- Microbial food web
-
The microbial food web refers the combined trophic interactions among microbes in aquatic environments. These microbes include viruses, bacteria, algae, heterotrophic protists (such as ciliates and flagellates).
In aquatic environments, microbes constitute the base of the food web. Single celled photosynthetic organisms such as diatoms and cyanobacteria are generally the most important primary producers in the open ocean. Many of these cells, especially cyanobacteria, are too small to be captured and consumed by small crustaceans and planktonic larvae. Instead, these cells are consumed by phagotrophic protists which are readily consumed by larger organisms. Viruses can infect and break open bacterial cells and (to a lesser extent), planktonic algae (a.k.a phytoplankton). Therefore, viruses in the microbial food web act to reduce the population of bacteria and, by lysing bacterial cells, release particulate and dissolved organic carbon (DOC). DOC may also be released into the environment by algal cells. One of the reasons phytoplankton release DOC termed "unbalanced growth" is when essential nutrients (e.g. nitrogen and phosphorus) are limiting. Therefore, carbon produced during photosynthesis is not used for the synthesis of proteins (and subsequent cell growth), but is limited due of a lack of the nutrients necessary for macromolecules. Excess photosynthate, or DOC is then released, or exuded.
The microbial loop describes a pathway in the microbial food web where DOC is returned to higher trophic levels via the incorporation into bacterial biomass.
Modelling ecosystems – trophic components General 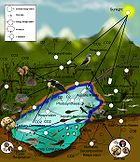
Producers Consumers - Apex predator
- Bacterivore
- Carnivores
- Chemoorganotroph
- Foraging
- Generalist and specialist species
- Intraguild predation
- Herbivores
- Heterotroph
- Heterotrophic nutrition
- Insectivore
- Mesopredator release hypothesis
- Omnivores
- Optimal foraging theory
- Predation
- Prey switching
Decomposers Microorganisms Food webs - Biomagnification
- Ecological efficiency
- Ecological pyramid
- Energy flow
- Food chain
- Trophic level
Example webs - Cold seeps
- Hydrothermal vents
- Intertidal
- Kelp forests
- Lakes
- North Pacific Subtropical Gyre
- Rivers
- San Francisco Estuary
- Soil
- Tidal pool
Processes - Ascendency
- Bioaccumulation
- Cascade effect
- Climax community
- Competitive exclusion principle
- Consumer-resource systems
- Copiotrophs
- Dominance
- Ecological network
- Ecological succession
- Energy quality
- Energy Systems Language
- f-ratio
- Feed conversion ratio
- Feeding frenzy
- Mesotrophic soil
- Nutrient cycle
- Oligotroph
- Paradox of the plankton
- Trophic cascade
- Trophic mutualism
- Trophic state index
Defense/counter - Animal coloration
- Antipredator adaptations
- Herbivore adaptations to plant defense
- Mimicry
- Plant defense against herbivory
- Predator avoidance in schooling fish
Modelling ecosystems – other components Population ecology - Abundance
- Allee effect
- Depensation
- Ecological yield
- Effective population size
- Intraspecific competition
- Logistic function
- Malthusian growth model
- Maximum sustainable yield
- Overpopulation in wild animals
- Overexploitation
- Population cycle
- Population dynamics
- Population modeling
- Population size
- Predator–prey equations
- Recruitment
- Resilience
- Small population size
- Stability
Species - Biodiversity
- Density-dependent inhibition
- Ecological effects of biodiversity
- Ecological extinction
- Endemic species
- Flagship species
- Gradient analysis
- Indicator species
- Introduced species
- Invasive species
- Latitudinal gradients in species diversity
- Minimum viable population
- Neutral theory
- Occupancy-abundance relationship
- Population viability analysis
- Priority effect
- Rapoport's rule
- Relative abundance distribution
- Relative species abundance
- Species diversity
- Species homogeneity
- Species richness
- Species distribution
- Species-area curve
- Umbrella species
Species interaction Spatial ecology - Biogeography
- Cross-boundary subsidy
- Ecocline
- Ecotone
- Ecotype
- Disturbance
- Edge effect
- Foster's rule
- Habitat fragmentation
- Ideal free distribution
- Intermediate Disturbance Hypothesis
- Island biogeography
- Landscape ecology
- Landscape epidemiology
- Landscape limnology
- Metapopulation
- Patch dynamics
- r/K selection theory
- Source–sink dynamics
Niche Other networks - Assembly rules
- Bateman's principle
- Bioluminescence
- Ecological collapse
- Ecological debt
- Ecological deficit
- Ecological energetics
- Ecological indicator
- Ecological threshold
- Ecosystem diversity
- Emergence
- Extinction debt
- Kleiber's law
- Liebig's law of the minimum
- Marginal value theorem
- Thorson's rule
- Xerosere
Other - Allometry
- Alternative stable state
- Balance of nature
- Biological data visualization
- Constructal theory
- Ecocline
- Ecological economics
- Ecological footprint
- Ecological forecasting
- Ecological humanities
- Ecological stoichiometry
- Ecopath
- Ecosystem based fisheries
- Endolith
- Evolutionary ecology
- Functional ecology
- Industrial ecology
- Macroecology
- Microecosystem
- Natural environment
- Systems ecology
- Theoretical ecology
List of ecology topics Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


