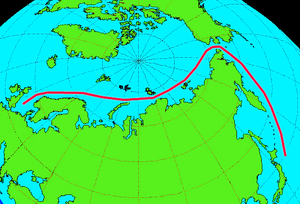
- Great Northern Expedition
-
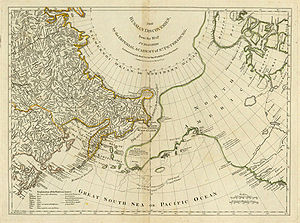 One of the most important achievements of the expedition was the mapping of the north east part of Asia. The geography department of the St. Petersburg Academy of Science published in 1754 a map with the title Nouvelle Carte des Découvertes faites par des Vaisseaux Russiens, which also depicted Vitus Bering's and Aleksei Chirikov's sea route. The new geographic information was quickly diffused and received widespread attention in all of Europe. The above is an English map entitled The Russian Discoveries prepared by the London cartographer Thomas Jefferys (this is a reprint published by Robert Sayer in the American Atlas of 1776).
One of the most important achievements of the expedition was the mapping of the north east part of Asia. The geography department of the St. Petersburg Academy of Science published in 1754 a map with the title Nouvelle Carte des Découvertes faites par des Vaisseaux Russiens, which also depicted Vitus Bering's and Aleksei Chirikov's sea route. The new geographic information was quickly diffused and received widespread attention in all of Europe. The above is an English map entitled The Russian Discoveries prepared by the London cartographer Thomas Jefferys (this is a reprint published by Robert Sayer in the American Atlas of 1776).
The Great Northern Expedition (Russian: Великая Северная экспедиция) or Second Kamchatka expedition (Russian: Вторая Камчатская экспедиция) was one of the largest organised exploration enterprises in history, resulting in mapping of the most of the Arctic coast of Siberia and some parts of the North America coastline, greatly reducing the "white areas" on the maps. The endeavour was initially conceived by Russian Emperor Peter I the Great and implemented in practice by Russian Empresses Anna and Elizabeth. The main organiser and leader of the expedition was Vitus Bering, who earlier had been commissioned by Peter I to lead the first Kamchatka expedition. The Second Kamchatka expedition lasted roughly from 1733–1743 and later became called the Great Northern due to the immense scale of its achievements.
The goal of the expedition was to find and map the eastern reaches of Siberia, and to hopefully continue onto the western shores of North America to map them, as well. Emperor Peter I had a vision for the 18th-century Russian Navy to map the entire Northern Sea Route. This far-reaching endeavour was sponsored by the Admiralty College in St. Petersburg.
With over 3,000 people directly and indirectly involved, the Second Kamchatka expedition was one the largest expedition projects in history. The total cost of the undertaking, completely financed by the Russian state, reach the estimated sum of 1.5 million rubles, an enormous amount for the period. This corresponded to one sixth of the income of the Russian state for year 1724.[1]
The important achievements of the expedition included the European discovery of Alaska, the Aleutian Islands, the Commander Islands, Bering Island, as well as a detailed cartographic assessment of the northern and north-eastern coast of Russia and the Kuril Islands. The expedition also definitively refuted the legend of a land mass in the north Pacific. It also included ethnographic, historic, and scientific research into Siberia and Kamchatka. When the expedition failed to round the north-east tip of Asia, the dream of finding an economically viable Northeast passage, alive since the 16th century, was definitively at an end.
Contents
Background: first scientific investigation of Siberia and Bering's first expedition
The start of the systematic exploration and scientific discovery in the eastern part of Asia in the 18th century was due to the initiative of Tsar Peter the Great (1672–1725). In 1697 and 1698, he made an exploratory trip through a number of European nations, and became enthused with the idea of founding a scientific academy in Russia. This plan came to fruition in 1723/24 when he decided to draw foreign scholars to Russia and create a scientific academy in St. Petersburg. He hoped to create an extension of the scientific culture of Europe in his own land, and eventually to educate native scholars.
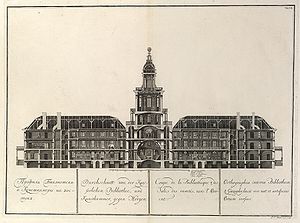 Contemporary depiction of the main building of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Saint Petersburg. Plate entitled Cross-section of the imperial library and art room towards morning, taken from a series of twelve etchings published in 1741. They were the first collaborative work from the workshops of the St. Petersburg academy.
Contemporary depiction of the main building of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Saint Petersburg. Plate entitled Cross-section of the imperial library and art room towards morning, taken from a series of twelve etchings published in 1741. They were the first collaborative work from the workshops of the St. Petersburg academy.
