- Oxidation number
-
Not to be confused with oxidation state.
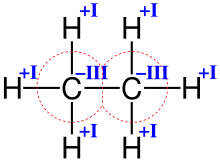 Oxidation numbers of carbon and hydrogen in ethane
Oxidation numbers of carbon and hydrogen in ethane
In coordination chemistry, the oxidation number of a central atom in a coordination compound is the charge that it would have if all the ligands were removed along with the electron pairs that were shared with the central atom.[1] Oxidation numbers are often confused with oxidation states.
The oxidation number is used in the nomenclature of inorganic compounds. It is represented by a Roman numeral. The oxidation number is placed either as a right superscript to the element symbol, for example FeIII, or in parentheses after the name of the element, iron(III): in the latter case, there is no space between the element name and the oxidation number.
Contents
Oxidation number versus oxidation state
The oxidation number is usually numerically equal to the oxidation state and so the terms oxidation state and oxidation number are often used interchangeably. However, oxidation number is used in coordination chemistry with a slightly different meaning since the rules used for counting electrons are different: every electron belongs to the ligand, regardless of electronegativity. Also, oxidation numbers are conventionally represented with Roman numerals while oxidation states are given in Arabic numerals. The oxidation number of a central atom may be part of the compound's name (for example iron(II,III) oxide); the oxidation state of atoms is not included in compound names.
The oxidation state can differ from the oxidation number in a few cases where the ligand atom is less electronegative than the central atom (e.g., in iridium phosphine complexes), resulting in a formal oxidation state that is different from the oxidation number.[citation needed]
Spectroscopic oxidation states
Although formal oxidation numbers can be helpful for classifying compounds, they are unmeasurable and their physical meaning can be ambiguous. Formal oxidation numbers require particular caution for molecules where the bonding is covalent, since the formal oxidation numbers require the heterolytic removal of ligands, which essentially denies covalency. Spectroscopic oxidation states, as defined by Jorgenson and reiterated by Wieghardt, are measurables that are bench-marked using spectroscopic and crystallographic data.[2]
See also
References
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "oxidation number".
- ^ Bill, E.; Bothe, E.; Chaudhuri, P.; Chlopek, K.; Herebian, D.; Kokatam, S.; Ray, K.; Weyhermueller, T.; Neese, F.; Wieghardt, K. (2005). "Molecular and electronic structure of four- and five-coordinate cobalt complexes containing two o-phenylenediamine- or two o-aminophenol-type ligands at various oxidation levels functional, and correlated ab initio study". Chemistry - A European Journal 11 (1): 204–224. doi:10.1002/chem.200400850. PMID 15549762.
Categories:- Chemical nomenclature
- Coordination chemistry
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
