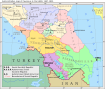
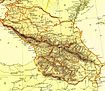
- Karachay-Cherkessia
-
Karachay-Cherkess Republic Карачаево-Черкесская Республика (Russian)
Къарачай-Черкес Республика (Karachay-Balkar)
Къэрэшей-Шэрджэс Республикэ (Kabardian)— Republic — 
Flag
Coat of armsAnthem: National Anthem of Karachay-Cherkessia Coordinates: 43°55′N 41°47′E / 43.917°N 41.783°ECoordinates: 43°55′N 41°47′E / 43.917°N 41.783°E Political status Country Russia Federal district North Caucasian[1] Economic region North Caucasus[2] Established January 9, 1957[3] Capital Cherkessk Government (as of August 2010) - President[4] Rashid Temrezov[5] - Legislature People's Assembly (Parliament)[4] Statistics Area (as of the 2002 Census)[6] - Total 14,100 km2 (5,444.0 sq mi) Area rank 77th Population (2010 Census)[7] - Total 478,517 - Rank 73rd - Density 33.94 /km2 (87.9 /sq mi) - Urban 42.3% - Rural 57.7% Population (2002 Census)[8] - Total 439,470 - Rank 75th - Density 31.17 /km2 (80.7 /sq mi) - Urban 44.0% - Rural 66.0% Time zone(s) MSD (UTC+04:00)[9] ISO 3166-2 RU-KC License plates 09 Official languages Russian;[10] Abaza, Cherkess, Karachay, Nogai[11] http://www.kchr.info/ The Karachay-Cherkess Republic (Russian: Карача́ево-Черке́сская Респу́блика, Karachayevo-Cherkesskaya Respublika; Karachay-Balkar: Къарачай-Черкес Республика; Kabardian: Къэрэшей-Шэрджэс Республикэ), or Karachay-Cherkessia (Карача́ево-Черке́ссия, Karachayevo-Cherkessiya) is a federal subject of Russia (a republic). Population: 478,517 (2010 Census preliminary results).[12]
Contents
Geography
- Area: 14,100 square kilometers (5,400 sq mi)
- Borders:
- internal: Krasnodar Krai (N/NE/E), Kabardino-Balkar Republic (E/SE), Stavropol Krai (W/NW).
- international: Georgia (S/SW) (including Abkhazia).
- Highest point: Mount Elbrus (5,642 m)
- Maximum N->S distance: no data
- Maximum E->W distance: no data
Rivers
There are 172 rivers on the territory of the republic. Major rivers include:
- Aksaut River
- Bolshaya Laba River
- Bolshoy Zelenchuk River
- Daut River
- Kuban River
- Kuma River
- Kyafar River
- Maly Zelenchuk River
- Marukha River
- Podkumok River
- Teberda River
- Urup River
Lakes
There are approximately 130 lakes in the republic.
Mountains
The landscape of the republic is mostly mountainous (~80% of the territory). Mount Elbrus, the highest mountain in Europe, is situated on the border with the Kabardino-Balkar Republic.
Natural resources
Karachay-Cherkessia's natural resources include gold, coal, clays, and more.