In December of 1725, the institution was inaugurated with celebrations. Young, mostly German speaking scholars formed the core of the Academy's personnel in the first decades of its existence. One of their tasks consisted of organizing and eventually accompanying scientific expeditions to the then unexplored parts of the Russian empire. During Peter’s lifetime, the German doctor Daniel Gottlieb Messerschmidt (1685–1735) made a journey from 1720 to 1727 to western and central Siberia. This marked the beginning of investigations in the areas of geography, mineralogy, botany, zoology, ethnography, and philology, in this zone, as well as opening up the region to trade and economic development. Messerschmidt's Expedition was the first in a what proved to be series of scientific explorations of Siberia.
Shortly before his death in February 1725, the Tsar signed an order authorizing a second great expedition to the east. Over the course of his life, Peter had met many time with Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (1646–1716). At their final meeting at Bad Pyrmont in 1716, Leibniz posed the question as to whether a land bridge existed between northeastern Asia and the North America, a point of great relevance in the contemporary discussion about the origins of humanity, among other matters. It was generally desired that the belief in the common origin of humans not be abandoned, which posed the problem of the origins of human settlements in the New World. In order to resolve the question about the existence of a land bridge between the two continents, Peter the Great sent in 1719 the geodesists Iwan Jewreinow (1694–1724) and Fjodor Luschin (died 1727) to the easternmost reaches of his empire. The expedition was unsuccessful, as least in regard to the land bridge question, and in 1724, Peter gave the same aim to another expedition, the First Kamchatka expedition.[2]
This undertaking, lasting from 1728 to 1730, was led by the Danish captain Vitus Jonassen Bering (1681–1741). Bering had been an officer in the Russian imperial navy since 1704. Using the ship St. Gabriel, which had been built at the outlet of the Kamchatka River, Bering made two voyages north east in successive years (1728 and 1729), and at one point reached 67 degrees north, from which point the coast no longer extended towards the north. In both cases, he failed to reach the North American coastline due to adverse weather. Despite the newly acquired knowledge about the geography of the north east coast of Siberia, Bering's report on the expedition prepared after his return led to divisive debate because the question about the connection with North America remained unanswered, and this prompted Bering to propose a second Kamchatka expedition.
The Expedition
Planning and preparation
Bering's expedition plan and the two fleets
The central goals in Bering's vision for the new expedition was the survey of the northern coast of the Russian Empire; the expansion of the port of Okhotsk as the gateway to the Pacific Ocean; the search for a sea route to North America and Japan; the opening of the Siberian natural resources; and finally, the securing of Russian sovereignty in the eastern parts of Asia. The conditions for this gigantic project proved to very favourable. Empress Anna (1693–1740), reigning from 1730, wanted to continue the Peter the Great's territorial and economic expansion of the empire. The empress issued an Ukase issued on April 17, 1732, ordering a new expedition. This was followed on May 2 and 15, 1732 by two further Ukases from the Russian Senate to the Admiralty ordering the preparation of the undertaking, and the commissioning of Vitus Bering as its commander. Another Ukase on June 2, 1732 obligated the Russian Academy of Sciences to prepare instructions for the scientific component of the journey. A further Ukase on December 27, 1732 concerned the organization and the formal commissioning of the expedition.
The expedition was separated into three groups, each with further subdivisions. The mission of the northern group was to measure and chart the northern coast of Russia between the Archangelsk on the White Sea and the Anadyr River in eastern Siberia. The completion of this mission set the foundations for determining the status of the north east passage as a possible connection between Europe and the Pacific Ocean. It was seen as a possible alternate for the land transport used in Russia's trade with China, as well as a north east route to India. The Pacific group of the expedition consisted of two divisions. The first, led by Bering himself, was to proceed from Okhotsk on Kamchatka and reconnoiter from there for the legendary "Joao-da-Gama-Land". This was named after the Protugese explorer Joao da Gama, who had claimed in 1589 to have discovered a land mass north of Japan. From "Joao-da-Gama-Land", Bering's group was to set out farther east to the coast of North America. The second Pacific division was under the command of the Danish captain Martin Spangberg (died 1759 or 1761), who had accompanied Bering on the First Kamchatka Expedition, and had been charged with exploring the sea route from Okhotsk to Japan and China.
The academic component
The academic portion of the expedition was led by three professors from the Russian Academy of Sciences. Johann Georg Gmelin (1709–1755) was responsible for research into the plant and animal world as well as the mineral characteristics of the regions to be explored. Gmelin was a natural philosopher and botanist from Württemberg, who had studied in Tübingen and had research the chemical composition of curative waters. At the urging of his former teacher Georg Bernhard Bilfinger (1693–1750), Gmelin had moved to Russia with him in 1727. There he received a teaching post in chemistry and natural history in 1731.
