G. N.; DeLucia, C., Essner, B., Kelly, L., Zebracki, K., Friedman, D., & Jandasek, B. (2010). "Trajectories of psychosocial adjustment in adolescents with spina bifida: A 6-year, four-wave longitudinal follow-up". Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 78 (4): 511–525. doi:10.1037/a0019599. PMID 20658808.
- ^ Zukerman, J. N.; Devine, K. A., & Holmbeck, G. N. (2011). "Adolescent predictors of emerging adult milestones in youth with spina bifida". Journal of Pediatric Psychology 36 (3): 265–276. doi:10.1093/jpepsy/jsq075. PMC 3062284. PMID 20855288. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=3062284.
- ^ Hommeyer, J. S.; Holmbeck, G. N., Wills, K. E., & Coers, S. (1999). "Condition severity and psychosocial functioning in pre-adolescents with spina bifida: Disentangling proximal functional status and distal adjustment outcomes". Journal of Pediatric Psychology 24 (6): 499–509. doi:10.1093/jpepsy/24.6.499. PMID 10608101.
- ^ Coakley, R. M.; Holmbeck, G. N., & Bryant, F. B. (2006). "Constructing a prospective model of psychosocial adaptation in young adolescents with spina bifida: An application of optimal data analysis". Journal of Pediatric Psychology 31 (10): 1084–1099. doi:10.1093/jpepsy/jsj032. PMID 15888643.
- ^ a b c T. Lissauer, G. Clayden. Illustrated Textbook of Paediatrics (Second Edition). Mosby, 2003. ISBN 0-7234-3178-7
- ^ Holmes LB (1988). "Does taking vitamins at the time of conception prevent neural tube defects?". JAMA 260 (21): 3181. doi:10.1001/jama.260.21.3181. PMID 3184398.
- ^ Milunsky A, Jick H, Jick SS et al. (1989). "Multivitamin/folic acid supplementation in early pregnancy reduces the prevalence of neural tube defects". JAMA 262 (20): 2847–52. doi:10.1001/jama.262.20.2847. PMID 2478730.
- ^ Mulinare J, Cordero JF, Erickson JD, Berry RJ (1988). "Periconceptional use of multivitamins and the occurrence of neural tube defects". JAMA 260 (21): 3141–5. doi:10.1001/jama.260.21.3141. PMID 3184392.
- ^ "Folic Acid Fortification". FDA. February 1996. http://vm.cfsan.fda.gov/~dms/wh-folic.html.
- ^ "Folic Acid - Public Health Agency of Canada". http://www.phac-aspc.gc.ca/fa-af/index.html.
- ^ a b "Why do I need folic acid?". NHS Direct. 2006-04-27. Archived from the original on April 13, 2006. http://web.archive.org/web/20060413083456/http://www.nhsdirect.nhs.uk/articles/article.aspx?articleId=913. Retrieved 2006-08-19.
- ^ Kibar Z, Torban E, McDearmid JR, Reynolds A, Berghout J, Mathieu M, Kirillova I, De Marco P, Merello E, Hayes JM, Wallingford JB, Drapeau P, Capra V, Gros P (2007). "Mutations in VANGL1 associated with neural-tube defects" (–Scholar search). N. Engl. J. Med. 356 (14): 1432–7. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa060651. PMID 17409324. http://content.nejm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=short&pmid=17409324&promo=ONFLNS19.[dead link]
- ^ "Center for Spina Bifida: Specialists and Services". Gillette Children's Hospital Center for Spina Bifida. Gillette Children's Hospital. http://www.gillettechildrens.org/default.cfm?PID=1.17.1.8. Retrieved 15 November 2011.
- ^ MOMS website and MOMS summary on ClinicalTrials.gov
- ^ Adzick, NS; Thom, Elizabeth A.; Spong, Catherine Y.; Brock, John W.; Burrows, Pamela K.; Johnson, Mark P.; Howell, Lori J.; Farrell, Jody A. et al. (February 9, 2011). "A Randomized Trial of Prenatal versus Postnatal Repair of Myelomeningocele". New England Journal of Medicine. Online First 364 (11): 993–1004. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1014379. PMID 21306277. http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1014379#.
- ^ "Universitätsklinikum Giessen und Marburg - Offener Rücken/ Spina bifida aperta". Ukgm.de. http://www.ukgm.de/ugm_2/deu/ugm_dzf/16799.html. Retrieved 2011-10-23.
- ^ Kohl T, Gembruch U, Thomas; Thomas Kohl, Ulrich Gembruch (October 3, 2008). "Current status and prospects of fetoscopic surgery for spina bifida in human fetuses". Fetal Diagnosis and Therapy 24: 318-320. http://content.karger.com/ProdukteDB/produkte.asp?doi=10.1159/000158549.
