- Archaeoglobaceae
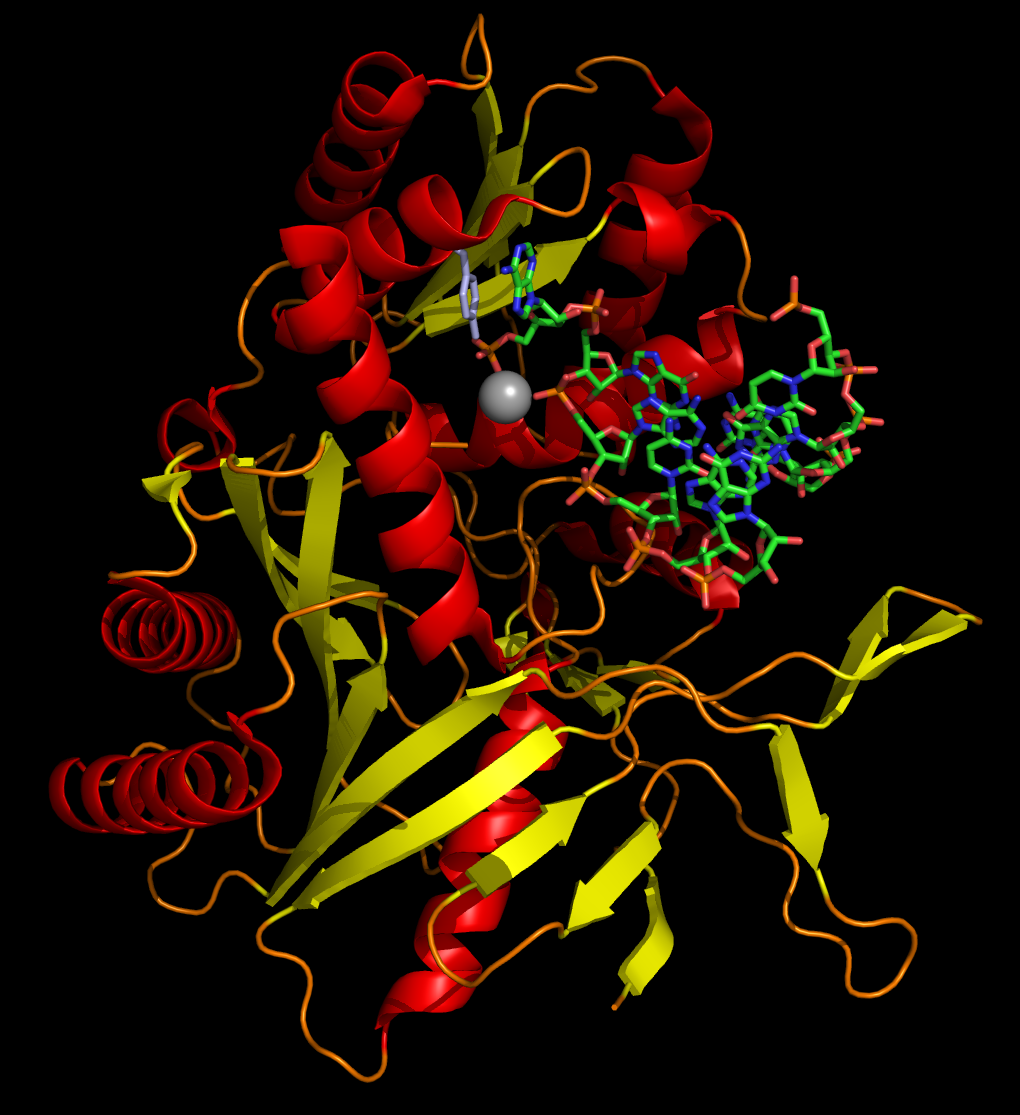
image_caption=The PIWI domain of anargonaute protein from A. fulgidus, bound to a short double-strandedRNA fragment and illustrating the base-pairing and aromatic stacking stabilization of the bound conformation.
name = Archaeoglobaceae
domain =Archaea
phylum =Euryarchaeota
classis =Archaeoglobi
ordo =Archaeoglobales
familia = Archaeoglobaceae
subdivision_ranks = Genera
subdivision =
* "Archaeoglobus "
* "Ferroglobus "
* "Geoglobus "
synonyms =
* Archaeoglobaceae Stetter 1989
* Archaeoglobaceae Huber and Stetter 2002In taxonomy, the Archaeoglobaceae are a family of the
Archaeoglobales . [See the NCBI [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&id=2232 webpage on Archaeoglobaceae] . Data extracted from the cite web | url=ftp://ftp.ncbi.nih.gov/pub/taxonomy/ | title=NCBI taxonomy resources | publisher=National Center for Biotechnology Information | accessdate=2007-03-19] All known genera within the Archaeoglobaceae are hyperthermophilic and can be found near underseahydrothermal vent s.While all genera within the Archaeoglobaceae are related to each other phylogenetically, the mode of metabolism used by each of these organisms is unique. "
Archaeoglobus " arechemoorganotroph ic sulfate-reducing archaea, the only known member of theArchaea that possesses this type of metabolism. "Ferroglobus ", in contrast, arechemolithotroph ic organisms that couple the oxidation of ferrous iron to the reduction ofnitrate . "Geoglobus " are iron reducing-archaea that usehydrogen gas ororganic compound s as energy sources. [* cite book | author=Madigan, M.T. and Martinko, J.M. | title=Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 11th Ed. | publisher=Pearson Prentice Hall | year=2005 ]References
Further reading
cientific journals
cientific books
*
*
*
cientific databases
External links
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.