The Academy chose the German historian and geographer Gerhard Friedrich Müller (1705–1783) to head the ethnographic and historical studies. Müller had studied in Rinteln and Leipzig and had gone to St. Petersbug in 1725 on the recommendation of a colleague. He became an extraordinary professor in 1730, and a year later was promoted to full professor. He research Russian history intensively, resulting in the publication in 1732 of the first volume of the Collected History of Russia. Because of Müller's haughty bearing as the chancellor's secretary, there was frequent friction between him and his colleagues. His participation in the expedition was due not only to his desire to have access to historical sources through the expedition, but to spend some time away from St. Petersburg.
On the suggestion of the astronomer Joseph Nicolas Delisle (1688–1768), who had been hired by Peter the Great to work in St. Petersburg, the Academy of Science entrusted the job of astronomical and geographic metrology to Delisle's younger brother, Louis De l'Isle de la Croyère (1690–1741). Louie had been working at the Academy as an adjunct for astronomy. In 1727 he was promoted to professor and was sent on a three year exploration survey of Arkhangelsk and the Kola peninsula, giving him some experience in exploration expeditions. Croyère's participation in the academic portion of the expedition later became controversial when his competence was questioned by Gmelin and Müller.
The participants in the academic portion of the expedition were answerable not to its leader Berings, but to the St. Petersburg academy. Each of the professors received a precise commission in regard to the accomplishment of his research program. The directions given to Croyère and his geodesists were written by his brother Joseph Nicolas. Gmelin wrote the instruction for his own research work in natural history. He received further instructions from the anatomist Johann Georg Duvernoi (1691–1759), who had been part of the teaching faculty in Tübingen, as had Georg Bernhard Bilfinger. Among other things, Duvernoi wanted to find out whether the peoples of Siberia could move their ears, whether their uvulas were simple, or split into two or three parts, whether Siberian males had milk in their breasts, etc.[3] The physicist Daniel Bernoulli (1700–1782) authored instructions intended for Croyère and Gmelin about the carrying out of series of physical observations. The historian Müller drafted his own plan of work. His chief goals consisted of researching the history of all the cities the expedition would visit and collecting information about the languages of the groups they would meet along the way. The painters Johann Christian Berckhan (died 1751) and Johann Wilhelm Lürsenius (died around 1770), both of whom were part of the academic component, got special instructions. The academy directed all the researchers to prepare reports about the state and the results of the expedition in Russian and Latin. The academic component of the expedition was provided with many astronomical, geodesic, and physical measuring instruments to pursue its research. The governor of Siberia and the various local authorities were ordered to provide the researchers all the aid they required.
The voyages of the three groups (1733–1743)
The academic group
The two Pacific divisions of the expedition, led by Martin Spangberg and Vitus Bering, left St. Petersburg in February and April of 1733, while the academic group departed on August 8, 1733. In addition to the Academy members Gmelin, Müller and Croyère, the group also included the Russian students Stepan Krascheninnikov, Alexei Grolanov, Luka Ivanov, Wassili Tretjakov and Fyodor Popov, the translator (also a student) Ilya Jaontov (died 1739), the geodesists Andrei Krassilnikov (1705–1773), Moisei Uschakov (died before 1743), Nikifor Tschekin and Alexandr Ivanov (died 1738), the instrument maker Stepan Ovsjanikov (died 1738) as well as the painters Johann Christian Berckhan and Johann Wilhelm Lürsenius. Two soldiers accompanied them for their protection, together with a corporal and a drummer. The group used horses as land transportation and barges on water.
The academic component's travel route took them first to Novgorod, Kasan, Jekaterinburg and Tyumen to Tobolsk, where they arrived in January of 1734. In May, Gmelin and Müller separated from the rest of the group, who were put under Croyères' the leadership, and travelled until December 1734 to the Irtysh River, and then onwards to Semipalatinsk, Kusnezk near Tomsk, and then onto Yeniseysk. Passing through Krasnoyarsk and Udinsk, they reached Irkutsk in March 1735. They left a portion of their baggage train there and began to survey the area around Lake Baikal. They studied trade in the Sino-Russian border city of Kyakhta in Transbaikal and visited the mines near Argun. They then returned to Irkutsk for the winter. In the meantime, Müller investigated locate archives and made copies and transcriptions, while Gmelin plants he had collected over the course of the summer.
 View of Irkutsk. Pencil drawing from 1735.
View of Irkutsk. Pencil drawing from 1735.
