- Hammer toe
-
Hammer toe Classification and external resources 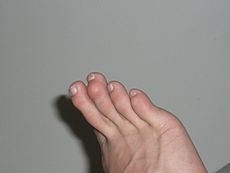
A mallet toe is evident on the 3rd digitICD-10 M20.4, Q66.8 ICD-9 735.4, 755.66 MeSH D037801 A hammer toe or contracted toe is a deformity of the proximal interphalangeal joint of the second, third, or fourth toe causing it to be permanently bent, resembling a hammer. Mallet toe is a similar condition affecting the distal interphalangeal joint.[1][2]
Claw toe is another similar condition, with dorsiflexion of the proximal phalanx on the lesser metatarsophalangeal joint, combined with flexion of both the proximal and distal interphalangeal joints. Claw toe can affect the second, third, fourth, or fifth toes.
Contents
Causes
Hammer toe most frequently results from wearing poorly fitting shoes that can force the toe into a bent position, such as excessively high heels or shoes that are too short or narrow for the foot. Having the toes bent for long periods of time can cause the muscles in them to shorten, resulting in the hammer toe deformity. This is often found in conjunction with bunions or other foot problems. It can also be caused by muscle, nerve, or joint damage resulting from conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, stroke, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease or diabetes.[3] Hammer toe can also be found in Friedrich's ataxia (GAA trinucleotide repeat).
 Corrective surgery for hammer toe
Corrective surgery for hammer toe
Treatment
In many cases, conservative treatment consisting of physical therapy and new shoes with soft, spacious toe boxes is enough to resolve the condition, while in more severe or longstanding cases orthopedic surgery may be necessary to correct the deformity. The patient's doctor may also prescribe some toe exercises that can be done at home to stretch and strengthen the muscles. For example, the individual can gently stretch the toes manually, or use the toes to pick things up off the floor. While watching television or reading, one can put a towel flat under the feet and use the toes to crumple it. The doctor can also prescribe a brace that pushes down on the toes to force them to stretch out their muscles.
References
- ^ American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- ^ Mayo Clinic, "Hammertoe and mallet toe"
- ^ "Hammer toe and mallet toe – causes". Mayo Clinic. http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/hammertoe-and-mallet-toe/DS00480/DSECTION=causes. Retrieved 2009-01-30.
External links
Musculoskeletal disorders: Acquired musculoskeletal deformities (M20–M25, M95, 734–738) Upper limb Lower limb foot deformity (Bunion/hallux valgus, Hallux varus, Hallux rigidus, Hammer toe, Foot drop, Flat feet, Club foot)Genu recurvatumHead General terms M: JNT
anat(h/c, u, t, l)/phys
noco(arth/defr/back/soft)/cong, sysi/epon, injr
proc, drug(M01C, M4)
Congenital malformations and deformations of musculoskeletal system / musculoskeletal abnormality (Q65–Q76, 754–756.3) Appendicular
limb / dysmeliahand deformity:Lowerhip:knee:Genu valgum · Genu varum · Genu recurvatum · Discoid meniscus · Congenital patellar dislocation · Congenital knee dislocationfoot deformity:Either / bothdactyly / digit:reduction deficits / limb:multiple joints:Axial Craniofacial dysostosis:other:spinal curvature (Scoliosis) · Klippel-Feil syndrome · Spondylolisthesis · Spina bifida occulta · SacralizationThoracic skeletonribs:sternum:M: JNT
anat(h/c, u, t, l)/phys
noco(arth/defr/back/soft)/cong, sysi/epon, injr
proc, drug(M01C, M4)
Categories:- Congenital disorders of musculoskeletal system
- Arthropathies
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
