- Fosphenytoin
-
Fosphenytoin 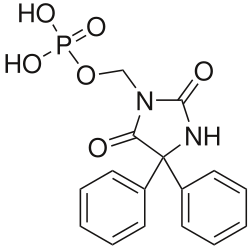

Systematic (IUPAC) name (2,5-dioxo-4,4-diphenyl-imidazolidin-1-yl)methoxyphosphonic acid Clinical data Trade names Cerebyx AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a604036 Pregnancy cat. D(US) Legal status ℞ Prescription only Routes Intravenous, intramuscular Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability 100% (IM) Protein binding 95 to 99% Metabolism Hepatic Half-life 15 minutes to convert to phenytoin Excretion Renal (as phenytoin) Identifiers CAS number 93390-81-9 
ATC code N03AB05 PubChem CID 56339 DrugBank APRD00241 ChemSpider 50839 
UNII B4SF212641 
KEGG D07993 
ChEMBL CHEMBL919 
Chemical data Formula C16H15N2O6P Mol. mass 362.274 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Fosphenytoin (Cerebyx, Parke-Davis; Prodilantin, Pfizer Holding France[1]) is a water-soluble phenytoin prodrug used only in hospitals for the treatment of epileptic seizures.
On 18 November 2004, Sicor (a subsidiary of Teva) received a tentative approval letter from the United States Food and Drug Administration for a generic version of fosphenytoin.[2]
Contents
Uses
Approved
Fosphenytoin is approved in the United States for the short term (five days or fewer) treatment of epilepsy when more widely used means of phenytoin administration are not possible or are ill-advised,[3] such as endotracheal intubation, status epilepticus or some other type of repeated seizures; vomiting, and/or the patient is unalert or not awake or both.[4]
Unapproved/off-label/investigational
In April 2003, Applebaum and colleagues at the Ben-Gurion University of the Negev in Beersheba reported that even though anticonvulsants are often very effective in mania, and acute mania requires rapid treatment, fosphenytoin had no antimanic effect even 60 minutes after administration of doses used in status epilepticus.[5]
Fosphenytoin was more successfully used to relieve pain refractory to opiates in a 37-year-old woman with neuroma, according to Dr. Gary J. McCleane of the Rampark Pain Center in Lurgan, Northern Ireland.[6] She was given 1,500 phenytoin equivalent units of fosphenytoin over a 24 hour period, producing pain relief that last three to fourteen weeks after each infusion, allowing her to use less opiates.[6]
Metabolism
One mmol (millimole) of phenytoin is produced for every mmol of fosphenytoin administered; the hydrolysis of fosphenytoin also yields phosphate and formaldehyde, the latter of which is subsequently metabolized to formate, which is in turn metabolized by a folate dependent mechanism.[3]
Side effects
Side effects are similar to phenytoin, except that fosphenytoin causes less hypotension and more paresthesia.[7] Fosphenytoin can cause hyperphosphatemia in end-stage renal failure patients.[8]
History
Phenytoin, in both its acidic and sodium salt forms, is erratically bioavailable whether it is injected or taken orally due to its high melting point, weak acidity, and its being only sparingly soluble in water.[9] Simply putting patients on other drugs is not always an option; this was especially true before 1993, when the number of anticonvulsants available was much more limited.[10] One solution was to develop a prodrug that did not have these drawbacks.
Fosphenytoin was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on August 5, 1996 for use in epilepsy.[11]
References
- ^ "PRODILANTIN 75 mg/ml sol inj IM et p perf IV". VIDAL, l'information de référence sur les produits de santé. http://www.vidal.fr/Medicament/prodilantin-13783.htm. Retrieved 23 October 2005.
- ^ "Fosphenytoin Sodium Approval History". http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/drugsatfda/index.cfm?fuseaction=Search.Label_ApprovalHistory#apphist. Retrieved 20 October 2005.
- ^ a b Parke-Davis (2001). "Cerebyx: Fosphenytoin Sodium Injection - Labeling Revision" (PDF). Cerebyx Approval History. Warner-Lambert Company. http://www.fda.gov/cder/foi/label/2001/20450s4s5lbl.pdf. Retrieved 20 October 2005.[dead link]
- ^ Johnson J, Wrenn K (2001). "Inappropriate fosphenytoin use in the ED". American Journal of Emergency Medicine 19 (4): 293–4. doi:10.1053/ajem.2001.24471. PMID 11447516. Fulltext options List of Library Holdings Worldwide
- ^ Applebaum J, Levine J, Belmaker RH (2003). "Intravenous fosphenytoin in acute mania" (PDF). Journal Clinical Psychiatry 64 (4): 408–9. doi:10.4088/JCP.v64n0408. PMID 12716241. http://www.psychiatrist.com/privatepdf/2003/v64n04/v64n0408.pdf.
- ^ a b McCleane GJ (2002). "Intravenous infusion of fosphenytoin produces prolonged pain relief: a case report". The Journal of Pain 3 (2): 156–8. doi:10.1054/jpai.2002.123004. PMID 14622802. List of Library Holdings Worldwide
- ^ Browne TR. (1997). "Fosphenytoin (Cerebyx)". Clinical Neuropharmacology 20 (1): 1–12. doi:10.1097/00002826-199702000-00001. PMID 9037568. List of Library Holdings Worldwide
- ^ McBryde KD, Wilcox J, Kher KK (2005). "Hyperphosphatemia due to fosphenytoin in a pediatric ESRD patient" (PDF). Pediatric Nephrology (Berlin, Germany) 20 (8): 1182–5. doi:10.1007/s00467-005-1947-0. PMID 15965770.
- ^ Yamaoka Y, Roberts RD, Stella VJ (April 1983). "Low-melting phenytoin prodrugs as alternative oral delivery modes for phenytoin: a model for other high-melting sparingly water-soluble drugs". J Pharm Sci 72 (4): 400–5. doi:10.1002/jps.2600720420. PMID 6864479.
- ^ Anticonvulsants before 1993 Neuroland
- ^ "Cerebyx Approval History". http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/drugsatfda/index.cfm?fuseaction=Search.Label_ApprovalHistory. Retrieved 20 October 2005.
See also
Anticonvulsants (N03) GABAA receptor agonist Clobazam • Clonazepam • Clorazepate • Diazepam# • Flutoprazepam • Lorazepam • Midazolam • Nimetazepam • Nitrazepam • TemazepamOther GABA agents Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor Channel blockers Primarily sodiumPrimarily calciumUnknown/ungroupedChannel openers PotassiumRetigabineIndirect GABA agents GABA transaminase inhibitor: Valproic acid# (Sodium valproate & Valproate semisodium) • Valpromide • Valnoctamide • Valproate pivoxil
GABA reuptake inhibitor: TiagabineUnknown/multiple/
unsortedPropionatesCategories:- Anticonvulsants
- Prodrugs
- Hydantoins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