Their next destination was Yakutsk, where the participants in the academic component were to meet with Bering and were then meant to travel on to Kamchatka together. After their departure from Irkutsk, the two scholars journeyed along the icy Angara River to Ilimsk, where they celebrated Easter. When the Lena River was free from ice, they resumed their voyage, travelling downstream with boats. They reached Yakutsk in September of 1736. Almost all the members of the two Pacific divisions of the expedition had gathered there in the meantime, and as a result, Gmelin and Müller experienced difficulties in locating accommodation. Unfortunately, on the night of November 8, 1736, the fire in Gmelin's room went out. In his memoirs of the voyage, written at a later date, he described the situation:
European discovery of Alaska
 Illustration from Stepan Krasheninnikov's Account of the Land of Kamchatka (1755)
Illustration from Stepan Krasheninnikov's Account of the Land of Kamchatka (1755)
 Mock-up of the ship St.Peter which can be seen in The Russian Black Sea Fleet Museum in Sevastopol.
Mock-up of the ship St.Peter which can be seen in The Russian Black Sea Fleet Museum in Sevastopol.
In June 1741, the St. Peter and the St. Paul set sail from Petropavlovsk. Six days later they lost sight of each other in a thick fog, but both vessels continued to sail east.
On July 15, Chirikov sighted land, probably the west side of Prince of Wales Island in Southeast Alaska.[4] He sent a group of men ashore in a long boat, making them the first Europeans to land on the northwestern coast of North America. When the first group failed to return, he sent a second, which also vanished. Chirikov weighed anchor and moved on.
On roughly July 16, 1741, Bering and the crew of St. Peter sighted a towering peak on the Alaska mainland, Mount Saint Elias. Bering was anxious to return to Russia and turned westward. He later anchored his vessel off Kayak Island while crew members went ashore to explore and find water. Georg Wilhelm Steller, the ship's naturalist, hiked along the island and took notes on the plants and wildlife. He also first recorded the Steller's Jay that bears his name.
Chirikov and the St. Paul headed back to Russia in October with news of the land they had found.
Bering's ship was battered by storms, and in November his ship was wrecked on the shore of Bering Island, which many of the crew thought to be the coast of Kamchatka. Bering fell ill with scurvy and died on December 8, 1741; soon after, the St. Peter was dashed to pieces by high winds. The stranded crew wintered on the island, and 28 crew members died. When weather improved, the 46 survivors built a 40 foot (12 m) boat from the wreckage and set sail for Petropavlovsk in August 1742. Bering's crew reached the shore of Kamchatka in 1742, carrying word of the expedition. The sea otter pelts they brought, soon judged to be the finest fur in the world, would spark Russian settlement in Alaska.
See also
- Northern Sea Route
- Northwest Passage
- Arctic Bridge
- Territorial claims in the Arctic
- Arctic policy of Russia
- Continental shelf of Russia
- List of Russian explorers
References
- ^ Hintzsche / Nickol, Die Große Nordische Expedition, p. 200.
- ^ The traditional presentation of the motivations behind the First Kamchatka expedition was the search for a land bridge. See, among others, Raymond H. Fisher in his 1977 book Bering's voyages: whither and why. In contrast to this view, Carol Urness claims that the mapping of the eastern parts of Russia was the main goal. See Carol Urness: The First Kamchatka Expedition in Focus, in: Møller / Lind, Under Vitus Bering's Command, Århus 2003, p. 17–31 (Summary of the thesis presented in the 1987 book Bering's First Expedition: A re-examination based on eighteenth-century books, maps, and manuscripts).
- ^ Hintzsche / Nickol, Die Große Nordische Expedition, p. 78.
- ^ "Russia's Great Voyages". http://www.calacademy.org/exhibits/science_under_sail/people.html. Retrieved 2005-09-23.
History of Alaska Timeline - Prehistory
- Russian America (1733-1867)
- Department of Alaska (1867-1884)
- District of Alaska (1884-1912)
- Territory of Alaska (1912-1959)
- Recent history (1959-present)
Topics and events - Alaska boundary dispute
- Klondike Gold Rush
- Alaska Purchase
- 1925 serum run to Nome
- Aleutian Islands Campaign
- Alaska Statehood Act
- 1964 Alaska earthquake
- Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act
- Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act
- Exxon Valdez oil spill
- History of Anchorage, Alaska
- History of Fairbanks, Alaska
- Other topics
Categories:- Colonial United States (Russian)
- Russian America
- North American expeditions
- History of Siberia
- History of Alaska
- History of the Russian Far East
- History of Northeast Asia
- Sea of Okhotsk
- Science and technology in Russia
- 1730s
- Arctic expeditions
- Russian Arctic expeditions
- Asian expeditions
- Pacific expeditions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.