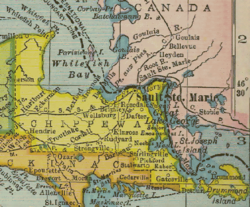
- Chippewa County, Michigan
-
Chippewa County, Michigan
Logo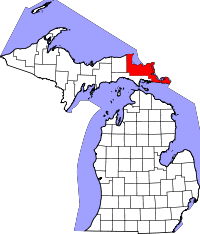
Location in the state of Michigan
Michigan's location in the U.S.Founded 1826 Seat Sault Ste. Marie Largest city Sault Ste. Marie Area
- Total
- Land
- Water
2,697.98 sq mi (6,988 km²)
1,561.06 sq mi (4,043 km²)
1,136.92 sq mi (2,945 km²), 42.14%Population
- (2000)
- Density
38,543
26/sq mi (10/km²)Website www.chippewacountymi.gov Chippewa County is a county in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2000 census, the population was 38,543. The county seat is Sault Ste. Marie[1].
Contents
Geography
- According to the 2000 census, the county has a total area of 2,697.98 square miles (6,987.7 km2), of which 1,561.06 square miles (4,043.1 km2) (or 57.86%) is land and 1,136.92 square miles (2,944.6 km2) (or 42.14%) is water.[2]
- The Michigan Meridian runs through the eastern portion of the county. South of Nine Mile Road, M-129 (Meridian Road) overlays the meridian. In Sault Ste. Marie, Meridian Street north of 12th Avenue overlays the meridian.
Transportation
Michigan State Trunklines
All Interstate and US Highways in MIchigan, like all state-maintained highways, are part of the Michigan State Trunkline Highway System.
 I-75 ends at the Sault Ste. Marie International Bridge at the Canada border.
I-75 ends at the Sault Ste. Marie International Bridge at the Canada border. M-28
M-28 M-48
M-48 M-80
M-80 M-123
M-123 M-129
M-129 M-134
M-134 M-221
M-221 BS I-75 travels from I-75 into downtown Sault Ste. Marie.
BS I-75 travels from I-75 into downtown Sault Ste. Marie.
County-Designated Highways
The following highways are maintained by the Chippewa County Road Commission as part of the county road system. They are assigned numbers by the Michigan Department of Transportation as part of the County-Designated Highway System.
 H-40
H-40 H-63 runs via Mackinac Trail, the former route of US 2 before it was replaced by I-75 in 1962.
H-63 runs via Mackinac Trail, the former route of US 2 before it was replaced by I-75 in 1962.
Adjacent counties
- Algoma District, Ontario, Canada (northeast, east)
- Manitoulin District, Ontario, Canada (east)
- Presque Isle County (southeast, water boundary only, in Lake Huron)
- Mackinac County (south)
- Luce County (west)

Lake Superior; Algoma District, Ontario Algoma District, Ontario, Canada 
Luce County 
Algoma District, Ontario / Manitoulin District, Ontario, Canada  Chippewa County, Michigan
Chippewa County, Michigan 

Mackinac County Mackinac County Presque Isle County National protected areas
- Harbor Island National Wildlife Refuge
- Hiawatha National Forest (part)
- Whitefish Point Unit of the Seney National Wildlife Refuge
Demographics
As of the census[3] of 2000, there were 38,543 people, 13,474 households, and 8,960 families residing in the county. The population density was 25 people per square mile (10/km²). There were 19,430 housing units at an average density of 12 per square mile (5/km²). The racial makeup of the county was 75.88% White, 5.52% Black or African American, 13.31% Native American, 0.46% Asian, 0.03% Pacific Islander, 0.37% from other races, and 4.43% from two or more races. 1.55% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. 14.9% were of German, 9.8% English, 9.0% Irish, 7.4% French and 6.0% Polish ancestry. 95.3% spoke English and 1.7% Spanish as their first language.
There were 13,474 households out of which 30.40% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 51.50% were married couples living together, 10.70% had a female householder with no husband present, and 33.50% were non-families. 27.50% of all households were made up of individuals and 10.70% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.42 and the average family size was 2.93.
In the county the population was spread out with 21.30% under the age of 18, 11.90% from 18 to 24, 31.80% from 25 to 44, 22.30% from 45 to 64, and 12.70% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 36 years. For every 100 females there were 125.50 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 132.10 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $34,464, and the median income for a family was $41,450. Males had a median income of $31,559 versus $22,321 for females. The per capita income for the county was $15,858. About 8.90% of families and 12.80% of the population were below the poverty line, including 15.60% of those under age 18 and 9.60% of those age 65 or over.
Government
The county government operates the jail, maintains rural roads, operates the major local courts, keeps files of deeds and mortgages, maintains vital records, administers public health regulations, and participates with the state in the provision of welfare and other social services. The county board of commissioners controls the budget but has only limited authority to make laws or ordinances. In Michigan, most local government functions — police and fire, building and zoning, tax assessment, street maintenance, etc. — are the responsibility of individual cities and townships.
Chippewa County elected officials
- Prosecuting Attorney: Brian Peppler
- Sheriff: Robert Savoie
- County Clerk: Diane Cork
- County Treasurer: Marilyn McDonald
- Register of Deeds: Sharon Kennedy
- Drain Commissioner: Anthony Bosley
- County Surveyor: William Karr
(information updated July 2010)
Cities, villages, and townships
Cities
Villages
Unincorporated communities
- Barbeau
- Bay Mills
- Bay Mills Indian Community
- Brimley
- Dafter
- Drummond
- Pickford
- Rudyard
- Stirlingville
Townships
See also
References
- ^ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. http://www.naco.org/Counties/Pages/FindACounty.aspx. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- ^ "Census 2000 U.S. Gazetteer Files: Counties". United States Census. http://www.census.gov/tiger/tms/gazetteer/county2k.txt. Retrieved 2011-02-13.
- ^ "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. http://factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
External links
- Chippewa County Government
- Clarke Historical Library, Central, Michigan University, Bibliography for Chippewa County
Municipalities and communities of Chippewa County, Michigan City Village Charter
townshipGeneral law
townshipsUnincorporated
communitiesCategories:- Michigan counties
- Chippewa County, Michigan
- 1826 establishments in the United States
- Populated places established in 1826
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.