Climate
- Average January temperature: −3.2 °C (26.2 °F)
- Average July temperature: 20.6 °C (69.1 °F)
- Average annual precipitation: 550 millimeters (22 in) (plains) to 2,500 millimeters (98 in) (mountains)
Administrative divisions
Demographics
- Population: 478,517 (2010 Census preliminary results)[12]
- Population: 439,470 (2002)
- Urban: 193,531 (44.0%)
- Rural: 245,939 (56.0%)
- Male: 205,481 (46.8%)
- Female: 233,989 (53.2%)
- Females per 1000 males: 1,139
- Average age: 33.2 years
- Urban: 33.4 years
- Rural: 33.1 years
- Male: 31.0 years
- Female: 35.2 years
- Number of households: 127,488 (with 437,338 people)
- Urban: 62,858 (with 192,642people)
- Rural: 65,130 (with 244,696 people)
- Vital statistics
- Source: Russian Federal State Statistics Service
Births Deaths Birth rate Death rate 1970 6,021 2,153 17.4 6.2 1975 6,619 2,288 18.5 6.4 1980 7,044 2,794 18.9 7.5 1985 8,119 3,350 20.6 8.5 1990 7,218 3,496 17.1 8.3 1991 7,145 3,713 16.7 8.7 1992 6,846 3,915 15.9 9.1 1993 5,569 4,336 12.9 10.0 1994 5,786 4,598 13.3 10.6 1995 5,633 4,501 12.9 10.3 1996 5,281 4,683 12.0 10.7 1997 4,987 4,615 11.3 10.5 1998 4,990 4,537 11.3 10.3 1999 4,523 4,707 10.3 10.7 2000 4,666 4,961 10.6 11.3 2001 4,778 4,911 10.9 11.2 2002 4,927 5,207 11.2 11.9 2003 5,088 5,427 11.6 12.4 2004 5,190 5,059 11.9 11.6 2005 5,194 5,131 12.0 11.9 2006 5,032 4,924 11.7 11.4 2007 6,066 4,626 14.2 10.8 2008 6,364 4,731 14.9 11.1 - Ethnic groups
According to the 2002 Census, Karachays make up 38.5% of the republic's population, followed by Russians (33.6%) and Cherkes (11.3%). Other groups include Abazins (7.4%), Nogais (3.4%), Ossetians (3,333, or 0.8%), Ukrainians (3,331, or 0.8%), Armenians (3,197, or 0.7%), Tatars (2,021, or 0.5%), and a host of smaller groups, each accounting for less than 0.5% of the total population.
census 1926 census 1939 census 1959 census 1970 census 1979 census 1989 census 2002 Karachays 52,875 (52.0%) 70,932 (29.2%) 67,830 (24.4%) 97,104 (28.2%) 109,196 (29.7%) 129,449 (31.2%) 169,198 (38.5%) Cherkess 16,186 (15.9%) 17,667 (7.3%) 24,145 (8.7%) 31,190 (9.0%) 34,430 (9.4%) 40,241 (9.7%) 49,591 (11.3%) Abazins 13,731 (13.5%) 14,138 (5.8%) 18,159 (6.5%) 22,896 (6.6%) 24,245 (6.6%) 27,475 (6.6%) 32,346 (7.4%) Russians 2,593 (2.6%) 118,785 (48.8%) 141,843 (51.0%) 162,442 (47.1%) 165,451 (45.1%) 175,931 (42.4%) 147,878 (33.6%) Nogais 6,263 (6.2%) 6,869 (2.8%) 8,903 (3.2%) 11,062 (3.2%) 11,872 (3.2%) 12,993 (3.1%) 14,873 (3.4%) Others 9,961 (9.8%) 14,810 (6.1%) 17,079 (6.1%) 19,957 (5.8%) 21,917 (6.0%) 28,881 (7.0%) 25,584 (5.8%) History
Karachay-Cherkess Autonomous Oblast was created on January 12, 1922. It was split into Karachay Autonomous Oblast and Cherkess National District on April 26, 1926. Cherkess National District was elevated to an autonomous oblast status on April 30, 1928. In 1943, Karachay Autonomous Oblast was abolished and the Karachay population was deported to Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan accused of collaboration with the Nazis. Most of the Karchay territory was split between Stavropol Krai and the Georgian SSR. The remaining territory populated by the Cherkessians was known as Cherkess Autonomous Oblast until January 9, 1957 when it was re-established into Karachay-Cherkess Autonomous Oblast in its former borders due to the re-habilitation of the Karachay. On July 3, 1991, the autonomous oblast was elevated to the status of the Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic of Karachay-Cherkessia (under the jurisdiction of the Russian SFSR). With the dissolution of the Soviet Union in December 1991, the words "Autonomous Soviet Socialist" was dropped from the name.
Politics
The head of the government in Karachay-Cherkessia is the President. Until February 2011, the president was Boris Safarovich Ebzeyev, a former judge of the Constitutional Court of Russian Federation. Rashid Temrezov is currently the acting president.[5]
Ethnic tension is a considerable problem in the republic. In May 1999 Karachay-Cherkessia conducted its first ever free regional presidential election. When Vladimir Semyonov, a Karachay, won the election over Stanislav Derev, a Circassian, there were protests by supporters of Derev, with widespread allegations of fraud. A court ruling later upheld the election result, prompting thousands of Derev's supporters to march in protest, many advocating partition of the republic.
