- Dactyly
-
In biology, dactyly is the arrangement of digits (fingers and toes) on the hands, feet, or sometimes wings of a tetrapod animal. It comes from the Greek word δακτυλος = "finger".
Sometimes the ending "-dactylia" is used. The derived adjectives end with "-dactyl" or "-dactylous".
Contents
As a normal feature
In Reptiles, the limbs are pentadactylous in condition.
Tetradactyly
Tetradactyly (from Greek tetra-="four" plus δακτυλος = "finger") is the condition of having four digits on a limb, as in many amphibians, birds, and theropod dinosaurs. Some mammals also exhibit tetradactyly (for example pigs and the hind limbs of dogs and cats). Cartoon characters are commonly drawn with four digits on each hand/foot as it's clearer to see than five.
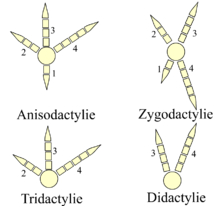
Tridactyly
Tridactyly (from Greek tri- = "three" plus δακτυλος = "finger") is the condition of having three digits on a limb, as in the Rhinoceros and ancestors of the horse such as Protohippus and Hipparion. These all belong to the Perissodactyla. Some birds also have three toes, including emus, bustards, and quail.
Didactyly
Didactyly (from Greek di-="two" plus δακτυλος = "finger") or bidactyly is the condition of having two digits on each limb, as in the Hypertragulidae and Two-toed Sloth, Choloepus didactylus. In humans this name is used for an abnormality in which the middle digits are missing, leaving only the thumb and fifth finger, or big and little toes. Cloven-hoofed mammals (such as deer, sheep and cattle - 'Artiodactyla') have only two digits, as do ostriches.
Monodactyly
Monodactyly (from Greek monos- = "one" plus δακτυλος = "finger") is the condition of having a single digit on a limb, as in modern horses. These belong to the Perissodactyla.
As a congenital defect
Syndactyly
Main article: SyndactylySyndactyly (from Greek συν- = "together" plus δακτυλος = "finger") is a condition where two or more digits are fused together. It occurs normally in some mammals, such as the siamang and most diprotodontid marsupials such as kangaroos. It occurs as an unusual condition in humans.
Polydactyly
Polydactyly (from Greek πολυ- = "many" plus δακτυλος = "finger") is when a limb has more than the usual number of digits. This can be:-
- As a result of congenital abnormality in a normally pentadactyl animal. Polydactyly is very common among domestic cats. For more information, see polydactyly.
- Polydactyly in early tetrapod aquatic animals, such as Acanthostega gunnari (Jarvik 1952), which is one of an increasing number of genera of stem-tetrapods known from the Upper Devonian, which are providing insights into the appearance of tetrapods and the origin of limbs with digits. It also occurs secondarily in some later tetrapods, such as ichthyosaurs. The use of a term normally reserved for congenital defects reflects that it was regarded as an anomaly at the time, as it was believed that all modern tetrapods have either five digits or ancestors that did.
Oligodactyly
Main article: OligodactylyOligodactyly (from Greek ὀλιγο- = "few" plus δακτυλος = "finger") is having too few digits when not caused by an amputation. It is sometimes incorrectly called hypodactyly or confused with aphalangia, the absence of the phalanx bone on one or (commonly) more digits. When all the digits on a hand or foot are absent, it is referred to as adactyly.[1]
Ectrodactyly
Main article: EctrodactylyEctrodactyly, also known as split-hand malformation, is the congenital absence of one or more central digits of the hands and feet. Consequently, it is a form of oligodactyly. News anchor Bree Walker is probably the best-known person with this condition, which affects about one in 91,000 people[citation needed]. It is conspicuously more common in the Vadoma in Zimbabwe.
In birds
Anisodactyly
Anisodactyly is the most common arrangement of digits in birds, with three toes forward and one back. This is common in songbirds and other perching birds, as well as hunting birds like eagles, hawks, and falcons.
Syndactyly
Syndactyly, as it occurs in birds, is like anisodactyly, except that the third and fourth toes (the outer and middle forward-pointing toes), or three toes, are fused together, as in the Belted Kingfisher Ceryle alcyon. This is characteristic of Coraciiformes (Kingfishers, Bee-eaters, Rollers, and relatives).
Zygodactyly
 A Green-winged Macaw has raised its right foot to its beak
A Green-winged Macaw has raised its right foot to its beak
Zygodactyly (from Greek ζυγον, a yoke) is an arrangement of digits in birds, with two toes facing forward (digits 2 and 3) and two back (digits 1 and 4). This arrangement is most common in arboreal species, particularly those that climb tree trunks or clamber through foliage. Zygodactyly occurs in the parrots, woodpeckers (including flickers), cuckoos (including roadrunners), and some owls. Zygodactyl tracks have been found dating to 120-110 Ma (early Cretaceous), 50 million years before the first identified zygodactyl fossils.[2]
Heterodactyly
Heterodactyly is like zygodactyly, except that digits 3 and 4 point forward and digits 1 and 2 point back. This is found only in trogons.
Pamprodactyl
Pamprodactyl is an arrangement in which all four toes point forward. It is a characteristic of swifts (Apodidae).
Chameleons
The feet of chameleons are fused into a group of two and a group of three toes which oppose one another to grasp branches in a pincer-like arrangement. This has been called zygodactyly or didactyly, though the details of the arrangements differ.
Schizodactyly
Schizodactyly is a primate term for grasping and clinging with the second and third digit, instead of the thumb and second digit.
References
- ^ József Zákány, Catherine Fromental-Ramain, Xavier Warot, and Denis Duboule (1997). "Regulation of number and size of digits by posterior Hox genes: A dose-dependent mechanism with potential evolutionary implications". PNAS 25 (94): 13695–13700. http://www.pnas.org/content/94/25/13695.abstract.
- ^ "Earliest zygodactyl bird feet: evidence from Early Cretaceous roadrunner-like tracks". Naturwissenschaften. 2007. http://www.springerlink.com/content/hl850l4128573g33/.
External links
- Coates, Michael (25 April 2005). "Why do most species have five digits on their hands and feet?". Scientific American. http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=why-do-most-species-have. Retrieved 2009-07-05.
Congenital malformations and deformations of musculoskeletal system / musculoskeletal abnormality (Q65–Q76, 754–756.3) Appendicular
limb / dysmeliahand deformity:Lowerhip:knee:Genu valgum · Genu varum · Genu recurvatum · Discoid meniscus · Congenital patellar dislocation · Congenital knee dislocationfoot deformity:Either / bothdactyly / digit:reduction deficits / limb:multiple joints:Axial Craniofacial dysostosis:other:spinal curvature (Scoliosis) · Klippel-Feil syndrome · Spondylolisthesis · Spina bifida occulta · SacralizationThoracic skeletonribs:sternum:M: JNT
anat(h/c, u, t, l)/phys
noco(arth/defr/back/soft)/cong, sysi/epon, injr
proc, drug(M01C, M4)
Categories:- Congenital disorders of musculoskeletal system
- Zoology
- Anatomy
- Comparative anatomy
- Bird anatomy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.