- Decomposer
-
For the Matches album of the same name, see Decomposer (album).
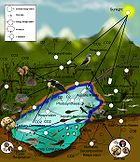
Decomposers (or saprotrophs) are organisms that break down dead or decaying organisms, and in doing so carry out the natural process of decomposition. Like herbivores and predators, decomposers are heterotrophic, meaning that they use organic substrates to get their energy, carbon and nutrients for growth and development. Decomposers use deceased organisms and non-living organic compounds as their food source. The primary examples are:
Contents
Bacteria
Main article: BacteriaBacteria are important decomposers; they are widely distributed and can break down just about any type of organic matter.[1] A gram of soil typically contains 40 million bacterial cells, and the bacteria on Earth form a biomass that exceeds that of all living plants and animals. Bacteria are vital in the recycling nutrients, and many steps in nutrient cycles depend on these organisms.
[[File:
 'Italic text''Italic text''''Bold text''''']]== Fungi == The primary decomposers of litter in many ecosystems are fungi. Unlike bacteria, which are unicellular organisms, most saprotrophic fungi grow as a branching network of hyphae. While bacteria are restricted to growing and feeding on the exposed surfaces of organic matter, fungi can use their hyphae to penetrate larger pieces of organic matter. Additionally, only wood-decay fungi have evolved the enzymes necessary to decompose lignin, a chemically complex substance found in wood. These two factors make fungi the primary decomposers in forests, where litter has high concentrations of lignin and often occurs in large pieces. Fungi eat the dead matter by releasing acid found in their body to melt the decaying material, then sucking in all the acid, along with the melted material.[citation needed] Over time, the fungi will eat all the material left. Hyphae are used to drain the melted material and acid are also used in sexual reproduction. When two fungi's hyphae grow close to each other, they will then fuse together and form another fungus.[citation needed] That new fungus will then mature. --173.67.232.18 (talk) 23:56, 22 November 2011 (UTC)[[File:
'Italic text''Italic text''''Bold text''''']]== Fungi == The primary decomposers of litter in many ecosystems are fungi. Unlike bacteria, which are unicellular organisms, most saprotrophic fungi grow as a branching network of hyphae. While bacteria are restricted to growing and feeding on the exposed surfaces of organic matter, fungi can use their hyphae to penetrate larger pieces of organic matter. Additionally, only wood-decay fungi have evolved the enzymes necessary to decompose lignin, a chemically complex substance found in wood. These two factors make fungi the primary decomposers in forests, where litter has high concentrations of lignin and often occurs in large pieces. Fungi eat the dead matter by releasing acid found in their body to melt the decaying material, then sucking in all the acid, along with the melted material.[citation needed] Over time, the fungi will eat all the material left. Hyphae are used to drain the melted material and acid are also used in sexual reproduction. When two fungi's hyphae grow close to each other, they will then fuse together and form another fungus.[citation needed] That new fungus will then mature. --173.67.232.18 (talk) 23:56, 22 November 2011 (UTC)[[File: ]]
]]Worms
Various types of worms are also considered decomposers, as they act as scavengers. For example, a worm that begins to consume an apple helps to hasten its decay by removing parts of the skin and flesh, exposing the interior of the fruit to the elements and to other decomposers. Certain species of roundworms will also help to decompose the bodies of animals[citation needed].
See also
References
- Beare MH, Hendrix PF, Cheng W (1992) Microbial and faunal interactions and effects on litter nitrogen and decomposition in agroecosystems. Ecological Monographs 62: 569-591
- Hunt HW, Colema9n DC, Ingham ER, Ingham RE, Elliot ET, Moore JC, Rose SL, Reid CPP, Morley CR (1987) "The detrital food web in a shortgrass prairie". Biology and Fertility of Soils 3: 57-68
- Smith TM, Smith RL (2006) Elements of Ecology. Sixth edition. Benjamin Cummings, San Francisco, CA.
- Swift MJ, Heal OW, Anderson JM (1979) Decomposition in Terrestrial Ecosystems. University of California Press, Berkeley, CA.
Feeding behaviours Carnivores adultHematophagy · Insectivore · Lepidophagy · Man-eater · Molluscivore · Mucophagy · Myrmecophagy · Ophiophagy · Piscivore · Avivore · Spongivore · Vermivore · Herpetivorereproductivecannibalistic
Herbivores Others Methods Apex predator · Bait balls · Bottom feeding · Browsing · Feeding frenzy · Filter feeding · Grazing · Hypercarnivore • Intraguild predation · Kleptoparasitism · Scavenging · TrophallaxisPredation · Antipredator adaptation · Carnivorous plant · Carnivorous fungus · Carnivorous protist · Category:Eating behaviorsCategories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.