A car-bomb that killed two people in March 2001 was blamed on Chechen separatists. In September 2007, the FSB killed Abubakar, the chief Islamic extremist of the republic.
Economy
Industry is mostly concentrated in the capital of the republic, Cherkessk. Chemical, wood, and food industries are the most developed. The republic is keen to develop its tourist industry and winter sports are particularly popular. However, poverty is widespread.
Science
The republic is the home of what was the largest telescope of the world when it was built (the BTA-6), a very large radiotelescope (600 meters in diameter, RATAN-600), and the Special Astrophysical Observatory of the Russian Academy of Science dedicated to the study of astronomy. These facilities are located on the bank of the Zelenchuk river, between the villages of Zelenchukskaya and Arkhyz.
References
Notes
- ^ Президент Российской Федерации. Указ №849 от 13 мая 2000 г. «О полномочном представителе Президента Российской Федерации в федеральном округе». Вступил в силу 13 мая 2000 г. Опубликован: "Собрание законодательства РФ", №20, ст. 2112, 15 мая 2000 г. (President of the Russian Federation. Decree #849 of May 13, 2000 On the Plenipotentiary Representative of the President of the Russian Federation in a Federal District. Effective as of May 13, 2000).
- ^ Госстандарт Российской Федерации. №ОК 024-95 27 декабря 1995 г. «Общероссийский классификатор экономических регионов. 2. Экономические районы», в ред. Изменения №5/2001 ОКЭР. (Gosstandart of the Russian Federation. #OK 024-95 December 27, 1995 Russian Classification of Economic Regions. 2. Economic Regions, as amended by the Amendment #5/2001 OKER. ).
- ^ Президиум Верховного Совета СССР. Указ от 9 февраля 1957 г. «О преобразовании Черкесской автономной области в Карачаево-Черкесскую автономную область». (Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR. Decree of February 9, 1957 On Transformation of Cherkess Autonomous Oblast into Karachay-Cherkess Autonomous Oblast. ).
- ^ a b Constitution, Article 4
- ^ a b Дмитрий Медведев подписал Указ «О досрочном прекращении полномочий Президента Карачаево-Черкесской Республики» (Russian)
- ^ Федеральная служба государственной статистики (Federal State Statistics Service) (2004-05-21). "Территория, число районов, населённых пунктов и сельских администраций по субъектам Российской Федерации (Territory, Number of Districts, Inhabited Localities, and Rural Administration by Federal Subjects of the Russian Federation)" (in Russian). Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2002). Federal State Statistics Service. http://perepis2002.ru/ct/html/TOM_01_03.htm. Retrieved 2011-11-01.
- ^ Федеральная служба государственной статистики (Federal State Statistics Service) (2011). "Предварительные итоги Всероссийской переписи населения 2010 года (Preliminary results of the 2010 All-Russian Population Census)" (in Russian). Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2010). Federal State Statistics Service. http://www.perepis-2010.ru/results_of_the_census/results-inform.php. Retrieved 2011-04-25.
- ^ Федеральная служба государственной статистики (Federal State Statistics Service) (2004-05-21). "Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек (Population of Russia, its federal districts, federal subjects, districts, urban localities, rural localities—administrative centers, and rural localities with population of over 3,000)" (in Russian). Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2002). Federal State Statistics Service. http://www.perepis2002.ru/ct/doc/1_TOM_01_04.xls. Retrieved 2010-03-23.
- ^ Правительство Российской Федерации. Постановление №725 от 31 августа 2011 г. «О составе территорий, образующих каждую часовую зону, и порядке исчисления времени в часовых зонах, а также о признании утратившими силу отдельных Постановлений Правительства Российской Федерации». Вступил в силу по истечении 7 дней после дня официального опубликования. Опубликован: "Российская Газета", №197, 6 сентября 2011 г. (Government of the Russian Federation. Resolution #725 of August 31, 2011 On the Composition of the Territories Included into Each Time Zone and on the Procedures of Timekeeping in the Time Zones, as Well as on Abrogation of Several Resolutions of the Government of the Russian Federation. Effective as of after 7 days following the day of the official publication).