- ^ Verbeek, R; Heep A, Maurits N, et al. (15). "Does fetal endoscopic closure of the myelomeningocele prevent loss of neurologic function in spina bifida aperta?". Cerebrospinal Fluid Research 7 (1): S18-S18. doi:10.1186/1743-8454-7-S1-S18. http://www.fluidsbarrierscns.com/content/7/S1/S18.
- ^ Farmer, DL; Cornelia S. von Koch, MD, PhD; Warwick J. Peacock, MD; Moise Danielpour, MD; Nalin Gupta, MD, PhD; Hanmin Lee, MD; Michael R. Harrison, MD (2003). "In utero repair of myelomeningocele: experimental pathophysiology, initial clinical experience, and outcomes". Arch Surg 138: 872-878. http://archsurg.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/abstract/138/8/872.
- ^ "Current status and prospects of fetoscopic surgery for spina bifida in human fetuses". Fetal Diagn Ther 24: 318-320. 2008. doi:10.1159/000158549. http://content.karger.com/ProdukteDB/produkte.asp?doi=10.1159/000158549.
- ^ a b c Lemire RJ (1988). "Neural tube defects". JAMA 259 (4): 558–62. doi:10.1001/jama.259.4.558. PMID 3275817.
- ^ a b c Cotton P (1993). "Finding neural tube 'zippers' may let geneticists tailor prevention of defects". JAMA 270 (14): 1663–4. doi:10.1001/jama.270.14.1663. PMID 8411482.
- ^ Shaffer, Beverly (1977). "I'll Find a Way". National Film Board of Canada Web site. http://www.nfb.ca/film/Ill_find_a_way. Retrieved 2009-05-27.
- ^ IMDB (2010-12-07). "Andy W. Clift IMDB page". imdb.com. http://www.imdb.com/name/nm4176135/. Retrieved 2010-07-07.
- ^ Martin, Dan (2008-06-14). "Dan Martin meets Blaine from the Mystery Jets". guardian.co.uk. http://www.guardian.co.uk/music/2008/jun/14/features16.theguide. Retrieved 2008-08-06.
- ^ "Interview with actress Sascha Knopf from Shallow Hal". Movies.about.com. 2009-12-17. http://movies.about.com/library/weekly/aa110201g.htm. Retrieved 2011-10-23.
- ^ John Mellencamp bio from Yahoo Music
- ^ Gavin, Kara (2001). "U-M Neurosurgeon Urges Women to Protect their Children by Taking Folic Acid". Medicine at Michigan 3 (2). http://www.medicineatmichigan.org/magazine/2001/spring/huron/huron12.asp. Retrieved 2008-07-03.
- ^ a b Lewine, Edward (March 1, 2009). "Domains: Country House". New York Times (The New York Times Company): pp. MM17. http://www.nytimes.com/2009/03/01/magazine/01wwln-domains-t.html. Retrieved 2009-03-02.
External links
- http://www.ifglobal.org/en/spina-bifida.html
- CDC: Spina Bifida
- The International Federation for Spina Bifida and Hydrocephalus - Umbrella organization
- Association for Spina Bifida and Hydrocephalus (of the UK)
- Spina Bifida Association of America
- Spina Bifida Support Forum (Global - not affiliated with any national organization)
- UCSF Fetal Treatment Center: Myelomeningocele (Spina Bifida)
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke: Spina Bifida Information Page
- Mayo Clinic: Spina bifida Symptoms
- The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia: Eligibility Guidelines for Prenatal Repair of Myelomeningocele
Congenital malformations and deformations of nervous system (Q00–Q07, 740–742) Brain Anencephaly (Acephaly, Acrania, Acalvaria, Iniencephaly) · Encephalocele · Arnold–Chiari malformationOtherSpinal cord OtherCongenital malformations and deformations of musculoskeletal system / musculoskeletal abnormality (Q65–Q76, 754–756.3) Appendicular
limb / dysmeliahand deformity:Lowerhip:knee:Genu valgum · Genu varum · Genu recurvatum · Discoid meniscus · Congenital patellar dislocation · Congenital knee dislocationfoot deformity:Either / bothdactyly / digit:reduction deficits / limb:multiple joints:Axial Craniofacial dysostosis:other:spinal curvature (Scoliosis) · Klippel-Feil syndrome · Spondylolisthesis · Spina bifida occulta · SacralizationThoracic skeletonribs:sternum:M: JNT
anat(h/c, u, t, l)/phys
noco(arth/defr/back/soft)/cong, sysi/epon, injr
proc, drug(M01C, M4)
Categories:- Dermal and subcutaneous growths
- Congenital disorders of nervous system
- Congenital disorders of musculoskeletal system
- Disability
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.