- Kabardino-Balkaria
-
Kabardino-Balkar Republic Кабардино-Балкарская Республика (Russian)
Къэбэрдей-Балъкъэр Республикэ (Kabardian)
Къабарты-Малкъар Республика (Balkar)— Republic — 
Flag
Coat of armsAnthem: National Anthem of the Kabardino-Balkar Republic Coordinates: 43°35′N 43°24′E / 43.583°N 43.4°ECoordinates: 43°35′N 43°24′E / 43.583°N 43.4°E Political status Country Russia Federal district North Caucasian[1] Economic region North Caucasus[2] Established January 5, 1936 Capital Nalchik[3] Government (as of August 2010) - President[4] Arsen Kanokov[5] - Legislature Parliament[4] Statistics Area (as of the 2002 Census)[6] - Total 12,500 km2 (4,826.3 sq mi) Area rank 78th Population (2010 Census)[7] - Total 859,802 - Rank 59th - Density 68.78 /km2 (178.1 /sq mi) - Urban 54.5% - Rural 45.5% Population (2002 Census)[8] - Total 901,494 - Rank 60th - Density 72.12 /km2 (186.8 /sq mi) - Urban 56.6% - Rural 43.4% Time zone(s) MSD (UTC+04:00)[9] ISO 3166-2 RU-KB License plates 07 Official languages Russian;[10] Kabardian, Balkar[11] None The Kabardino-Balkar Republic (Russian: Кабарди́но-Балка́рская Респу́блика, Kabardino-Balkarskaya Respublika; Kabardian: Къэбэрдей-Балъкъэр Республикэ; Balkar: Къабарты-Малкъар Республика), or Kabardino-Balkaria (Russian: Кабарди́но-Балка́рия, Kabardino-Balkariya), is a federal subject of Russia (a republic) located in the North Caucasus. Population: 859,802 (2010 Census preliminary results).[7]
Contents
Geography
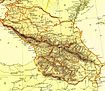
The republic is situated in the North Caucasus mountains, with plains in the northern part.
- Area: 12,500 square kilometers (4,800 sq mi)
- Borders:
- internal: Stavropol Krai (N/NE), Republic of North Ossetia-Alania (E/SE/S), Karachay-Cherkess Republic (W/NW)
- international: Georgia (S/SW)
- Highest point: Mount Elbrus (5,642 m)
- Maximum N->S distance: 167 kilometers (104 mi)
- Maximum E->W distance: 123 kilometers (76 mi)
Kabardino-Balkaria is traversed by the northeasterly line of equal latitude and longitude.
Rivers
Major rivers include:
- Terek River (623 km)
- Malka River (216 km)
- Baksan River (173 km)
- Urukh River (104 km)
- Chegem River (102 km)
- Cherek River (76 km)
- Argudan River
- Kurkuzhin River
- Lesken River
Lakes
There are around 100 lakes in the republic, none of which are large. Just over half (fifty-five) are located between the Baksan and Malka Rivers, the largest each of an area of no more than 0.01 square kilometers (0.0039 sq mi). Some of the lakes are:
- Tserikkel Lake (area 26,000 m²; depth 368 m)
- Lower Goluboye Lake
- Kel-Ketchen Lake (depth 177 m)
- Upper Goluboye Lake (depth 18 m)
- Sekretnoye Lake
- Tambukan Lake (area 1.77 km²; depth 1.5 to 2 m), partially within Stavropol Krai.
Mountains
- Mount Elbrus (5,642 m), a volcanic mountain and the highest peak in Europe, Russia, and the Caucasus
Other major mountains include:
- Mount Dykhtau (5,402 m)
- Mount Koshkhatau (5,151 m)
- Mount Shkhara (5,068 m)
- Pushkin Peak (5,033 m)
- Mount Mizhergi (5,025 m)
Natural resources
Kabardino-Balkaria's natural resources include molybdenum, tungsten, and coal.
Climate
The republic has a continental type climate.
- Average January temperature: −12 °C (10 °F) (mountains) to −4 °C (25 °F) (plains)
- Average July temperature: 4 °C (39 °F) (mountains) to 23 °C (73 °F) (plains)
- Average annual precipitation: 500-2,000 mm.
