- Lithoautotroph
-
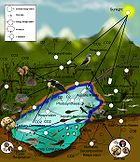
A lithoautotroph is a microbe which derives energy from reduced compounds of mineral origin. They may also be referred to as chemolithoautotrophs, a type of lithotrophs, reflecting their autotrophic metabolic pathways. Lithoautotrophs are exclusively microbes; macrofauna do not possess the capability to utilize mineral sources of energy. For lithoautotrophic bacteria, only inorganic molecules can be used as energy sources. Most lithoautotrophs belong to the domain Bacteria. The term "Lithotroph" is created from the terms 'lithos' (rock) and 'troph' (consumer); literally, it may be read "eaters of rock." Many lithoautotrophs are extremophiles, but this is not universally so.
Geological processes
Lithoautotrophs participate in many geological processes, such as the weathering of parent material (bedrock) to form soil, as well as biogeochemical cycling of sulfur, potassium, and other elements. They may be present in the deep terrestrial subsurface (they have been found well over a 3km below the surface of the planet), in soils, and in endolith communities. As they are responsible for the liberation of many crucial nutrients, and participate in the formation of soil, lithoautotrophs play a crucial role in the maintenance of life on Earth.
Acid mine drainage
Lithoautotrophic microbial consortia are responsible for the phenomenon known as acid mine drainage, whereby energy-rich pyrite present in mine tailing heaps and in exposed rock faces is metabolized to form sulfites, which form potentially toxic sulfuric acid when dissolved in water. Acid mine drainage drastically alters the acidity and chemistry of groundwater and streams, and may endanger plant and animal populations. Activity similar to acid mine drainage, but on a much lower scale, is also found in natural conditions such as the rocky beds of glaciers, in soil and talus, and in the deep subsurface.
Lithoautotrophs are extremely specific in using their energy source. Thus, despite the diversity in using inorganic molecules in order to obtain energy that lithoautotrophs exhibit as a group, one particular lithoautotroph would use only one type of inorganic molecules to get its energy.
References
- Ramos JL. (May 2003). "Lessons from the genome of a lithoautotroph: making biomass from almost nothing". J Bacteriol. 185 (9): 2690–1. doi:10.1128/JB.185.9.2690-2691.2003. PMC 154387. PMID 12700247. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=154387.
Extremophiles Types Acidophile · Alkaliphile · Capnophile · Cryozoa · Endolith · Halophile · Hypolith · Lipophile · Lithoautotroph · Lithophile · Methanogen · Metallotolerant · Oligotroph · Osmophile · Piezophile · Polyextremophile · Psychrophile · Radioresistant · Thermophile/Hyperthermophile · Thermoacidophile · Xerophile
Notable
extremophilesPyrococcus furiosus · Strain 121 · Pyrolobus fumarii
Paralvinella sulfincola · Halicephalobus mephisto · Pompeii worm · Tardigrada
Related articles Abiogenic petroleum origin · Acidithiobacillales · Acidobacteria · Acidophiles in acid mine drainage · Archaeoglobaceae · Berkeley Pit · Blood Falls · Crenarchaeota · Grylloblattidae · Halobacteria · Halobacterium · Helaeomyia petrolei · Hydrothermal vent · Methanopyrus · Movile Cave · Radiotrophic fungus · Rio Tinto · Taq polymerase · Thermostability · Thermotogae
Categories:- Soil biology
- Trophic ecology
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.