- ^ Official the whole territory of Russia according to Article 68.1 of the Constitution of Russia.
- ^ Constitution, Article 11.1
- ^ a b Федеральная служба государственной статистики (Federal State Statistics Service) (2011). "Предварительные итоги Всероссийской переписи населения 2010 года (Preliminary results of the 2010 All-Russian Population Census)" (in Russian). Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2010). Federal State Statistics Service. http://www.perepis-2010.ru/results_of_the_census/results-inform.php. Retrieved 2011-04-25.
Sources
- 5 марта 1996 г. «Конституция Карачаево-Черкесской Республики», в ред. Конституционного закона №87-РЗ от 12 ноября 2007 г. (March 5, 1996 Constitution of the Karachay-Cherkess Republic, as amended by the Constitutional Law #87-RZ of November 12, 2007. ).
External links
- (Russian) Official website of the Karachay-Cherkess Republic, kchr.info
- (English) (Russian) Collection of images of Karachay-Cherkessia, trombicula.narod.ru
- (English) Images of Karachay-Cherkessia, travel-images.com
- (English) An account of the disputed 1999 election, nupi.no
- (English) Collection of images of Karachay-Cherkessia, with a focus on caves, tls-msu.narod.ru
- (English) (Turkish) Ulu Cami: A Karachay Mosque serving Muslim Community in Northern Jersey, ulucami.org
- Folk Song Mingitav, tika.gov.tr
- Tika.gov.tr
- Circassianworld.com
- Karachay-Cherkess Republic News Portal
Subdivisions of Russia Republics Krais Oblasts - Amur
- Arkhangelsk
- Astrakhan
- Belgorod
- Bryansk
- Chelyabinsk
- Irkutsk
- Ivanovo
- Kaliningrad
- Kaluga
- Kemerovo
- Kirov
- Kostroma
- Kurgan
- Kursk
- Leningrad
- Lipetsk
- Magadan
- Moscow
- Murmansk
- Nizhny Novgorod
- Novgorod
- Novosibirsk
- Omsk
- Orenburg
- Oryol
- Penza
- Pskov
- Rostov
- Ryazan
- Sakhalin
- Samara
- Saratov
- Smolensk
- Sverdlovsk
- Tambov
- Tomsk
- Tula
- Tver
- Tyumen
- Ulyanovsk
- Vladimir
- Volgograd
- Vologda
- Voronezh
- Yaroslavl
Federal cities Autonomous oblasts Autonomous okrugs 1administratively subordinated to Tyumen Oblast 2 administratively subordinated to Arkhangelsk Oblast
Countries and regions of the Caucasus History of Europe Prehistoric Europe Classical Antiquity Classical Greece · Roman Republic · Hellenistic period · Roman Empire · Late Antiquity · Early Christianity · Crisis of the 3rd century · Fall of the Roman EmpireMiddle Ages Early Middle Ages · Migration Period · Byzantine Empire · Christianization · Kievan Rus · High Middle Ages · Holy Roman Empire · Crusades · Feudalism · Late Middle Ages · Hundred Years' War · RenaissanceEarly Modern Europe Reformation · Age of Discovery · Baroque · Thirty Years' War · Absolutism · Ottoman Empire · Portuguese Empire · Spanish Empire · Early modern France · Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth · Swedish Empire · Dutch Republic · British Empire · Habsburg Empire · Russian EmpireModern history See also Politics of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territories- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jan Mayen
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
Other entities - European Union
Turkic-speaking regions Federal subjects of Russia shown in italics.Western Turkic
 Azerbaijan1
Azerbaijan1
 Bashkortostan
Bashkortostan
 Chuvashia
Chuvashia
 Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus
 Gagauzia (Moldova)
Gagauzia (Moldova)
 Kabardino-Balkaria
Kabardino-Balkaria
 Karachay-Cherkessia
Karachay-Cherkessia
 Karakalpakstan (Uzbekistan)
Karakalpakstan (Uzbekistan)
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 Xinjiang (China)1 Includes the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic.Categories:
Xinjiang (China)1 Includes the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic.Categories:- Karachay-Cherkessia
- States and territories established in 1991
- Geography of Southern Russia
- Geography of the Caucasus
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.