Density-dependent inhibition
- Density-dependent inhibition
-
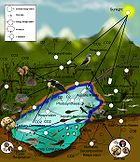
In population ecology, density-dependent inhibition describes a situation in which population growth is curtailed by crowding, predators and competition. In cell biology, it describes the reduction in cell division. When a cell population reaches a certain density, the amount of required growth factors and nutrients available to each cell becomes insufficient to allow continued cell growth.
This is also true for other organisms because an increased density means an increase in intraspecific competition. Greater competition means an individual has a decreased contribution to the next generation i.e. offspring. Density dependent mortality can be overcompensating, undercompensating or exactly compensating.
Density dependent fecundity also exists, where the birth rate falls as competition increases.
There also exists density-independent inhibition, where other factors such as weather or environmental conditions and disturbances may affect a population's carrying capacity.
An example of a density dependent variable is crowding and competition.
External links
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
density dependent inhibition of growth — The phenomenon exhibited by most normal (anchorage dependent) animal cells in culture that stop dividing once a critical cell density is reached. The critical density is considerably higher for most cells than the density at which a monolayer is… … Dictionary of molecular biology
Delayed density dependence — In population ecology delayed density dependence describes a situation where population growth is controlled by negative feedback operating with a time lag[1]. Contents 1 Population cycles 2 Causes … Wikipedia
contact inhibition of division — See density dependent inhibition … Dictionary of molecular biology
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase — Calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II association domain crystal structure of calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase Identifiers Symbol CaMKII AD … Wikipedia
Mevalonate inhibition — is used to define the effects of medicines based on HMG CoA reductase enzyme inhibitors to control the products of the mevalonate pathway. This term addresses the effects of long term restriction of mevalonate production in cell membranes by the… … Wikipedia
Cyclin-dependent kinase — Schematic of the cell cycle. outer ring: I=Interphase, M=Mitosis; inner ring: M=Mitosis; G1=Gap phase 1; S=Synthesis; G2=Gap phase 2. The duration of mitosis in relation to the other phases has been exaggerated in this diagram Cyclin dependent… … Wikipedia
Voltage-dependent calcium channel — Voltage dependent calcium channels (VDCC) are a group of voltage gated ion channels found in excitable cells (e.g., muscle, glial cells, neurons, etc.) with a permeability to the ion Ca2+.[1][2] These channels are slightly permeable to sodium… … Wikipedia
Occupancy-abundance relationship — In macroecology, the occupancy abundance (O A) relationship is the relationship between the abundance of species and the size of their ranges within a region. This relationship is perhaps one of the most well documented relationships in… … Wikipedia
Maximum sustainable yield — In population ecology and economics, maximum sustainable yield or MSY is, theoretically, the largest yield (or catch) that can be taken from a species stock over an indefinite period. Fundamental to the notion of sustainable harvest, the concept… … Wikipedia
Microbial cooperation — Microorganisms engage in a wide variety of social interactions, including cooperation. A cooperative behavior is one that benefits an individual (the recipient) other than the one performing the behavior (the actor).[1] This article outlines the… … Wikipedia