- Valence (chemistry)
-
For other uses, see Valence (disambiguation).
In chemistry, valence, also known as valency or valence number, is a measure of the number of bonds formed by an atom of a given element. "Valence" can be defined as the number of valence bonds[1] a given atom has formed, or can form, with one or more other atoms. For most elements the number of bonds can vary. The IUPAC definition limits valence to the maximum number of univalent atoms that may combine with the atom, that is the maximum number of valence bonds that is possible for the given element.[2]
The valence of an element depends on the number of valence electrons that may be involved in the forming of valence bonds. A univalent (monovalent) atom, ion or group has a valence of one and thus can form one covalent bond. A divalent molecular entity has a valence of two and can form two sigma bonds to two different atoms or one sigma bond plus one pi bond to a single atom.[3] Alkyl groups and hydroxyl ions are univalent examples; oxo ligands are divalent.
Over the last century, the concept of valence evolved into a range of approaches for describing the chemical bond, including Lewis structures (1916), valence bond theory (1927), molecular orbitals (1928), valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (1958) and all the advanced methods of quantum chemistry.
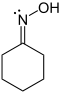
In cyclohexanonoxime (image left), the nitrogen atom has three valence bonds and by the first definition it has a valence of three. Nitrogen has five valence electrons and by IUPAC definition it has a valence of five, because it can form maximal five valence bonds, as in N-methyl-1-phenylmethanimine oxide [1]. In cyclohexanonoxime, nitrogen has the oxidation state −1 and oxygen −2. Contents
History
The etymology of the word "valence" traces back to 1425, meaning "extract, preparation," from Latin valentia "strength, capacity," and the chemical meaning referring to the "combining power of an element" is recorded from 1884, from German Valenz.[4]
 William Higgins' combinations of ultimate particles (1789)
William Higgins' combinations of ultimate particles (1789)
In 1789, William Higgins published views on what he called combinations of "ultimate" particles, which foreshadowed the concept of valency bonds.[5] If, for example, according to Higgins, the force between the ultimate particle of oxygen and the ultimate particle of nitrogen were 6, then the strength of the force would be divided accordingly, and similarly for the other combinations of ultimate particles (see illustration).
The exact inception, however, of the theory of chemical valencies can be traced to an 1852 paper by Edward Frankland, in which he combined the older theories of free radicals and “type theory” with thoughts on chemical affinity to show that certain elements have the tendency to combine with other elements to form compounds containing 3, i.e. in the three atom groups (e.g. NO3, NH3, NI3, etc.) or 5, i.e. in the five atom groups (e.g. NO5, NH4O, PO5, etc.), equivalents of the attached elements. It is in this manner, according to Frankland, that their affinities are best satisfied. Following these examples and postulates, Frankland declares how obvious it is that:[6]
“ A tendency or law prevails (here), and that, no matter what the characters of the uniting atoms may be, the combining power of the attracting element, if I may be allowed the term, is always satisfied by the same number of these atoms. ” This “combining power” was afterwards called quantivalence or valency (and valence by American chemists).[5]
Covalence
The concept of covalence was developed in the middle of the nineteenth century in an attempt to rationalize the formulae of different chemical compounds. In 1919, Irving Langmuir, borrowed the term to explain Gilbert N. Lewis's cubical atom model by stating that "the number of pairs of electrons which any given atom shares with the adjacent atoms is called the covalence of that atom." The prefix co- means "together", so that a co-valent bond means that the atoms share valence. Hence, if an atom, for example, had a +1 valence, meaning it has one valence electron beyond the complete shell, and another a −1 valence, meaning it requires one electron to complete its outer shell (missing an electron) , then a bond between these two atoms would result because they would be complementing or sharing their out of balance valence tendencies. Subsequently, it is now more common to speak of covalent bonds rather than "valence", which has fallen out of use in higher level work with the advances in the theory of chemical bonding, but is still widely used in elementary studies where it provides a heuristic introduction to the subject.
Common valences
For elements in the main groups of the periodic table, the valence can vary between one to seven, but usually these elements form a number of valence bonds between one and four. The number of bonds formed by a given element was originally thought to be a fixed chemical property. In fact, in most cases this is not true. For example, phosphorus often has a valence of three, but can also have other valences.
Nevertheless, many elements have a common valence related to their position in the periodic table, following the octet rule. Elements in the main groups 1 (alkali metals) and 17 (halogens) commonly have a valence of 1; elements in groups 2 (alkaline earth metals) and 16 (chalcogens) valence 2; elements in groups 13 (boron group) and 15 (nitrogen group) valence 3; elements in group 14 (carbon group) valence 4.
Valence versus oxidation state
Because of the ambiguity of the term valence,[3] nowadays other notations are used in practice. Beside the system of oxidation numbers as used in Stock nomenclature for coordination compounds ,[7] and the lambda notation, as used in the IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry ,[8] "oxidation state" is a more clear indication of the electronic state of atoms in a molecule.
The "oxidation state" of an atom in a molecule gives the number of valence electrons it has gained or lost.[9] In contrast to the valency number, the oxidation state can be positive (for an electropositive atom) or negative (for an electronegative atom).
Elements in a high oxidation state can have a valence larger than four. For example, in perchlorates, chlorine has seven valence bonds and ruthenium, in the +8 oxidation state in ruthenium(VIII) tetroxide, has even eight valence bonds.
