- South Magnetic Pole
-
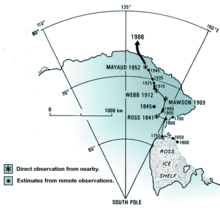 Locations of South Magnetic Pole from direct observation and model prediction.[1]
Locations of South Magnetic Pole from direct observation and model prediction.[1] For additional general information about the Earth's magnetic poles, see North Magnetic Pole.
For additional general information about the Earth's magnetic poles, see North Magnetic Pole.The Earth's South Magnetic Pole is the wandering point on the Earth's surface where the geomagnetic field lines are directed vertically upwards. It should not be confused with the lesser known South Geomagnetic Pole described later.
For historical reasons, the "end" of a magnet that points (roughly) north is itself called the "north pole" of the magnet, and the other end, pointing south, is called magnet's "south pole". Because opposite poles attract, the Earth's South Magnetic Pole is physically actually a magnetic north pole (see also North Magnetic Pole – Polarity).
The South Magnetic Pole is constantly shifting due to changes in the Earth's magnetic field. As of 2005 it was calculated to lie at 64°31′48″S 137°51′36″E / 64.53°S 137.86°E,[2] just off the coast of Adelie Land, French Antarctica. That point lies outside the Antarctic Circle. Due to polar drift, the pole is moving north west by about 10 to 15 kilometers per year.
North Magnetic Pole[3] (2001) 81°18′N 110°48′W / 81.3°N 110.8°W (2004 est) 82°18′N 113°24′W / 82.3°N 113.4°W (2005 est) 82°42′N 114°24′W / 82.7°N 114.4°W South Magnetic Pole (1998) 64°36′S 138°30′E / 64.6°S 138.5°E (2004 est) 63°30′S 138°00′E / 63.5°S 138.0°E (2007) 64°29′49″S 137°41′02″E / 64.497°S 137.684°E[4] Contents
Expeditions
Early unsuccessful attempts to reach the South Magnetic Pole included those of French explorer Dumont d'Urville (1840), American Charles Wilkes (expedition of 1838–42) and Briton James Clark Ross (expedition of 1839–43).[5]
On January 16, 1909 three men (Douglas Mawson, Edgeworth David, and Alistair Mackay) from Sir Ernest Shackleton's Nimrod Expedition claimed to have found the South Magnetic Pole,[6] which was at that time located on land. However, there is now some doubt as to whether their location was correct.[7]
The approximate position of the pole on 16 January 1909 was 72°15′S 155°09′E / 72.25°S 155.15°E.[8]
Fits to global data sets
The South Magnetic Pole has also been estimated by fits to global sets of data such as the World Magnetic Model (WMM) and the International Geomagnetic Reference Model (IGRF).[1] For earlier years back to about 1600, the model GUFM1 is used, based on a compilation of data from ship logs.[9]
South Geomagnetic Pole
Main article: Geomagnetic poleThe Earth's geomagnetic field can be approximated by a tilted dipole (like a bar magnet) placed at the center of the Earth. The South Geomagnetic Pole is the point where the axis of this best-fitting tilted dipole intersects the Earth's surface in the southern hemisphere. As of 2005 it was calculated to be located at 79°44′S 108°13′E / 79.74°S 108.22°E [1], near the Vostok Station. Because the field is not an exact dipole, the South Geomagnetic Pole does not coincide with the South Magnetic Pole. Furthermore, the South Geomagnetic Pole is wandering for the same reason its northern magnetic counterpart wanders.
See also
References
- ^ a b NOAA National Geophysical Data Center. "Wandering of the Geomagnetic Poles". http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/geomag/GeomagneticPoles.shtml. Retrieved 2011.
- ^ "Geomagnetism Frequently Asked Questions". NGDC. http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/geomag/faqgeom.shtml. Retrieved January 11, 2009.
- ^ "Geomagnetism, North Magnetic Pole". Geological Survey of Canada. Natural Resources Canada. http://gsc.nrcan.gc.ca/geomag/nmp/northpole_e.php. Retrieved 11 January 2009.
- ^ "Poles and Directions". Australian Antarctic Division. 2011. http://www.antarctica.gov.au/about-antarctica/fact-files/geography/poles-and-directions. Retrieved October 2011.
- ^ Antarctic Treaty System: an Assessment, p. 90, US National Research Council, 1986
- ^ http://www.antarctica.ac.uk/About_Antarctica/FAQs/faq_05.html
- ^ "The Magnetic South Pole". Ocean Bottom Magnetology Laboratory. Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute. http://deeptow.whoi.edu/southpole.html. Retrieved October 2011.
- ^ Shackleton, Roland Huntford
- ^ Jackson, Andrew; Jonkers, Art R. T.; Walker, Matthew R. (2000). "Four centuries of geomagnetic secular variation from historical records". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A 358 (1768): 957–990. doi:10.1098/rsta.2000.0569.
- Barton, Charles (2002). "Survey tracks current position of South Magnetic Pole". EOS 83 (27): 291. doi:10.1029/2002EO000210.
External links
Categories:- Poles
- Geography of Antarctica
- Geomagnetism
- Orientation
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