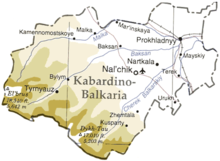
Administrative divisions
Main article: Administrative divisions of Kabardino-BalkariaDemographics
- Populatin: 859,802 (2010 Census preliminary results)[7]
- Population: 901,494 (2002)[8]
- Urban: 510,346 (56.6%)
- Rural: 391,148 (43.4%)
- Male: 422,720 (46.9%)
- Female: 478,774 (53.1%)
- Females per 1000 males: 1,133
- Average age: 30.9 years
- Urban: 32.4 years
- Rural: 29.0 years
- Male: 29.1 years
- Female: 32.8 years
- Number of households: 227,922 (with 891,783 people)
- Urban: 144,872 (with 504,085 people)
- Rural: 83,050 (with 387,698 people)
- Vital statistics
- Source: Russian Federal State Statistics Service
Births Deaths Birth rate Death rate 1970 11,683 3,913 19.7 6.6 1975 12,315 4,717 19.4 7.4 1980 14,098 5,457 20.7 8.0 1985 15,941 5,854 22.0 8.1 1990 15,412 6,573 20.0 8.5 1991 14,952 6,995 19.0 8.9 1992 13,728 7,093 17.2 8.9 1993 11,781 7,864 14.6 9.7 1994 11,407 8,052 14.0 9.9 1995 10,844 8,236 13.1 9.9 1996 10,293 8,199 12.2 9.8 1997 10,016 7,985 11.7 9.4 1998 9,997 8,201 11.5 9.5 1999 9,221 8,292 10.5 9.5 2000 9,207 8,792 10.4 10.0 2001 8,892 8,778 10.0 9.9 2002 9,119 8,954 10.2 10.0 2003 9,294 9,202 10.3 10.2 2004 9,414 8,695 10.5 9.7 2005 8,991 9,034 10.0 10.1 2006 9,308 8,764 10.4 9.8 2007 11,397 8,441 12.8 9.5 2008 12,052 8,095 13.5 9.1 Ethnic groups
Kabardino-Balkaria consists of two ethnic territories, one predominantly of Kabardin (speakers of a North-West Caucasian language) and the other predominantly Balkars (Bulgar or descended from Bulgars) (speakers of a Turkic language). According to the 2002 Census, Kabardin make up 55.3% of the republic's population, followed by Russians (25.1%) and Balkars (11.6%). Other groups include Ossetians (9,845, or 1.1%), Turks (8,770, or 1.0%), Ukrainians (7,592, or 0.8%), Armenians (5,342, or 0.6%), Koreans (4,722, or 0.5%), Chechens (4,241, or 0.5%), and a host of smaller groups, each accounting for less than 0.5% of the total population.
The majority of the population is Muslim.[12]
census 1926 census 1939 census 1959 census 1970 census 1979 census 1989 census 2002 Kabardins 122,402 (60.0%) 152,237 (42.4%) 190,284 (45.3%) 264,675 (45.0%) 303,604 (45.5%) 364,494 (48.2%) 498,702 (55.3%) Balkars 33,197 (16.3%) 40,747 (11.3%) 34,088 (8.1%) 51,356 (8.7%) 59,710 (9.0%) 70,793 (9.4%) 104,951 (11.6%) Russians 15,344 (7.5%) 129,067 (35.9%) 162,586 (38.7%) 218,595 (37.2%) 234,137 (35.1%) 240,750 (31.9%) 226,620 (25.1%) Ossetians 4,078 (2.0%) 4,608 (1.3%) 6,442 (1.5%) 9,167 (1.6%) 9,710 (1.5%) 9,996 (1.3%) 9,845 (1.1%) Ukrainians 17,213 (8.4%) 11,142 (3.1%) 8,400 (2.0%) 10,620 (1.8%) 12,139 (1.8%) 12,826 (1.7%) 7,592 (0.8%) Others 11,772 (5.8%) 21,328 (5.9%) 18,315 (4.4%) 33,790 (5.7%) 47,246 (7.1%) 55,672 (7.4%) 53,784 (6.0%) History
Main article: History of Kabardino-BalkariaPolitics
The head of government in Kabardino-Balkaria is the President. The current President is Arsen Kanokov, who has held the position since September 2005.
The legislative body of the Republic is the Parliament comprising 72 deputies elected for a five year term.[4][13]
The Constitution of Kabardino-Balkaria was adopted on September 1, 1997.
Economy
The economy of Kabardino-Balkaria is primarily agricultural, with lumber production and mining. Most of the industry centers on agricultural processing. The fall of the Soviet Union and the outbreak of the various conflicts in the Caucasus have hit the republic hard, causing a collapse in tourism in the region and producing an unemployment level estimated to be as high as 90%. Poverty is reported to be an endemic problem in the republic. Russian investors have invested in local ski resorts in order to attract more tourists.
See also
- Caucasian Avars
- Bulgars
- List of the Chairmen of the Parliament of the Kabardino-Balkar Republic
- Mount Imeon
References
- ^ Президент Российской Федерации. Указ №849 от 13 мая 2000 г. «О полномочном представителе Президента Российской Федерации в федеральном округе». Вступил в силу 13 мая 2000 г. Опубликован: "Собрание законодательства РФ", №20, ст. 2112, 15 мая 2000 г. (President of the Russian Federation. Decree #849 of May 13, 2000 On the Plenipotentiary Representative of the President of the Russian Federation in a Federal District. Effective as of May 13, 2000).
- ^ Госстандарт Российской Федерации. №ОК 024-95 27 декабря 1995 г. «Общероссийский классификатор экономических регионов. 2. Экономические районы», в ред. Изменения №5/2001 ОКЭР. (Gosstandart of the Russian Federation. #OK 024-95 December 27, 1995 Russian Classification of Economic Regions. 2. Economic Regions, as amended by the Amendment #5/2001 OKER. ).