"Maximum number of bonds" definition
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has made several attempts to arrive at an unambiguous definition of valence. The current version, adopted in 1994,[10]:
- The maximum number of univalent atoms (originally hydrogen or chlorine atoms) that may combine with an atom of the element under consideration, or with a fragment, or for which an atom of this element can be substituted.[2]
Hydrogen and chlorine were originally used as examples of univalent atoms, because of their nature to form only one single bond. Hydrogen has only one valence electron and can form only one bond with an atom that has an incomplete outer shell. Chlorine has seven valence electrons and can form only one bond with an atom that donates a valence electron to complete chlorine's outer shell. However, chlorine can also have oxidation states from +1 to +7 and can form more than one bond by donating valence electrons.
Although hydrogen has only one valence electron, it can form bonds with more than one atom in hypervalent bonds. In the bifluoride ion ([HF2]−), for example, it forms a three-center four-electron bond with two fluoride atoms:
![[\ F \frac{\quad}{\quad} H\ {}^-\!F \quad \longleftrightarrow \quad F^- \ {}\!H \frac{\quad}{\quad} F\ ]](b/5cbaae4d03828c23dfec98f4bd143cee.png)
Another example is the Three-center two-electron bond in diborane (B2H6).
Examples
(valencies according to the number of valence bonds definition and conform oxidation states)
COMPOUND FORMULA VALENCE OXIDATION STATE Hydrogen chloride HCl H=1 Cl=1 H=+1 Cl=−1 Chlorine Cl2 Cl=1 Cl=1 Cl=+1 Cl=−1 Perchlorate * HClO4 H=1 Cl=7 O=2 H=+1 Cl=+7 O=−2 Sodium hydride NaH Na=1 H=1 Na=+1 H=−1 Ferrous oxide ** FeO Fe=2 O=2 Fe=+2 O=−2 Ferric oxide ** Fe2O3 Fe=3 O=2 Fe=+3 O=−2 * The univalent perchlorate ion (ClO4−) has valence 1.
** Iron oxide appears in a crystal structure, so no typical molecule can be identified.
In ferrous oxide, Fe has oxidation number II, in ferric oxide, oxidation number III.Valences of the elements
Maximum valences for the majority of elements are based on the highest known fluoride. Note that valence of hydrogen (H) and of fluorine (F) are both one. Astatine (At) is predicted to have valence of seven but is not known to have compounds with a valency above one.
Group → 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 ↓ Period 1 1
H2
He2 3
Li4
Be5
B6
C7
N8
O9
F10
Ne3 11
Na12
Mg13
Al14
Si15
P16
S17
Cl18
Ar4 19
K20
Ca21
Sc22
Ti23
V24
Cr25
Mn26
Fe27
Co28
Ni29
Cu30
Zn31
Ga32
Ge33
As34
Se35
Br36
Kr5 37
Rb38
Sr39
Y40
Zr41
Nb42
Mo43
Tc44
Ru45
Rh46
Pd47
Ag48
Cd49
In50
Sn51
Sb52
Te53
I54
Xe6 55
Cs56
Ba*
72
Hf73
Ta74
W75
Re76
Os77
Ir78
Pt79
Au80
Hg81
Tl82
Pb83
Bi84
Po85
At86
Rn7 87
Fr88
Ra**
104
Rf105
Db106
Sg107
Bh108
Hs109
Mt110
Ds111
Rg112
Cn113
Uut114
Uuq115
Uup116
Uuh117
Uus118
Uuo* Lanthanides 57
La58
Ce59
Pr60
Nd61
Pm62
Sm63
Eu64
Gd65
Tb66
Dy67
Ho68
Er69
Tm70
Yb71
Lu** Actinides 89
Ac90
Th91
Pa92
U93
Np94
Pu95
Am96
Cm97
Bk98
Cf99
Es100
Fm101
Md102
No103
LrValences of chemical elements
NoneOneTwoThreeFourFiveSixSevenAtomic number colors show state of matter at standard conditions (0 °C and 1 atm): Solids Liquids Gases Unknown Borders show natural occurrence: Primordial From decay Synthetic See also
References
- ^ Note: A valence bond (or bonding equivalent) is a covalent or ionic bond, formed by the interaction of two bonding electrons.
- ^ a b IUPAC Gold Book definition: valence
- ^ a b The Free Dictionary: valence
- ^ Valence - Online Etymology Dictionary.
- ^ a b Partington, J.R. (1989). A Short History of Chemistry. Dover Publications, Inc. ISBN 0-486-65977-1.
- ^ Frankland, E. (1852). Phil. Trans., vol. cxlii, 417.
- ^ IUPAC, Gold Book definition: oxidation number
- ^ IUPAC, Gold Book definition: lambda
- ^ IUPAC Gold Book definition: oxidation state
- ^ Pure Appl. Chem. 66: 1175 (1994).
Periodic tables Layouts Standard · Large table · Inline f-block · Vertical · Text only · Metals and nonmetals · Blocks · Valences · Extension beyond the 7th period · Large extended table · Electron configurations · Electronegativities · Alternatives · Crystal structure · Discovery periodsList of elements by Name etymology (symbol) · Discovery · Oxidation state · Abundance (in humans) · Nuclear stability · Hardness · Atomic properties · ProductionGroups 1 (Alkali metals) · 2 (Alkaline earth metals) · 3 · 4 · 5 · 6 · 7 · 8 · 9 · 10 · 11 · 12 · 13 (Boron group) · 14 (Carbon group) · 15 (Pnictogens) · 16 (Chalcogens) · 17 (Halogens) · 18 (Noble gases)Other element categories Periods · Metals · Transition metals · Metalloids · Nonmetals · Lanthanides · Actinides · Rare earth elements · Platinum group metals (PGMs) · Post-transition metals · Refractory metalsBlocks Periods  Book:Periodic table ·
Book:Periodic table ·  Category:Periodic table ·
Category:Periodic table ·  Portal:ChemistryCategories:
Portal:ChemistryCategories:- Chemical bonding
- Chemical properties
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