- ^ http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/country_profiles/4338292.stm BBC:Country profile
- ^ a b c Constitution, Article 11.1
- ^ Official website of the President of the Kabardino-Balkar Republic. Biography (Russian)
- ^ Федеральная служба государственной статистики (Federal State Statistics Service) (2004-05-21). "Территория, число районов, населённых пунктов и сельских администраций по субъектам Российской Федерации (Territory, Number of Districts, Inhabited Localities, and Rural Administration by Federal Subjects of the Russian Federation)" (in Russian). Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2002). Federal State Statistics Service. http://perepis2002.ru/ct/html/TOM_01_03.htm. Retrieved 2011-11-01.
- ^ a b c Федеральная служба государственной статистики (Federal State Statistics Service) (2011). "Предварительные итоги Всероссийской переписи населения 2010 года (Preliminary results of the 2010 All-Russian Population Census)" (in Russian). Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2010). Federal State Statistics Service. http://www.perepis-2010.ru/results_of_the_census/results-inform.php. Retrieved 2011-04-25.
- ^ a b Федеральная служба государственной статистики (Federal State Statistics Service) (2004-05-21). "Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек (Population of Russia, its federal districts, federal subjects, districts, urban localities, rural localities—administrative centers, and rural localities with population of over 3,000)" (in Russian). Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2002). Federal State Statistics Service. http://www.perepis2002.ru/ct/doc/1_TOM_01_04.xls. Retrieved 2010-03-23.
- ^ Правительство Российской Федерации. Постановление №725 от 31 августа 2011 г. «О составе территорий, образующих каждую часовую зону, и порядке исчисления времени в часовых зонах, а также о признании утратившими силу отдельных Постановлений Правительства Российской Федерации». Вступил в силу по истечении 7 дней после дня официального опубликования. Опубликован: "Российская Газета", №197, 6 сентября 2011 г. (Government of the Russian Federation. Resolution #725 of August 31, 2011 On the Composition of the Territories Included into Each Time Zone and on the Procedures of Timekeeping in the Time Zones, as Well as on Abrogation of Several Resolutions of the Government of the Russian Federation. Effective as of after 7 days following the day of the official publication).
- ^ Official the whole territory of Russia according to Article 68.1 of the Constitution of Russia.
- ^ Constitution, Article 76.1
- ^ [1]
- ^ Constitution, Article 94.
Sources
- Парламент Кабардино-Балкарской Республики. №28-РЗ 1 сентября 1997 г. «Конституция Кабардино-Балкарской Республики», в ред. Закона №39-РЗ от 10 июля 2008 г. (Parliament of the Kabardino-Balkar Republic. #28-RZ September 1, 1997 Constitution of the Kabardino-Balkar Republic, as amended by the Law #39-RZ of July 10, 2008. ).
External links
- (Russian) Official website of the President of the Republic
- (Russian) KavkazWeb.net - Daily news from Kabardino-Balkaria
- (Russian) Adyga.org - Most popular website of Kabardian people
- (English) Kabardino-Balkaria information and photo gallery
- (English) Images of Kabardino-Balkaria
- (English) [2]
- (Russian) Kabardino-Balkaria News Portal
Subdivisions of Russia Republics Krais Oblasts - Amur
- Arkhangelsk
- Astrakhan
- Belgorod
- Bryansk
- Chelyabinsk
- Irkutsk
- Ivanovo
- Kaliningrad
- Kaluga
- Kemerovo
- Kirov
- Kostroma
- Kurgan
- Kursk
- Leningrad
- Lipetsk
- Magadan
- Moscow
- Murmansk
- Nizhny Novgorod
- Novgorod
- Novosibirsk
- Omsk
- Orenburg
- Oryol
- Penza
- Pskov
- Rostov
- Ryazan
- Sakhalin
- Samara
- Saratov
- Smolensk
- Sverdlovsk
- Tambov
- Tomsk
- Tula
- Tver
- Tyumen
- Ulyanovsk
- Vladimir
- Volgograd
- Vologda
- Voronezh
- Yaroslavl
Federal cities Autonomous oblasts Autonomous okrugs 1administratively subordinated to Tyumen Oblast 2 administratively subordinated to Arkhangelsk Oblast
Countries and regions of the Caucasus Politics of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territories- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jan Mayen
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
Other entities - European Union
Turkic-speaking regions Federal subjects of Russia shown in italics.Western Turkic
 Azerbaijan1
Azerbaijan1
 Bashkortostan
Bashkortostan
 Chuvashia
Chuvashia
 Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus
 Gagauzia (Moldova)
Gagauzia (Moldova)
 Kabardino-Balkaria
Kabardino-Balkaria
 Karachay-Cherkessia
Karachay-Cherkessia
 Karakalpakstan (Uzbekistan)
Karakalpakstan (Uzbekistan)
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
 Xinjiang (China)1 Includes the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic.Categories:
Xinjiang (China)1 Includes the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic.Categories:- Kabardino-Balkaria
- States and territories established in 1936
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.